Jariatu Kargbo hauled a wooden spoon longer than her arm through a vat of rice as customers patiently waited their turn to buy lunch on the side of a busy road. The 38-year-old widow runs a stall called a “cookery” — the cheapest option for many Sierra Leoneans to grab what is often their only meal of the day.
Cookeries in this impoverished West African state are a crucial part of the economy as well as a social safety net.
However, the cherished institution is under pressure from a brutal external force: inflation.
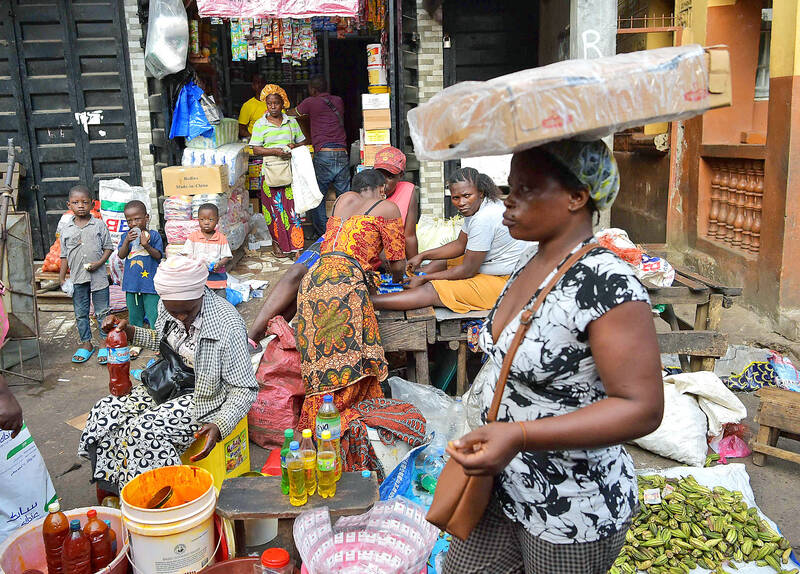

Photo: AFP
“Prices for major food items — rice, cooking oil, onion, sugar and flour — have quadrupled,” Kargbo said, as the smell of boiled beans wafted over from behind her.
Cookeries in Freetown, the capital, sell rice and stew at a fraction of what they would cost in a restaurant.
“These predominantly women are kind of the backbone of the city in terms of keeping it fed, because a lot of people ... don’t have the facilities to cook at home,” said Jamie Hitchen, a researcher.
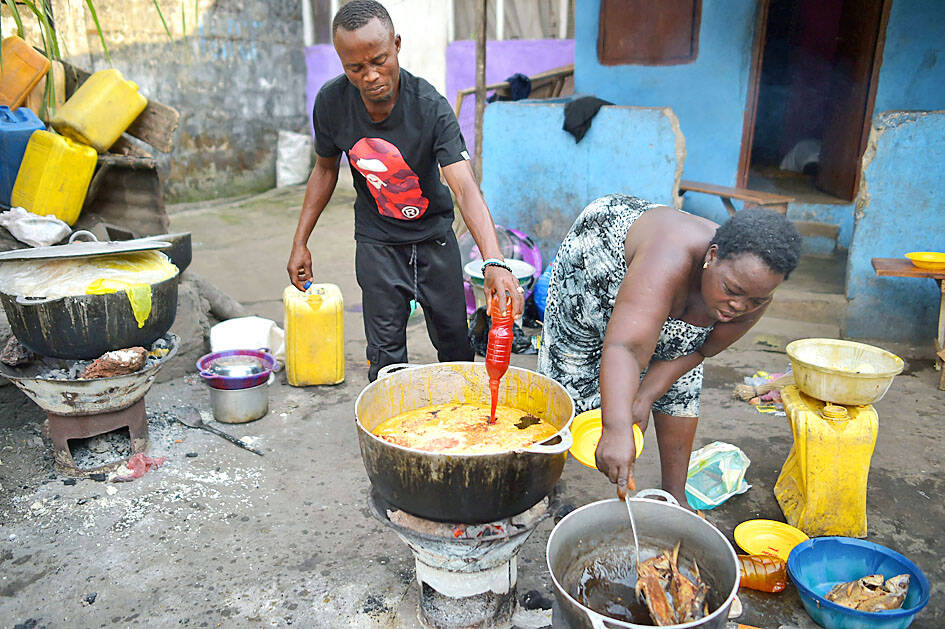
Photo: AFP
The densely-populated metropolis does not have any urban agriculture, so food is trucked in from the countryside or imported from abroad.
Ever since the COVID-19 pandemic and war in Ukraine sent global inflation soaring, trucking in food has become painfully expensive.
As of November last year, the latest month on record, inflation had risen 35 percent year-on-year in Sierra Leone.
“We were buying a cup of rice for 1,500 leones [US$0.08 at the current exchange rate] in 2021 — now its 3,500 leones,” said Kargbo, who opened her business to support her six children after her husband died of Ebola in 2014.
Sierra Leone in July last year slashed three zeros off its currency hoping to restore confidence in the inflation-hit leone. Many, including Kargbo, still quote prices in the former denomination.
In August, riots broke out over the rising cost of living in the Shell Old Road Junction neighborhood where Kargbo lives and works.
Twenty-seven civilians and six police officers were killed.
Kargbo’s customers consist mainly of motorcycle taxi drivers known as okada men, street hawkers and, occasionally, office workers.
“My family depends on the cookery to eat for dinner during the week — we only cook at home on weekends due to rising cost of living,” said Francis Koroma, a teacher who was holding two plastic bowls to fill for his family of five.
Often, cookery meals are more affordable than buying products from the market, but the stalls have had to increase prices.
Kargbo now sells her dishes of rice with potato leaf sauce or groundnut soup for 8,000 leones, up from 5,000 leones in 2021. Market vendors, too, are not turning as much profit.
“We have slow sales,” Sierra Leone Market Women Association head Haja Marie Bob-Kandeh said. “People are now prioritizing what they should [spend] for the day because of inflation.”
She said that vendors were worried about the cost of fresh vegetables, which have a short shelf life, and instead focused on selling ingredients for basic meals, such as rice with sauce.
At a large cookery in the more affluent Hill Cot Road area, Fatmata Bangura, 48, sits on a low wooden bench and cuts up cow kanda — cow skin — while her daughter, Isata Dumbuya, and four employees stir onions, plantain, cabbage and beans in large metal pots over wood and coal fires.
They have been awake since 3:30am, when Dumbuya, 32, sets out each day for the market. By 6am she is at the roadside shop and beginning to cook the day’s meals: cassava leaf, beans or tola stew for breakfast, often crain crain — a local dish made with okra — for lunch.
Their business is stable, but their bottom line has nonetheless taken a hit.
“The palm oil was sold at 200,000 leones, now it’s 585,000 leones,” Dumbuya said. “The rice, before, we bought it at 280,000, but now the price is 550,000.”
There is a limit to how much of the cost increase can be passed on to customers, say stall holders.
Sitting on a picnic bench outside Dumbuya’s shop, Hassan Mohamed Vamboi, a 29-year-old motorcycle driver, digs into a plate of green, leafy stew. He eats here at least once a day.
Vamboi said he has been feeling the pinch of rising fuel prices and has had to extend his workdays from 12 to 16 hours to get by.
“It’s very challenging in the country presently,” he said.
He has also moved his wife and two children to his village to save money.
“My pocket cannot uphold them here,” Vamboi said.
For now, he continues to eat at Dumbuya’s, and she continues to cook.
“If people come to my shop and eat my food and say: ‘Oh you know how to cook,’ it inspires me,” she said. “So every day I do the same thing, for people to come and eat.”

