Like many US political watchers, a Nevada resident named Domer had an opinion about who would emerge from turmoil within the Republican Party to become the next speaker of the US House of Representatives.
Unlike most of them, he made US$13,000 when Mike Johnson was finally elected last month.
That political gambling is illegal in the US has not deterred Domer (a nickname he provided) or others like him from using online overseas markets to wager on US politics.

Photo: AFP
Domer, who said he earns about US$500,000 a year betting on politics across the globe including in Italy and South Africa, is often active in chatrooms on Discord and other sites that buzz with debate among aficionados.
“There’s a lot of trash talk — it’s similar to sports betting,” he said. “It’s combative and congenial at the same time.”
Political betting was common — and legal — in the US until the rise of relatively accurate polling in the 1930s.
Futures trading regulations passed in 1936, as well as crackdowns on sports betting and the perception of gambling as seedy all helped put an end to markets that once populated Wall Street and the politics pages of newspapers.
Today, critics still worry gambling could fuel corruption or the gamification of the political system.
However, as the Internet has made gambling easier, people like Domer use virtual private networks to skirt around government regulators that have closed down sites or halted the entry of platforms that try to offer political betting to Americans.
Only two have been able to stay alive, due to their affiliations with university research projects.
The government moved last year to shut down one of them, PredictIt, alleging it had exceeded its research-focused mandate. It was granted a lifeline by a July court decision in its favor that would keep its lights on as litigation continues.
Supporters say legal markets offer benefits to the public and traders alike, and the effect is negligible as bets are capped at a few hundred dollars.
“These markets encourage attention to political events, and they serve as an antidote to fake news,” PredictIt CEO John Phillips said.
“Prediction markets are not perfect,” he said, but they are “better than polling.”
There are studies backing him up, although it is a contention that not all political scientists agree with. For better or worse, journalists stick almost exclusively with polls — which, traders say, also inform their bets.
PredictIt is currently offering shares in US President Joe Biden being a presidential nominee for US$0.68, meaning a trader who bought a share would earn US$0.32 if he is the Democratic candidate in next year’s election, which is likely.
However, bet big on California Governor Gavin Newsom, who has not even entered the race, and each share bought for US$0.23 would earn US$0.77, minus fees.
Markets also deliver insights that polls do not always capture — not just about politics, but also economics, said Tom Gruca, director of the Iowa Electronic Markets, a political betting operation run at the University of Iowa, where he also teaches.
“When you answer a poll, you tell people what you wish is going to happen,” unlike a market, which captures “what you think is going to happen,” he said.
“Even a small amount of money changes the stakes for people,” Gruca said, describing a class where, after giving students money to trade, they were “ready to rip each other limb from limb over movements of US$0.10.”
Political gambling expert Pratik Chougule also cashed in on a House speaker bet, cleaning up US$130 after Jim Jordan lost, and has most recently put about US$1,000 into Biden being the Democratic nominee.
Chougule cohosts a betting podcast, and started an advocacy group to push for legalization.
“I was a pretty true believer in the Iraq war... I had gotten that issue very wrong,” Chougule said. “I basically realized that bad prediction, bad forecasting in our policymaking is actually the norm, not the exception.”
“Having skin in the game is at least an important consideration in doing better,” he added.
For markets to work — for academic insights to be gleaned and riches to be won — there must also be losers.
“I’m currently betting a lot of money that [former US president Donald] Trump will not be the GOP [Republican] nominee — which was what I thought was a smart bet a year ago, and is now looking like the world’s dumbest bet ever,” Domer said.
Despite — or perhaps, because of — the court indictments stacking up against the former president, he looks almost certain to grab the Republican presidential nomination.
So just how dumb was Domer’s bet?
“Oh, I’m gonna lose a couple hundred thousand,” he said.

Merida Industry Co (美利達) has seen signs of recovery in the US and European markets this year, as customers are gradually depleting their inventories, the bicycle maker told shareholders yesterday. Given robust growth in new orders at its Taiwanese factory, coupled with its subsidiaries’ improving performance, Merida said it remains confident about the bicycle market’s prospects and expects steady growth in its core business this year. CAUTION ON CHINA However, the company must handle the Chinese market with great caution, as sales of road bikes there have declined significantly, affecting its revenue and profitability, Merida said in a statement, adding that it would
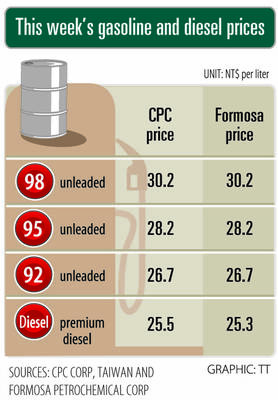
i Gasoline and diesel prices at fuel stations are this week to rise NT$0.1 per liter, as tensions in the Middle East pushed crude oil prices higher last week, CPC Corp, Taiwan (台灣中油) and Formosa Petrochemical Corp (台塑石化) said yesterday. International crude oil prices last week rose for the third consecutive week due to an escalating conflict between Israel and Iran, as the market is concerned that the situation in the Middle East might affect crude oil supply, CPC and Formosa said in separate statements. Front-month Brent crude oil futures — the international oil benchmark — rose 3.75 percent to settle at US$77.01

RISING: Strong exports, and life insurance companies’ efforts to manage currency risks indicates the NT dollar would eventually pass the 29 level, an expert said The New Taiwan dollar yesterday rallied to its strongest in three years amid inflows to the nation’s stock market and broad-based weakness in the US dollar. Exporter sales of the US currency and a repatriation of funds from local asset managers also played a role, said two traders, who asked not to be identified as they were not authorized to speak publicly. State-owned banks were seen buying the greenback yesterday, but only at a moderate scale, the traders said. The local currency gained 0.77 percent, outperforming almost all of its Asian peers, to close at NT$29.165 per US dollar in Taipei trading yesterday. The

RECORD LOW: Global firms’ increased inventories, tariff disputes not yet impacting Taiwan and new graduates not yet entering the market contributed to the decrease Taiwan’s unemployment rate last month dropped to 3.3 percent, the lowest for the month in 25 years, as strong exports and resilient domestic demand boosted hiring across various sectors, the Directorate-General of Budget, Accounting and Statistics (DGBAS) said yesterday. After seasonal adjustments, the jobless rate eased to 3.34 percent, the best performance in 24 years, suggesting a stable labor market, although a mild increase is expected with the graduation season from this month through August, the statistics agency said. “Potential shocks from tariff disputes between the US and China have yet to affect Taiwan’s job market,” Census Department Deputy Director Tan Wen-ling