Europe’s Hera probe is tentatively scheduled to launch on Monday on a mission to inspect the damage a NASA spacecraft made when it smashed into an asteroid during the first test of Earth’s planetary defenses.
In a scene that sounds straight out of science fiction, the spacecraft deliberately crashed into the pyramid-sized asteroid Dimorphos in 2022, roughly 11 million kilometers from Earth.
The fridge-sized impactor used in the Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) successfully knocked the asteroid well off its course.

Photo: AFP / NASA / Johns Hopkins APL
This demonstrated that the idea worked — humanity might no longer be powerless against potential planet-killing asteroids that could approach — but much about the impact remains unknown, including how much damage was done and exactly what the asteroid was like before it was hit.
So the European Space Agency (ESA) said it was sending Hera to the asteroid to conduct a “crime scene investigation” in the hope of learning how Earth can best fend off asteroids that pose a threat.
The spacecraft is scheduled to blast off on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral, Florida, on Monday.
However an “anomaly” involving a Falcon 9 rocket during the launch of SpaceX’s Crew-9 astronaut mission last Saturday could potentially delay the launch date, ESA Hera project manager Ian Carnelli said at a news conference.
The ESA is hoping to receive approval by tomorrow from the US Federal Aviation Administration, NASA and SpaceX, Carnelli said.
The launch window for the mission would remain open until Oct. 27.
Once launched, Hera is planned to fly past Mars next year and then arrive near Dimorphos in December 2026 to begin its six-month investigation.
An asteroid wider than 1km — which could trigger a global catastrophe on a scale that wiped out the dinosaurs — is estimated to strike Earth every 500,000 years.
An asteroid about 140m wide — which is a little smaller than Dimorphos, but could still take out a major city — hits our home planet about every 20,000 years.
Most of these celestial objects come from the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Almost all those bigger than 1km wide are known to scientists, and none are expected to threaten Earth in the next century.
There are also no known 140m asteroids on a collision course with Earth — but only 40 percent of those space rocks are believed to have been identified.
Although asteroids are one of the least likely natural disasters to strike the planet, people now have the “advantage of being able to protect ourselves against them,” Hera mission principal investigator Patrick Michel said.
Dimorphos, which is actually a moonlet orbiting its big brother, Didymos, never posed a threat to the Earth.
After DART’s impact, Dimorphos shed material to the point where its orbit around Didymos was shortened by 33 minutes — proof that it was successfully deflected. Analysis of the DART mission has suggested that rather than being a single hard rock, Dimorphos was more a loose pile of rubble held together by gravity.
“The consequence of this is that, instead of making a crater” on Dimorphos, DART might have “completely deformed” the asteroid, Michel said.
However, there are other possibilities, he said, adding that the behavior of these low-gravity objects is little understood and “defies intuition.”
The 363 million euros (US$400 million) mission is equipped with 12 scientific instruments and two nanosatellites.
The Juventas nanosatellite will aim to land on Dimorphos, which would be a first on such a small asteroid. It plans to use radar to probe deep inside the asteroid and a gravimeter to measure its gravity.
From farther away, the Milani nanosatellite plans to use cameras and other instruments to study the asteroid’s composition and assess DART’s impact.
Once its job is done, the team on the ground hopes that Hera can land gently on Dimorphos or Didymos, where it would spend the rest of its days.
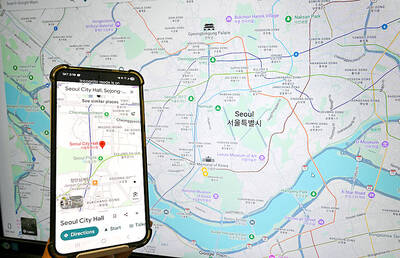
South Korea would soon no longer be one of the few countries where Google Maps does not work properly, after its security-conscious government reversed a two-decade stance to approve the export of high-precision map data to overseas servers. The approval was made “on the condition that strict security requirements are met,” the South Korean Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport said. Those conditions include blurring military and other sensitive security-related facilities, as well as restricting longitude and latitude coordinates for South Korean territory on products such as Google Maps and Google Earth, it said. The decision is expected to hurt Naver and Kakao

THE TRAGEDY OF PUNCH: Footage of the seven-month-old Japanese macaque has gone viral online after he was rejected by his mother and formed a bond with a soft toy A baby monkey in Japan has captured hearts around the world after videos of him being bullied by other monkeys and rejected by his mother went viral last week. Punch, a Japanese macaque, was born in July last year at Ichikawa City Zoo. He has drawn international attention after zookeepers gave him a stuffed orangutan toy after he was abandoned by his mother. Without maternal guidance to help him integrate, Punch has turned to the toy for comfort. He has been filmed multiple times being dragged and chased by older Japanese macaques inside the enclosure. Early clips showed him wandering alone with

MONEY GRAB: People were rushing to collect bills scattered on the ground after the plane transporting money crashed, which an official said hindered rescue efforts A cargo plane carrying money on Friday crashed near Bolivia’s capital, damaging about a dozen vehicles on highway, scattering bills on the ground and leaving at least 15 people dead and others injured, an official said. Bolivian Minister of Defense Marcelo Salinas said the Hercules C-130 plane was transporting newly printed Bolivian currency when it “landed and veered off the runway” at an airport in El Alto, a city adjacent to La Paz, before ending up in a nearby field. Firefighters managed to put out the flames that engulfed the aircraft. Fire chief Pavel Tovar said at least 15 people died, but

Australian Prime Minister Anthony Albanese yesterday said he did not take his security for granted, after he was evacuated from his residence for several hours following a bomb threat sent to a Chinese dance group. Albanese was evacuated from his Canberra residence late on Tuesday following the threat, and returned a few hours later after nothing suspicious was found. The bomb scare was among several e-mails threatening Albanese sent to a representative of Shen Yun, a classical Chinese dance troupe banned in China that is due to perform in Australia this month, a spokesperson for the group said in a statement. The e-mail