The Burmese junta has said that detained former leader Aung San Suu Kyi is “in good health,” a day after her son said he has received little information about the 80-year-old’s condition and fears she could die without him knowing. In an interview in Tokyo earlier this week, Kim Aris said he had not heard from his mother in years and believes she is being held incommunicado in the capital, Naypyidaw. Aung San Suu Kyi, a Nobel Peace Prize laureate, was detained after a 2021 military coup that ousted her elected civilian government and sparked a civil war. She is serving a

REVENGE: Trump said he had the support of the Syrian government for the strikes, which took place in response to an Islamic State attack on US soldiers last week The US launched large-scale airstrikes on more than 70 targets across Syria, the Pentagon said on Friday, fulfilling US President Donald Trump’s vow to strike back after the killing of two US soldiers. “This is not the beginning of a war — it is a declaration of vengeance,” US Secretary of Defense Pete Hegseth wrote on social media. “Today, we hunted and we killed our enemies. Lots of them. And we will continue.” The US Central Command said that fighter jets, attack helicopters and artillery targeted ISIS infrastructure and weapon sites. “All terrorists who are evil enough to attack Americans are hereby warned

Seven wild Asiatic elephants were killed and a calf was injured when a high-speed passenger train collided with a herd crossing the tracks in India’s northeastern state of Assam early yesterday, local authorities said. The train driver spotted the herd of about 100 elephants and used the emergency brakes, but the train still hit some of the animals, Indian Railways spokesman Kapinjal Kishore Sharma told reporters. Five train coaches and the engine derailed following the impact, but there were no human casualties, Sharma said. Veterinarians carried out autopsies on the dead elephants, which were to be buried later in the day. The accident site

RUSHED: The US pushed for the October deal to be ready for a ceremony with Trump, but sometimes it takes time to create an agreement that can hold, a Thai official said Defense officials from Thailand and Cambodia are to meet tomorrow to discuss the possibility of resuming a ceasefire between the two countries, Thailand’s top diplomat said yesterday, as border fighting entered a third week. A ceasefire agreement in October was rushed to ensure it could be witnessed by US President Donald Trump and lacked sufficient details to ensure the deal to end the armed conflict would hold, Thai Minister of Foreign Affairs Sihasak Phuangketkeow said after an ASEAN foreign ministers’ meeting in Kuala Lumpur. The two countries agreed to hold talks using their General Border Committee, an established bilateral mechanism, with Thailand