The US is considering unilateral restrictions on China’s access to artificial intelligence (AI) memory chips and equipment capable of making those semiconductors as soon as next month, a move that would further escalate the tech rivalry between the world’s biggest economies.
The measure is designed to keep Micron Technology Inc and South Korea’s leading memorychip makers SK Hynix Inc and Samsung Electronics Co from supplying Chinese firms with so-called high-bandwidth memory (HBM) chips, people familiar with the matter said. The three firms dominate the global HBM market.
US President Joe Biden’s administration is working on several restrictions aimed at keeping vital technology out of the hands of Chinese manufacturers, including limits on sales of chipmaking equipment. This rule would deliver a new set of constraints against memory chips for AI, the latest arena of US-China competition.
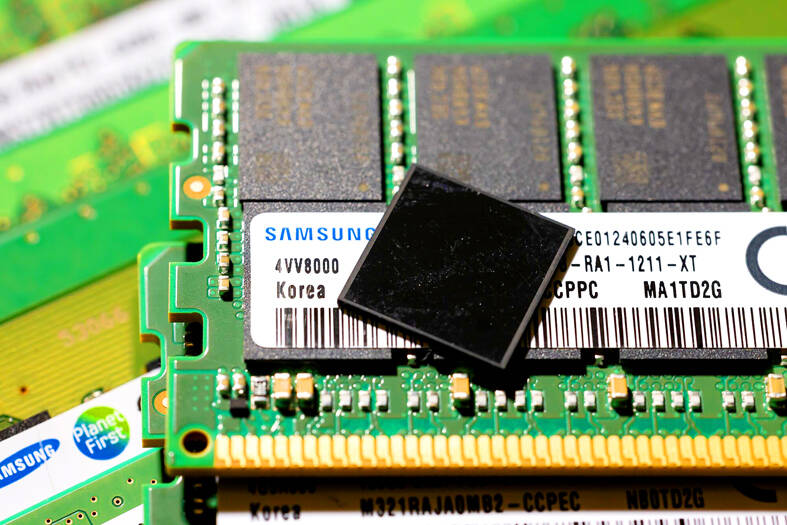
Photo: Bloomberg
If enacted, the measure would capture HBM2 and more advanced chips including HBM3 and HBM3E, the most cutting-edge AI memory chips being produced right now, as well as the tools required to make them, the sources said.
HBM chips are required to run AI accelerators like those offered by Nvidia Corp and Advanced Micro Devices Inc.
Micron would largely be unaffected as the Boise, Idaho-based chipmaker has refrained from selling its HBM products to China after Beijing banned its memory chips from critical infrastructure last year, the people said.
It is unclear what authority the US would use to restrict the South Korean firms, the people said. One possibility is the Foreign Direct Product Rule, which lets Washington impose controls on foreign-made products that use even the tiniest amount of US technology. SK Hynix and Samsung rely on US chip design software and equipment from the likes of Cadence Design Systems Inc and Applied Materials Inc.
Micron, Samsung and SK Hynix representatives declined to comment.
The new restrictions are likely to be unveiled later this month as part of a broader package that also includes sanctions against more than 120 Chinese firms and fresh limits on various types of chip equipment, with carve-outs for key allies including Japan, the Netherlands and South Korea, the people said.
As part of its comprehensive HBM-related curbs in the same export control package, the US plans to lower the threshold for what qualifies as advanced DRAM. A single HBM chip contains several DRAM dies.
New restrictions on HBM equipment and DRAM aim to deter leading Chinese memorychip maker ChangXin Memory Technologies Inc (長鑫存儲) from advancing its technology, the sources said. ChangXin is now capable of making HBM2, which first became commercially available in 2016.
Biden administration officials also plan to create a list of the critical components that China needs to keep producing semiconductors. They are also eyeing what is called a zero de-minimis rule, an even tighter standard for Foreign Direct Product Rule under which any products containing US technology would be subject to potential restrictions. A large group of US allies would be exempted from that measure, including Japan and the Netherlands.

Sweeping policy changes under US Secretary of Health and Human Services Robert F. Kennedy Jr are having a chilling effect on vaccine makers as anti-vaccine rhetoric has turned into concrete changes in inoculation schedules and recommendations, investors and executives said. The administration of US President Donald Trump has in the past year upended vaccine recommendations, with the country last month ending its longstanding guidance that all children receive inoculations against flu, hepatitis A and other diseases. The unprecedented changes have led to diminished vaccine usage, hurt the investment case for some biotechs, and created a drag that would likely dent revenues and

Macronix International Co (旺宏), the world’s biggest NOR flash memory supplier, yesterday said it would spend NT$22 billion (US$699.1 million) on capacity expansion this year to increase its production of mid-to-low-density memory chips as the world’s major memorychip suppliers are phasing out the market. The company said its planned capital expenditures are about 11 times higher than the NT$1.8 billion it spent on new facilities and equipment last year. A majority of this year’s outlay would be allocated to step up capacity of multi-level cell (MLC) NAND flash memory chips, which are used in embedded multimedia cards (eMMC), a managed

CULPRITS: Factors that affected the slip included falling global crude oil prices, wait-and-see consumer attitudes due to US tariffs and a different Lunar New Year holiday schedule Taiwan’s retail sales ended a nine-year growth streak last year, slipping 0.2 percent from a year earlier as uncertainty over US tariff policies affected demand for durable goods, data released on Friday by the Ministry of Economic Affairs showed. Last year’s retail sales totaled NT$4.84 trillion (US$153.27 billion), down about NT$9.5 billion, or 0.2 percent, from 2024. Despite the decline, the figure was still the second-highest annual sales total on record. Ministry statistics department deputy head Chen Yu-fang (陳玉芳) said sales of cars, motorcycles and related products, which accounted for 17.4 percent of total retail rales last year, fell NT$68.1 billion, or

In the wake of strong global demand for AI applications, Taiwan’s export-oriented economy accelerated with the composite index of economic indicators flashing the first “red” light in December for one year, indicating the economy is in booming mode, the National Development Council (NDC) said yesterday. Moreover, the index of leading indicators, which gauges the potential state of the economy over the next six months, also moved higher in December amid growing optimism over the outlook, the NDC said. In December, the index of economic indicators rose one point from a month earlier to 38, at the lower end of the “red” light.