Deepening Chinese activities in the Arctic could pave the way for a strengthened military presence, including the deployment of submarines to act as deterrents against nuclear attack, the Pentagon said in a report on Thursday.
The assessment is included in the military’s annual report to the US Congress on China’s armed forces and follows Beijing’s publication of its first official Arctic policy white paper in June last year.
In that paper, China outlined plans to develop shipping lanes opened up by global warming to form a “Polar Silk Road” — building on Chinese President Xi Jinping’s (習近平) Belt and Road Initiative.
China, despite being a non-Arctic state, is increasingly active in the polar region and became an observer member of the Arctic Council in 2013.
This has prompted concerns from Arctic states over Beijing’s long-term strategic objectives.
US Secretary of State Mike Pompeo is to attend a meeting of the eight-nation Arctic Council in Rovaniemi, Finland, starting on Monday, which comes amid concerns over China’s increased commercial interests in the Arctic.
The Pentagon report said that Denmark has expressed concern about China’s interest in Greenland, including proposals to establish a research station and a satellite ground station, renovate airports and expand mining.
“Civilian research could support a strengthened Chinese military presence in the Arctic Ocean, which could include deploying submarines to the region as a deterrent against nuclear attacks,” the report said.
China’s military has made modernizing its submarine fleet a high priority and currently operates four nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines, six nuclear-powered attack submarines and 50 conventionally powered attack submarines, the report said.
“The speed of growth of the submarine force has slowed and [it] will likely grow to between 65 and 70 submarines by 2020,” it added.
China had built six Jin-class submarines, with four operational and two under construction at Huludao Shipyard, the report said.
In a January report, the Pentagon’s Defense Intelligence Agency said that the Chinese navy would need at least five Jin-class submarines to maintain a continuous nuclear deterrence at sea.
The US and its allies are expanding their anti-submarine naval deployments across East Asia, including stepped-up patrols of advanced, sub-hunting P-8 Poseidon planes out of Singapore and Japan.
The expansion of China’s submarine forces is just one element of a broad modernization of its military, which US experts have said is designed largely to deter any action by the US’ armed forces.
Although Beijing’s official defense budget for last year was US$175 billion, the Pentagon estimated that it actually topped US$200 billion when including research, development and foreign weapons procurement.
It estimated that China’s official defense budget would likely grow to about US$260 billion by 2022.
The Pentagon also said that it expects China to add military bases around the world to protect its Belt and Road Initiative investments.
Beijing currently has just one overseas military base, in Djibouti, but is believed to be planning others, including possibly Pakistan.
“China will seek to establish additional military bases in countries with which it has a long-standing friendly relationship and similar strategic interests, such as Pakistan, and in which there is a precedent for hosting foreign militaries,” the report said.
That effort could be constrained by other nations’ wariness of hosting a full-time presence of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army, the report said.
Target locations could include the Middle East, Southeast Asia and the western Pacific.
China already has well-armed outposts on contested atolls in the South China Sea.
Last year, there were reportedly discussions for a base in the Wakhan Corridor of northwest Afghanistan.
The Washington Post has also identified an outpost hosting many Chinese troops in eastern Tajikistan, near the strategic junction of the Wakhan Corridor, China and Pakistan.

NATIONAL SECURITY THREAT: An official said that Guan Guan’s comments had gone beyond the threshold of free speech, as she advocated for the destruction of the ROC China-born media influencer Guan Guan’s (關關) residency permit has been revoked for repeatedly posting pro-China content that threatens national security, the National Immigration Agency said yesterday. Guan Guan has said many controversial things in her videos posted to Douyin (抖音), including “the red flag will soon be painted all over Taiwan” and “Taiwan is an inseparable part of China,” while expressing hope for expedited “reunification.” The agency received multiple reports alleging that Guan Guan had advocated for armed reunification last year. After investigating, the agency last month issued a notice requiring her to appear and account for her actions. Guan Guan appeared as required,

Japan and the Philippines yesterday signed a defense pact that would allow the tax-free provision of ammunition, fuel, food and other necessities when their forces stage joint training to boost deterrence against China’s growing aggression in the region and to bolster their preparation for natural disasters. Japan has faced increasing political, trade and security tensions with China, which was angered by Japanese Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi’s remark that a Chinese attack on Taiwan would be a survival-threatening situation for Japan, triggering a military response. Japan and the Philippines have also had separate territorial conflicts with Beijing in the East and South China
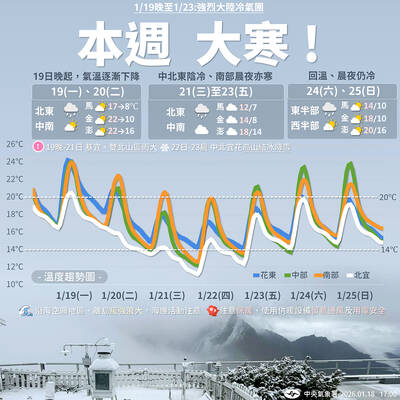
A strong cold air mass is expected to arrive tonight, bringing a change in weather and a drop in temperature, the Central Weather Administration (CWA) said. The coldest time would be early on Thursday morning, with temperatures in some areas dipping as low as 8°C, it said. Daytime highs yesterday were 22°C to 24°C in northern and eastern Taiwan, and about 25°C to 28°C in the central and southern regions, it said. However, nighttime lows would dip to about 15°C to 16°C in central and northern Taiwan as well as the northeast, and 17°C to 19°C elsewhere, it said. Tropical Storm Nokaen, currently

PAPERS, PLEASE: The gang exploited the high value of the passports, selling them at inflated prices to Chinese buyers, who would treat them as ‘invisibility cloaks’ The Yilan District Court has handed four members of a syndicate prison terms ranging from one year and two months to two years and two months for their involvement in a scheme to purchase Taiwanese passports and resell them abroad at a massive markup. A Chinese human smuggling syndicate purchased Taiwanese passports through local criminal networks, exploiting the passports’ visa-free travel privileges to turn a profit of more than 20 times the original price, the court said. Such criminal organizations enable people to impersonate Taiwanese when entering and exiting Taiwan and other countries, undermining social order and the credibility of the nation’s