On the ceiling of a limestone cave in South Sulawesi, scientists have discovered artwork depicting three human-like figures interacting with a wild pig in what they have determined is the oldest-known confidently dated cave painting — created at least 51,200 years ago.
The researchers used a new scientific approach to determine the minimum age of the newly disclosed painting by using a laser to date a type of crystal called calcium carbonate that formed naturally on top of the painting.
“The method is a significant improvement over other methods and should revolutionize rock art dating worldwide,” said Maxime Aubert, a specialist in archeological science at Griffith University in Australia and one of the leaders of the research published on Wednesday in the journal Nature.
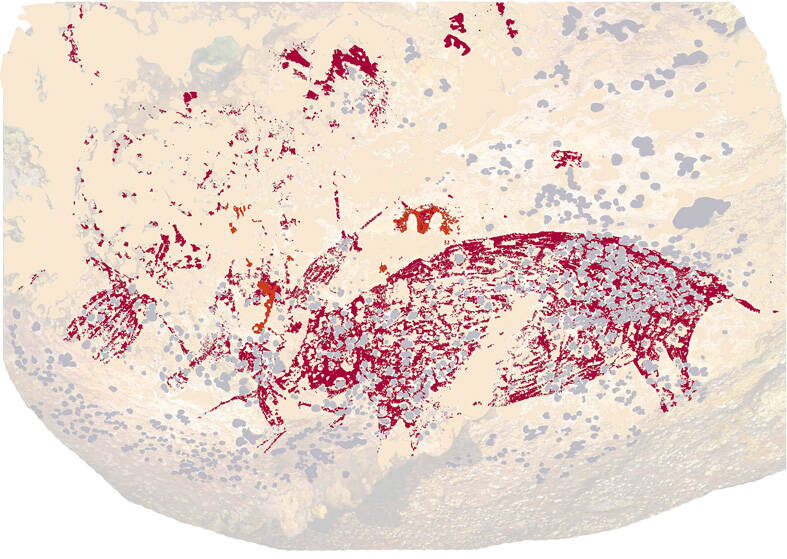
Photo: Griffith University via AFP
The scene, dominated by a representation of a pig measuring 92cm by 38cm that is standing upright along with three smaller human-like figures, is painted in a single shade of dark red pigment. There are other images of pigs in the cave as well.
The researchers interpreted the painting as a narrative scene, which they said would make it the oldest-known evidence of storytelling in art.
“The three human-like figures and the pig figure were clearly not depicted in isolation in separate parts of the rock art panel,” said Griffith University archeologist Adam Brumm, another of the study leaders.
“Rather, the juxtaposition of the figures — how they are positioned in relation to each other — and the manner in which they are interacting were clearly deliberate, and it conveys an unmistakable sense of action. There is something happening between these figures. A story is being told. Obviously, we don’t know what that story was,” Brumm added.
The researchers used the same dating method to reassess the age of another Sulawesi cave painting from a site called “Leang Bulu’ Sipong 4,” also depicting a narrative scene, this time depicting apparent part-human, part-animal figures hunting pigs and dwarf buffalo. It turned out to be at least 48,000 years old.
“We, as humans, define ourselves as a species that tells stories, and these are the oldest evidence of us doing that,” Aubert said.
In the former painting, the interaction between the human-like figures and the pig, a species still inhabiting the island, is somewhat cryptic.
“Two of these figures are holding objects of some kind, and at least one figure seems to be reaching towards the pig’s face. Another figure is positioned directly above the pig’s head in an upside down position,” Brumm said.
Little is known about the people who created the Sulawesi cave paintings.
Aubert said the paintings might turn out to be older than the minimum age determined by the new testing and possibly date to the first Homo sapiens wave to sweep through the region, eventually reaching Australia about 65,000 years ago, on their migration out of Africa.
Until now, the oldest-known cave painting was one at Leang Tedongnge cave, also in Sulawesi, from at least 45,500 years ago.
“This discovery of very old cave art in Indonesia drives home the point that Europe was not the birthplace of cave art, as had long been assumed. It also suggests that storytelling was a much older part of human history, and the history of art in particular, than previously recognized,” Brumm said.
“The earliest Sulawesi rock art is not simple,” Aubert added. “It is quite advanced and shows the mental capacity of people at the time.”

Auschwitz survivor Eva Schloss, the stepsister of teenage diarist Anne Frank and a tireless educator about the horrors of the Holocaust, has died. She was 96. The Anne Frank Trust UK, of which Schloss was honorary president, said she died on Saturday in London, where she lived. Britain’s King Charles III said he was “privileged and proud” to have known Schloss, who cofounded the charitable trust to help young people challenge prejudice. “The horrors that she endured as a young woman are impossible to comprehend and yet she devoted the rest of her life to overcoming hatred and prejudice, promoting kindness, courage, understanding

‘DISRESPECTFUL’: Katie Miller, the wife of Trump’s most influential adviser, drew ire by posting an image of Greenland in the colors of the US flag, captioning it ‘SOON’ US President Donald Trump on Sunday doubled down on his claim that Greenland should become part of the US, despite calls by the Danish prime minister to stop “threatening” the territory. Washington’s military intervention in Venezuela has reignited fears for Greenland, which Trump has repeatedly said he wants to annex, given its strategic location in the arctic. While aboard Air Force One en route to Washington, Trump reiterated the goal. “We need Greenland from the standpoint of national security, and Denmark is not going to be able to do it,” he said in response to a reporter’s question. “We’ll worry about Greenland in

PERILOUS JOURNEY: Over just a matter of days last month, about 1,600 Afghans who were at risk of perishing due to the cold weather were rescued in the mountains Habibullah set off from his home in western Afghanistan determined to find work in Iran, only for the 15-year-old to freeze to death while walking across the mountainous frontier. “He was forced to go, to bring food for the family,” his mother, Mah Jan, said at her mud home in Ghunjan village. “We have no food to eat, we have no clothes to wear. The house in which I live has no electricity, no water. I have no proper window, nothing to burn for heating,” she added, clutching a photograph of her son. Habibullah was one of at least 18 migrants who died

Russia early yesterday bombarded Ukraine, killing two people in the Kyiv region, authorities said on the eve of a diplomatic summit in France. A nationwide siren was issued just after midnight, while Ukraine’s military said air defenses were operating in several places. In the capital, a private medical facility caught fire as a result of the Russian strikes, killing one person and wounding three others, the State Emergency Service of Kyiv said. It released images of rescuers removing people on stretchers from a gutted building. Another pre-dawn attack on the neighboring city of Fastiv killed one man in his 70s, Kyiv Governor Mykola