Holding long-term global warming to 2°C — the fallback target of the Paris climate accord — is now “impossible,” according to a new analysis published by leading scientists.
Led by renowned climatologist James Hansen, the paper appears in the journal Environment: Science and Policy for Sustainable Development and concludes that Earth’s climate is more sensitive to rising greenhouse gas emissions than previously thought.
Compounding the crisis, Hansen and colleagues argued, is a recent decline in sunlight-blocking aerosol pollution from the shipping industry, which had been mitigating some of the warming.
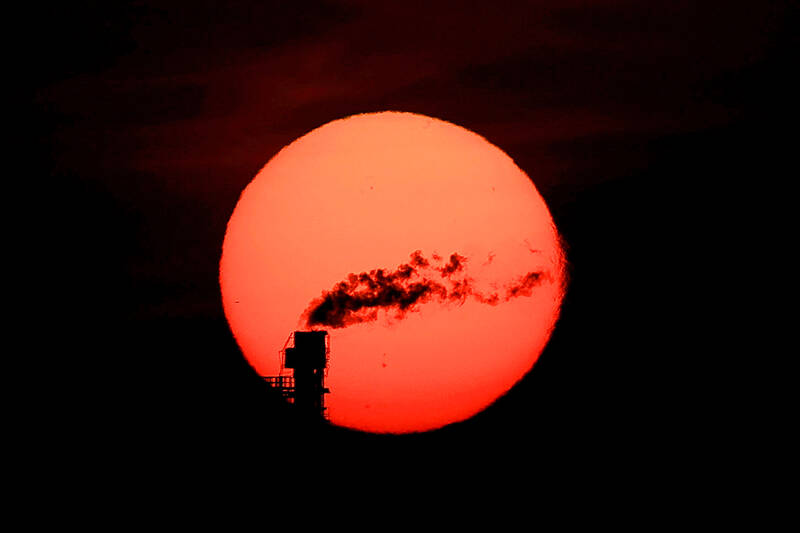

Photo: Reuters
An ambitious climate change scenario outlined by the UN’s climate panel, which gives the planet a 50 percent chance of keeping warming under 2°C by the year 2100, “is an implausible scenario,” Hansen told a briefing on Tuesday.
“That scenario is now impossible,” said Hansen, formerly a top NASA climate scientist who famously announced to the US Congress in 1988 that global warming was underway.
“The 2°C target is dead,” he said.
Instead, he and coauthors argued, the amount of greenhouse gases already pumped into the atmosphere by burning fossil fuels meant increased warming is now guaranteed.
Temperatures would stay at or above 1.5°C in the coming years — devastating coral reefs and fueling more intense storms — before rising to about 2.0°C by 2045, they forecast.
They estimated polar ice melt and freshwater injection into the North Atlantic would trigger the shutdown of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) within the next 20 to 30 years.
The current brings warmth to various parts of the globe and also carries nutrients necessary to sustain ocean life.
Its end “will lock in major problems including sea level rise of several meters — thus, we describe AMOC shutdown as the ‘point of no return,’” the paper argued.
The world’s nations agreed during the landmark Paris climate accord of 2015 to try to hold end-of-century warming to 1.5°C above preindustrial levels.
Scientists identified the threshold as critical to preventing the breakdown of major ocean circulation systems, the abrupt thawing of boreal permafrost, and the collapse of tropical coral reefs.
The 1.5°C target has already been breached over the past two years, data from the EU’s climate monitoring system Copernicus showed, although the Paris agreement referred to a long-term trend over decades.
At 2°C, the impacts would be even greater, including irreversible loss to Earth’s ice sheets, mountain glaciers and snow, sea ice and permafrost.
The authors acknowledged the findings appeared grim, but argued that honesty is a necessary ingredient for change.
“Failure to be realistic in climate assessment and failure to call out the fecklessness of current policies to stem global warming is not helpful to young people,” they said.
“Today, with rising crises including global climate change, we have reached a point where we must address the problem of special interests,” they added, stressing they were “optimistic” for the future.

Yemen’s separatist leader has vowed to keep working for an independent state in the country’s south, in his first social media post since he disappeared earlier this month after his group briefly seized swathes of territory. Aidarous al-Zubaidi’s United Arab Emirates (UAE)-backed Southern Transitional Council (STC) forces last month captured two Yemeni provinces in an offensive that was rolled back by Saudi strikes and Riyadh’s allied forces on the ground. Al-Zubaidi then disappeared after he failed to board a flight to Riyadh for talks earlier this month, with Saudi Arabia accusing him of fleeing to Abu Dhabi, while supporters insisted he was

The Chinese Embassy in Manila yesterday said it has filed a diplomatic protest against a Philippine Coast Guard spokesman over a social media post that included cartoonish images of Chinese President Xi Jinping (習近平). Philippine Coast Guard spokesman Jay Tarriela and an embassy official had been trading barbs since last week over issues concerning the disputed South China Sea. The crucial waterway, which Beijing claims historic rights to despite an international ruling that its assertion has no legal basis, has been the site of repeated clashes between Chinese and Philippine vessels. Tarriela’s Facebook post on Wednesday included a photo of him giving a

Syrian President Ahmed al-Sharaa on Sunday announced a deal with the chief of Kurdish-led forces that includes a ceasefire, after government troops advanced across Kurdish-held areas of the country’s north and east. Syrian Kurdish leader Mazloum Abdi said he had agreed to the deal to avoid a broader war. He made the decision after deadly clashes in the Syrian city of Raqa on Sunday between Kurdish-led forces and local fighters loyal to Damascus, and fighting this month between the Kurds and government forces. The agreement would also see the Kurdish administration and forces integrate into the state after months of stalled negotiations on
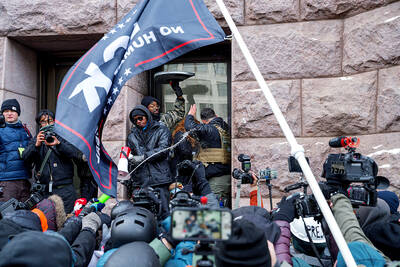
‘MOBILIZED’: While protesters countered ICE agents, Minnesota Governor Tim Walz activated the state’s National Guard to ‘support the rights of Minnesotans’ to assemble Hundreds of counterprotesters drowned out a far-right activist’s attempt to hold a small rally in support of US President Donald Trump’s latest immigration crackdown in Minneapolis, Minnesota, on Saturday, as the governor’s office announced that National Guard troops were mobilized and ready to assist law enforcement, although not yet deployed to city streets. There have been protests every day since the US Department of Homeland Security (DHS) ramped up immigration enforcement in the Twin Cities of Minneapolis and Saint Paul by bringing in more than 2,000 federal officers. Conservative influencer Jake Lang organized an anti-Islam, anti-Somali and pro-US Immigration and Customs Enforcement