The three Han Dynasty tombs excavated in 1972 at Mawangdui in Hunan’s Changsha was an extremely significant archaeological discovery. Tomb no. 1, in particular, found in a state of complete preservation, contained not only the perfectly mummified corpse of the tomb occupant Lady Dai — personal name Xin Zhui — but also a wealth of cultural artifacts. Among these, the most spectacular was an exquisite T-shaped silk banner.
The banner painting, on purplish-red dyed silk, was divided into three sections, depicting Heaven, the human realm and the Underworld. The horizontal top section represents Heaven, with a sun on the top right corner containing the Golden Crow and a moon to the top left with a toad. Between these sits a creature with a human head upon a serpent’s torso: the mythological creator of humans Nuwa (or Fuxi). At the base of this section sit two deities — thought to be a senior and junior judge of life — lying sentry to the entrance of Heaven.
The vertical section of the painting below this shows a noblewoman (Lady Dai) standing, with the aid of a cane, in the middle of a platform, accompanied by servants in front and behind her, as if preparing her for her ascension to Heaven.
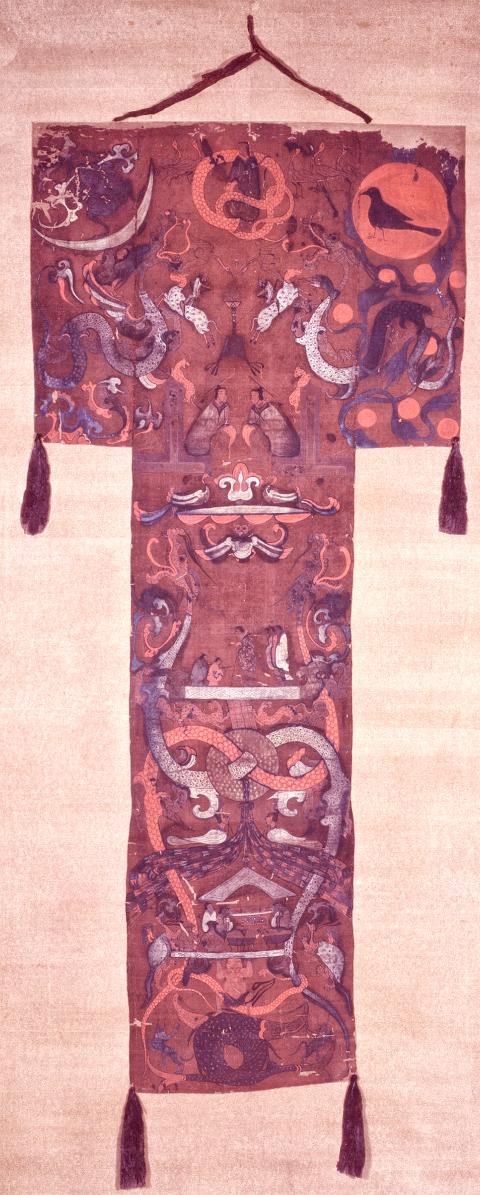

