In the heartland of the tequila industry, in Mexico’s western state of Jalisco, a worsening shortage of agave caused by mounting demand for the liquor from New York to Tokyo has many producers worried.
The price of Agave tequilana, the blue-tinged, spiky-leaved succulent used to make the alcoholic drink, has risen sixfold in the past two years, squeezing smaller distillers’ margins and leading to concerns that shortages could hit even the larger players.
In front of a huge metal oven that cooks agave for tequila, one farmer near the town of Amatitan said he had been forced to use young plants to compensate for the shortage of fully grown agave, which take seven to eight years to reach maturity.

Photo: Reuters
He asked not to be identified, because he did not want his clients to know he was using immature plants.
The younger plants produce less tequila, meaning more plants have to be pulled up early from a limited supply — creating a downward spiral.
“They are using four-year-old plants, because there aren’t any others. I can guarantee it, because I have sold them,” said Marco Polo Magdaleno, a worried grower in Guanajuato, one of the states allowed to produce tequila under strict denomination of origin rules.
More than a dozen tequila industry experts interviewed by Reuters said that the early harvesting will mean the shortage is even worse this year.
Already, the 17.7 million blue agaves planted in 2011 in Mexico for use this year fall far short of the 42 million the industry needs to supply 140 registered companies, according to figures from the Tequila Regulatory Council and the National Tequila Industry Chamber (CNIT).
The shortages are likely to continue until 2021, as improved planting strategies take years to bear fruit, producers said.
The result is agave prices at 22 pesos (US$1.18) per kilogram — up from 3.85 pesos in 2016.
Those higher prices mean that low-cost tequila producers, which make a cheaper, less pure drink that once dominated the market, find it harder to compete with premium players.
“It doesn’t make sense for tequila to be a cheap drink, because agave requires a big investment,” CNIT president Luis Velasco said.
Small-scale distillers of quality tequilas are also feeling the pinch, and some have warned that drinkers are seeking alternative tipples.
“At more than 20 pesos per kilogram, it’s impossible to compete with other spirits like vodka and whisky,” said Salvador Rosales, manager of small producer Tequila Cascahuin, in El Arenal, a rural town in Jalisco.
“If we continue like this, a lot of companies will disappear,” he said.
Exports to the US of pure tequila jumped by 198 percent over the past decade, while cheaper blended tequila exports rose by just 11 percent, CNIT data showed.
Over the same period, Mexican production declined 4 percent, with blended tequila leading the fall.
As it sheds its image as a fiery booze drunk by desperados and frat boys, while moving into the ranks of top-shelf liquors, the tequila industry has seen a flurry of deals in recent years.
Last month, Bacardi Ltd said it would buy fine tequila maker Patron Spirits International for US$5.1 billion.
Last year, after years of speculation, Mexico’s Beckmann family launched an initial public offering of Jose Cuervo, raising more than US$900 million.
Britain’s Diageo PLC swapped its Bushmills Irish whiskey label for full ownership of high-end Don Julio tequila in 2014.
The question posed by many distillers is how to keep pace with tequila’s success.
“The growth has overtaken us. It’s a crisis of success of the industry,” said Francisco Soltero, director of strategic planning at Patron, which buys agave under various contracts.
“We thought that we were going to grow a certain amount, and we’re growing double,” he said.
Large sellers, such as Patron and Sauza Tequila Import Co, have said they have not experienced problems paying for agave, and forecast that their inventories will keep growing.
“If you sell value, the costs don’t worry you,” Soltero said.
Sauza, which mostly grows its own agave, does not foresee supply problems, CEO Servando Calderon said.
However, some think it is simply a matter of time before the higher production costs and scarcity pressures bigger players.
“We are sure this will have a strong impact on the big firms, such as Cuervo or Sauza,” said Raul Garcia, president of the National Committee for Agave Production in Tequila, a group that includes most agave producers in the country. “We don’t see that the problem will be resolved soon, and that’s what worries us.”
Demand is also being driven by other, fashionable agave-derived products, including agave syrup and health supplement inulin, which use the equivalent of 20 percent of the plants needed this year, the council said.
Rising prices are also leading to growing theft, driving out smaller producers, Tepatitlan-based blue agave producer Jose de Jesus said.
Criminals enter the area with large trucks in the middle of the night to steal agave, he said.
Last year, 15,000 plants were reported stolen, more than triple the number in 2016, the council said.

Merida Industry Co (美利達) has seen signs of recovery in the US and European markets this year, as customers are gradually depleting their inventories, the bicycle maker told shareholders yesterday. Given robust growth in new orders at its Taiwanese factory, coupled with its subsidiaries’ improving performance, Merida said it remains confident about the bicycle market’s prospects and expects steady growth in its core business this year. CAUTION ON CHINA However, the company must handle the Chinese market with great caution, as sales of road bikes there have declined significantly, affecting its revenue and profitability, Merida said in a statement, adding that it would
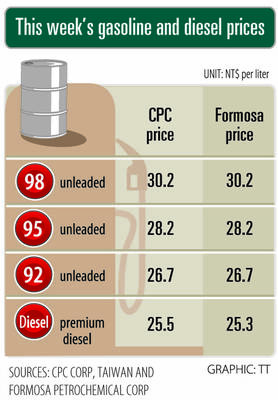
i Gasoline and diesel prices at fuel stations are this week to rise NT$0.1 per liter, as tensions in the Middle East pushed crude oil prices higher last week, CPC Corp, Taiwan (台灣中油) and Formosa Petrochemical Corp (台塑石化) said yesterday. International crude oil prices last week rose for the third consecutive week due to an escalating conflict between Israel and Iran, as the market is concerned that the situation in the Middle East might affect crude oil supply, CPC and Formosa said in separate statements. Front-month Brent crude oil futures — the international oil benchmark — rose 3.75 percent to settle at US$77.01

RISING: Strong exports, and life insurance companies’ efforts to manage currency risks indicates the NT dollar would eventually pass the 29 level, an expert said The New Taiwan dollar yesterday rallied to its strongest in three years amid inflows to the nation’s stock market and broad-based weakness in the US dollar. Exporter sales of the US currency and a repatriation of funds from local asset managers also played a role, said two traders, who asked not to be identified as they were not authorized to speak publicly. State-owned banks were seen buying the greenback yesterday, but only at a moderate scale, the traders said. The local currency gained 0.77 percent, outperforming almost all of its Asian peers, to close at NT$29.165 per US dollar in Taipei trading yesterday. The

RECORD LOW: Global firms’ increased inventories, tariff disputes not yet impacting Taiwan and new graduates not yet entering the market contributed to the decrease Taiwan’s unemployment rate last month dropped to 3.3 percent, the lowest for the month in 25 years, as strong exports and resilient domestic demand boosted hiring across various sectors, the Directorate-General of Budget, Accounting and Statistics (DGBAS) said yesterday. After seasonal adjustments, the jobless rate eased to 3.34 percent, the best performance in 24 years, suggesting a stable labor market, although a mild increase is expected with the graduation season from this month through August, the statistics agency said. “Potential shocks from tariff disputes between the US and China have yet to affect Taiwan’s job market,” Census Department Deputy Director Tan Wen-ling