Chinese apps are a potential national security risk because of China’s authoritarian political system, two Institute for National Defense and Security Research (INDSR) experts said.
“Information security risks are national security risks,” said Tzeng Yi-suo (曾怡碩), an associate research fellow at the INDSR’s Division of Cyber Security and Decision-making Simulation.
“As long as the app is under the jurisdiction of the Chinese government, there will basically be security concerns,” he added.

Photo: Reuters
Tzeng said that commercial companies collect data about app users and then use algorithms to tailor information and marketing.
This is not a problem in a democratic country governed by the rule of law such as Taiwan, because if the information involves judicial cases, the government would be required to go through legal procedures to obtain the information, he said.
However, the National Intelligence Law of the People’s Republic of China and the Law of the People’s Republic of China on Guarding State Secrets empower Chinese government agencies to require platform service providers to hand over users’ data “as long as they determine that national security is involved,” he said.
“How the Chinese government obtains the data and what it does with it is not transparent,” he added.
In areas under China’s authoritarian control, including Hong Kong and Macau, China “can assert its sovereignty” and “investigate the words and actions of users” using data collected by Chinese apps, he said.
In places outside its jurisdiction, “China’s authoritarian system” still poses risks to users, said Lee Jyun-yi (李俊毅), an associate research fellow at the INDSR’s Division of National Security Research.
Lee cited the US court testimony of former employees of ByteDance, TikTok’s parent company, as evidence that “TikTok does indeed transmit users’ personal information back to China.”
In addition to the security of personal data, Chinese apps such as Douyin and TikTok pose risks relating to the spread of false information, Lee said.
Lee said that although misleading information is not limited to Chinese apps, popular Western platforms such as Facebook, Instagram and YouTube have adopted new methods to crack down on bot accounts and mark state-funded media.
“TikTok’s lack of effort to do so makes it relatively easy for false information to spread,” he said, adding that Chinese apps might “shape users’ perceptions” with the use of algorithms.
Up to 40 percent of popular videos on Chinese apps come from accounts controlled by the Chinese government, he said.
“The Chinese government has implemented legislation which requires media platforms’ algorithm recommendation models to comply with the values of the Chinese Communist Party,” he said.
Taking Douyin as an example, Lee said that the platform promotes content that is “beneficial to China,” and the Chinese government requires the platform to self-censor.
This makes it “difficult for short videos that are negative or critical of China to appear or spread, which has a long-term effect in shaping people’s perceptions,” he added.
The two security experts are not alone in their concerns about Chinese apps such as TikTok.
In March, then-minister of digital affairs Audrey Tang (唐鳳) said TikTok had been classified as a “dangerous product.”
The use of the app is banned in government agencies and on their premises in Taiwan.
In April, US President Joe Biden signed into law a bill titled Protecting Americans from Foreign Adversary Controlled Applications Act, which requires ByteDance to divest its US assets or face a nationwide ban. The earliest such a ban could go into effect would be Jan. 19 next year.
India completely banned TikTok in June 2020, while countries including Australia, the UK, France, the Netherlands, Norway, Belgium, Denmark, Canada and New Zealand have separately imposed rules limiting certain people, especially government employees, from using the app due to cyber-security concerns.

The manufacture of the remaining 28 M1A2T Abrams tanks Taiwan purchased from the US has recently been completed, and they are expected to be delivered within the next one to two months, a source said yesterday. The Ministry of National Defense is arranging cargo ships to transport the tanks to Taiwan as soon as possible, said the source, who is familiar with the matter. The estimated arrival time ranges from late this month to early next month, the source said. The 28 Abrams tanks make up the third and final batch of a total of 108 tanks, valued at about NT$40.5 billion

Travel agencies in Taiwan are working to secure alternative flights for travelers bound for New Zealand for the Lunar New Year holiday, as Air New Zealand workers are set to strike next week. The airline said that it has confirmed that the planned industrial action by its international wide-body cabin crew would go ahead on Thursday and Friday next week. While the Auckland-based carrier pledged to take reasonable measures to mitigate the impact of the workers’ strike, an Air New Zealand flight arriving at Taipei from Auckland on Thursday and another flight departing from Taipei for Auckland on Saturday would have to
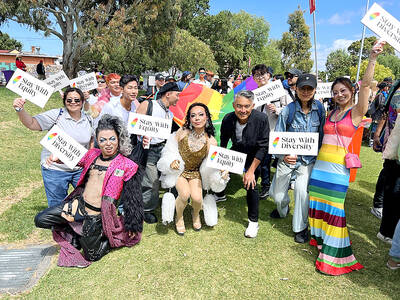
A group from the Taiwanese Designers in Australia association yesterday represented Taiwan at the Midsumma Pride March in Melbourne. The march, held in the St. Kilda suburb, is the city’s largest LGBTQIA+ parade and the flagship event of the annual Midsumma Festival. It attracted more than 45,000 spectators who supported the 400 groups and 10,000 marchers that participated this year, the association said. Taiwanese Designers said they organized a team to march for Taiwan this year, joining politicians, government agencies, professionals and community organizations in showing support for LGBTQIA+ people and diverse communities. As the first country in Asia to legalize same-sex

MOTIVES QUESTIONED The PLA considers Xi’s policies toward Taiwan to be driven by personal considerations rather than military assessment, the Epoch Times reports Chinese President Xi Jinping’s (習近平) latest purge of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army (PLA) leadership might have been prompted by the military’s opposition to plans of invading Taiwan, the Epoch Times said. The Chinese military opposes waging war against Taiwan by a large consensus, putting it at odds with Xi’s vision, the Falun Gong-affiliated daily said in a report on Thursday, citing anonymous sources with insight into the PLA’s inner workings. The opposition is not the opinion of a few generals, but a widely shared view among the PLA cadre, the Epoch Times cited them as saying. “Chinese forces know full well that