Thailand, Cambodia, Myanmar and Laos today begin three days of exuberant, water-soaked celebrations marking the traditional new year, refusing to be deterred by historically low levels on the Mekong which connects them.
Water is at the heart of the mid-April festival in the four Buddhist-majority countries, signifying the washing away of sins and rancor, and refreshing the region as it is embraced by scorching summer weather.

PHOTO: REUTERS
"It will be a symbolic cleansing and washing away of sins accumulated during the old year and to prepare for the new one," a Buddhist scholar in Myanmar said of the ancient ceremony.
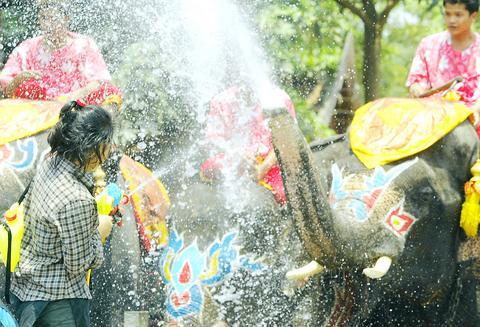
The water festival represents the most popular, raucous and colorful celebration of the year for more than 120 million people who will abandon any thoughts of work and bring their nations to a standstill.
Cambodia and Laos are both entering year 2548 of the Buddhist era, while Thailand will do so on Jan. 1 after adopting the Gregorian calendar. Myanmar is only passing into the year 1366 according to its numbering system.

The celebration is called Songkran in Thailand, Chaul Chnam Thmey in Cambodia, Thingyan in Myanmar and Pimai in Laos but at street corners everywhere, everyone can expect to be splashed with icy cold water.

From basic plastic buckets to high-tech pump-action water pistols which allow revellers long-range, high-precision soaking, every type of container is deployed to throw water, sometimes laced with talcum powder, colored flour, charcoal, mud and ice cubes.
City-dwellers embark on a massive exodus to the countryside for family reunions punctuated by visits to pagodas, offerings to monks, ancestor worship, traditional games and dances, sports competitions, gift-giving to parents and symbolic bathing of elders -- all to acquire "merit" in the Buddhist tradition.
The new year is also a highlight of the tourist season, for visitors who are lucky to see splendid processions of monks wrapped in saffron robes who remain composed amid the revelries in Luang Prabang, the former royal capital of Laos.
In Cambodia, small sand pagodas are built along the banks of the Mekong, while newly ordained monks are paraded on elephants deep in northern Myanmar, and music shows are staged in platforms on the rivers of northern Thailand.
The festival is also an occasion for people to wear new clothing, give Buddha statues and their houses a thorough washing, and even to donate blood.
The governor of Phnom Penh has asked residents to scrub the city clean with vast amounts of water, despite the region's drought which has helped reduce the once-mighty Mekong to a trickle in some stretches.
The effort "is to welcome the upcoming traditional Khmer New Year ... by making Phnom Penh more and more clean and create a better environment," Keb Chuktema said.
Thingyan has taken on political dimensions in Myanmar this year. As it is customary to release birds from cages at this time, many hope opposition leader Aung San Suu Kyi could be freed from house arrest at the dawn of the new year.
In Thailand, the explosive situation in the Muslim south is overshadowing Songkran. A heavy security presence has been deployed in fear that Muslim extremists who have killed 60 people this year could mount a major attack.
In all four countries, traditional New Year's day also is also well lubricated with alcohol, usually cheap local whisky or rice alcohol which fuels rampant drink-driving and carnage on the roads.
Authorities in Bangkok, Phnom Penh, Yangon and Vientiane have once again issued urgent warnings and bans to try to curb the problem.
In Thailand, where 20,000 police officers have been mobilized, blood-alcohol tests will be carried out at checkpoints. Last Songkran, more than 800 people were killed on the roads, 70 percent due to drunk-driving.
Water-throwing is prohibited after 6pm and parents have been warned they face up to three months in jail if their offspring use the festivities as an excuse to sexually harass women. The young women themselves have been asked not to wear "provocative" clothing like miniskirts.
In Myanmar, the official press noted: "It is important that people take part in the festival in line with Myanmar tradition and avoid behaviors and wearing clothes that are foreign to our culture."
In Yangon, hundred of makeshift wooden structures have been thrown up as platforms for water-throwing, especially around the capital's Inya Lake -- although revelries are banned near Aung San Suu Kyi's home.
In Cambodia, where the new year is rung in at precisely 5:36pm on Tuesday, newspapers have published official directives against "theft and other crimes, especially gambling" and security forces have been warned they will "will have to work very hard" according to a city official quoted by Cambodge Soir.
In Laos, the authorities noted that last year, "Pimai saw hundreds of people driving drunk or involved in pick-up wars which resulted in loss of life" and encouraged citizens to meet on the banks of the Mekong and leave their cars at home.

Late last month Philippines Foreign Affairs Secretary Theresa Lazaro told the Philippine Senate that the nation has sufficient funds to evacuate the nearly 170,000 Filipino residents in Taiwan, 84 percent of whom are migrant workers, in the event of war. Agencies have been exploring evacuation scenarios since early this year, she said. She also observed that since the Philippines has only limited ships, the government is consulting security agencies for alternatives. Filipinos are a distant third in overall migrant worker population. Indonesia has over 248,000 workers, followed by roughly 240,000 Vietnamese. It should be noted that there are another 170,000

Hannah Liao (廖宸萱) recalls the harassment she experienced on dating apps, an experience that left her frightened and disgusted. “I’ve tried some voice-based dating apps,” the 30-year-old says. “Right away, some guys would say things like, ‘Wanna talk dirty?’ or ‘Wanna suck my d**k?’” she says. Liao’s story is not unique. Ministry of Health and Welfare statistics show a more than 50 percent rise in sexual assault cases related to online encounters over the past five years. In 2023 alone, women comprised 7,698 of the 9,413 reported victims. Faced with a dating landscape that can feel more predatory than promising, many in
“This is one of those rare bits of TikTok fitness advice with a lot of truth behind it,” says Bethan Crouse, performance nutritionist at Loughborough University. “Sometimes it’s taken a bit too literally, though! You see people chugging protein drinks as they’re scanning out of their gym.” Crouse recommends the athletes she works with consume 20-30g of protein within 30-60 minutes of finishing a resistance training session. “The act of exercising our muscles increases the breakdown of muscle proteins,” she says. “In order to restore, or hopefully improve them — and get gains such as increased muscle mass or strength —
“Far from being a rock or island … it turns out that the best metaphor to describe the human body is ‘sponge.’ We’re permeable,” write Rick Smith and Bruce Lourie in their book Slow Death By Rubber Duck: The Secret Danger of Everyday Things. While the permeability of our cells is key to being alive, it also means we absorb more potentially harmful substances than we realize. Studies have found a number of chemical residues in human breast milk, urine and water systems. Many of them are endocrine disruptors, which can interfere with the body’s natural hormones. “They can mimic, block