Photo: Wikimedia Commons
照片:維基共享資源
A pair of dragons, intertwined through a ritual jade bi disc, serve as a divider between the platform above and a scene below of the woman’s descendants making offerings of delicacies. This scene is being supported from below by the mythical creature Gun, who is himself standing upon a pair of whales with interlocking tails.
The T-shaped banner was to be used in the “calling of the soul” ritual following a death. It would have been hung at the front of the funeral procession to guide the soul into the burial chamber, and from there on its journey to Heaven. Above and beyond this function, the banner is testament to the exquisite artistry of the time, and tells us much about the folk religion and world view of the period.
The painting as a whole uses heavenly bodies together with the symbols and iconography of the creation of the universe and mythological creatures to represent the cosmological order; its vertical composition not only portrays the structure of the world view, it also encapsulates a chronological narrative, reading almost like a comic strip.
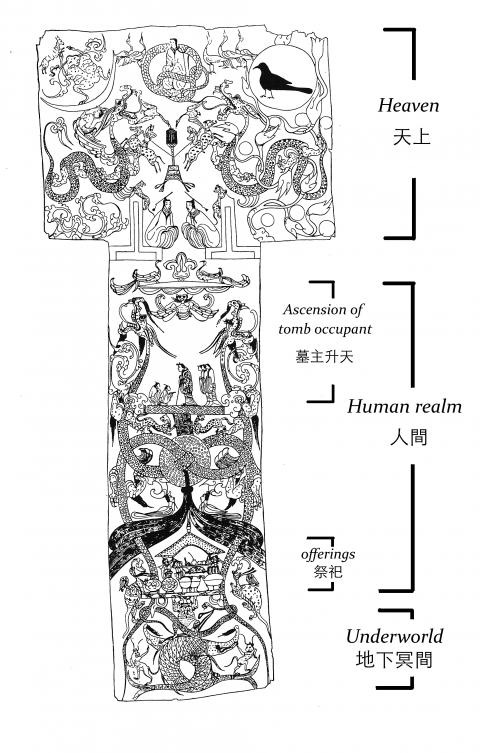
Photo: Paul Cooper, Taipei Times
照片:台北時報古德謙
At the same time, the individual scenes are filled with profound decorative and symbolic meaning, with the jade bi discs, musical instruments such as the zhong bells and qing chime stones and the flowing lines of the four dragons — two in Heaven and another two interlocking dragons extending up from the Underworld into the human realm — hold the entire composition together. The banner is a perfect example of the linear beauty of traditional Chinese visual art.
(Translated by Paul Cooper)
一九七二年於湖南長沙馬王堆出土的三座漢墓,是極重要的考古發現,尤其是保存完整的一號墓,不但有墓主軑侯夫人辛追未腐化的身軀,還有豐富的文物藝品。其中最引人注目的,是一件精美的T形帛畫。
這幅在染成絳色絲絹上的彩繪,分成天上、人間、地底三個部分。置頂橫向畫面描繪的是天上:有右上方的太陽(金烏)、左上的月亮(蟾蜍),及中間人首蛇身的女媧(或伏羲);底下則有看守天界入口的兩位神祇(一般認為是大司命與少司命)。
以下垂直部分的畫幅,是一位貴婦(即軑侯夫人)拄杖站在一平台中央,前後有隨從服侍,似正準備升天。
在這之下以龍和玉璧交穿的圖樣做出分隔,再往下是子孫奉上山珍海味的祭祀場景。這祭祀場景,是由地底下的神話人物鯀所撐起,鯀腳底下踩著兩尾互相交錯的鯨鯢。
這T形幡是用來招魂的特定形式,出殯時懸掛在前,引導亡靈至墓中,然後升天。這件帛畫更讓我們一窺當時精美的工藝,以及民間的信仰與世界觀。
它整個畫面以日月星辰、創世神話人物、神獸等符號圖騰布局,鋪陳出宇宙的秩序;其上下分層及位置安排,不僅是世界觀的構築,也是時間上的敘事,如同連環漫畫的分鏡。
然而其「分鏡」,本身即深具裝飾性與圖騰意義,例如玉璧,和鐘、磬等樂器的運用,以及用四條龍(天上兩條,及貫穿人間與地底的兩條交纏的龍)的靈動線條,來羅織貫穿整個畫面構圖。咸認中國傳統視覺藝術是「線條」的藝術,由此可見。
(台北時報林俐凱)

Beatboxing is the art of making drum sounds using nothing but your mouth, lips, tongue, and voice. This incredible skill turns your voice into a personal drum kit, allowing you to create beats and rhythms that sound just like those of real instruments. Born from hip-hop culture in the 1980s, beatboxing has evolved into a global form of musical expression found in various genres. What makes beatboxing so special? First, it requires no equipment at all. This accessibility allows you to develop your musical sense and rhythm skills wherever you are. Plus, beatboxing is a fantastic way to express

A: I’m glad that the Grammys will honor the late pop diva Whitney Houston with a Lifetime Achievement Award. Who are this year’s leading nominees? B: Kendrick Lamar is leading the nominations with nine nods, followed by Lady Gaga with seven nods. Bad Bunny, Sabrina Carpenter and Leon Thomas each gained six nods. A: I heard that the song “Golden” from global animated blockbuster KPop Demon Hunters received three nominations, including Song of the Year. B: Blackpink’s Rose and Bruno Mars’ “APT.” also received major recognition with multiple nominations, including Record of the Year, setting a milestone for

A: British singer Calum Scott is currently touring Taiwan again, staging a show at the K-Arena on Saturday. B: Didn’t Calum release a reimagined duet with the late pop diva Whitney Houston for her classic “I Wanna Dance with Somebody (Who Loves Me)?” A: Yup the track uses the legendary singer’s original vocal, transforming into a new ballad duet. B: I remember that the 1987 megahit topped the charts around the world, winning Whitney a second Grammy Award for Best Female Pop Vocal Performance. A: And she will receive her Grammy Lifetime Achievement Award on the eve

It graced statues, colored coffins, and decorated artifacts. It is Egyptian blue, the world’s oldest-known synthetic pigment born in ancient Egypt. Despite its name, it is not limited to a single hue. It ranges from deep blue to greenish tones, often glowing with an almost unearthly brilliance. __1__ In response, the ancient Egyptians developed a synthetic alternative. Not only was it visually striking, but it was also more affordable than imported indigo or natural lapis lazuli. Traces of the pigment have been discovered far beyond Egypt, from wall paintings in Pompeii to tiles in Mesopotamia. However, Egyptian blue began to fall