Academia Sinica yesterday unveiled the results of its research into the effects a protein complex has on the development of colorectal cancer, providing a possible solution to the treatment of the disease, which is the most common cancer in the nation.
Meng Tzu-ching (孟子青), a research fellow at the institute, said colorectal cancer is triggered by the mutation of the Kristen ras (K-Ras) gene, which regulates cell division.
He said that research in the past had determined that the dephosphorylation of protein kinase 12 is directly related to the spreading of colorectal cancer cells, but scientists were not able to validate a widely-held hypothesis that links the process to the effects of tyrosine phosphatase N3 (PTPN3).
Drawing upon concepts in structural biology, the team — led by research fellow Andrew Wang (王惠鈞) and comprising Chen Kai-en (陳凱恩) and Meng — devised a hybrid methodology, whereby they successfully created the PTPN3-protein kinase 12 complex.
By observing the interactions between the two proteins found inside the human body, they discovered that early-stage colorectal cancer degenerates and goes out of control when PTPN3 aggravated by the mutation of K-Ras comes into an abnormally high level of contact with protein kinase 12, through which process the PTTN3 “bites into” the protein kinase 12, the researchers said.
Furthermore, with the help of the hybrid methodology — which determines the protein complex’s outline through small-angle X-ray scattering, its structure through X-ray crystallography, and the connecting points between the proteins through chemical cross-linking/mass spectrometry — the team was able to create the protein complex, by which they confirmed the hypothesis that the dephosphorylation of protein kinase 12 was caused by PTTN3.
Wang said the ability to identify the points of linkage between the two proteins is especially helpful to developing new therapies and drugs to combat the cancer, which could help develop new methods to cut off the pathway by which PTTN3 comes into contact with protein kinase 12, instead of targeting the mutated gene, as most drugs do, which causes many side effects and inflicts more pain on the patient because it affects the normal functions of the gene.
The findings could be a major step forward for cancer therapeutic drugs, he added.
The trio’s work was the cover story of the Oct. 14 version of the Science Signaling journal.
Statistics published by the Ministry of Health and Welfare in April put colorectal cancer on the top of a list of 10 most common cancers in the nation, with a person contracting the disease every 50 minutes.
The cancer has topped the list for six consecutive years, statistics showed.

Taiwanese can file complaints with the Tourism Administration to report travel agencies if their activities caused termination of a person’s citizenship, Mainland Affairs Council Minister Chiu Chui-cheng (邱垂正) said yesterday, after a podcaster highlighted a case in which a person’s citizenship was canceled for receiving a single-use Chinese passport to enter Russia. The council is aware of incidents in which people who signed up through Chinese travel agencies for tours of Russia were told they could obtain Russian visas and fast-track border clearance, Chiu told reporters on the sidelines of an event in Taipei. However, the travel agencies actually applied

New measures aimed at making Taiwan more attractive to foreign professionals came into effect this month, the National Development Council said yesterday. Among the changes, international students at Taiwanese universities would be able to work in Taiwan without a work permit in the two years after they graduate, explainer materials provided by the council said. In addition, foreign nationals who graduated from one of the world’s top 200 universities within the past five years can also apply for a two-year open work permit. Previously, those graduates would have needed to apply for a work permit using point-based criteria or have a Taiwanese company

The Shilin District Prosecutors’ Office yesterday indicted two Taiwanese and issued a wanted notice for Pete Liu (劉作虎), founder of Shenzhen-based smartphone manufacturer OnePlus Technology Co (萬普拉斯科技), for allegedly contravening the Act Governing Relations Between the People of the Taiwan Area and the Mainland Area (臺灣地區與大陸地區人民關係條例) by poaching 70 engineers in Taiwan. Liu allegedly traveled to Taiwan at the end of 2014 and met with a Taiwanese man surnamed Lin (林) to discuss establishing a mobile software research and development (R&D) team in Taiwan, prosecutors said. Without approval from the government, Lin, following Liu’s instructions, recruited more than 70 software
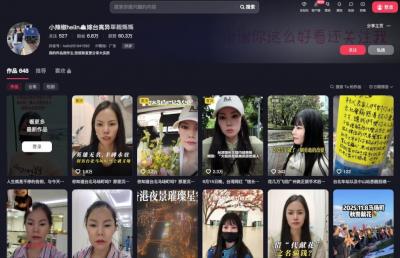
Chinese spouse and influencer Guan Guan’s (關關) residency permit has been revoked for repeatedly posting pro-China videos that threaten national security, the National Immigration Agency confirmed today. Guan Guan has said many controversial statements in her videos posted to Douyin (抖音), including “the red flag will soon be painted all over Taiwan” and “Taiwan is an inseparable part of China,” and expressing hope for expedited reunification. The agency last year received multiple reports alleging that Guan Guan had advocated for armed reunification. After verifying the reports, the agency last month issued a notice requiring her to appear and explain her actions. Guan