About 30,000 years ago, ancient inhabitants of Taiwan might have intentionally crossed the Kuroshio, one of the world’s strongest currents, researchers found.
They might have searched for a new habitat and reached the Ryukyu Islands in Japan, said a study, titled “Palaeolithic voyage for invisible islands beyond the horizon,” which was published in the journal Scientific Reports on Thursday.
The study, led by anthropologist Yousuke Kaifu, a ancient history researcher at the University of Tokyo, is part of a project on maritime migration of Paleolithic people 35,000 to 30,000 years ago.
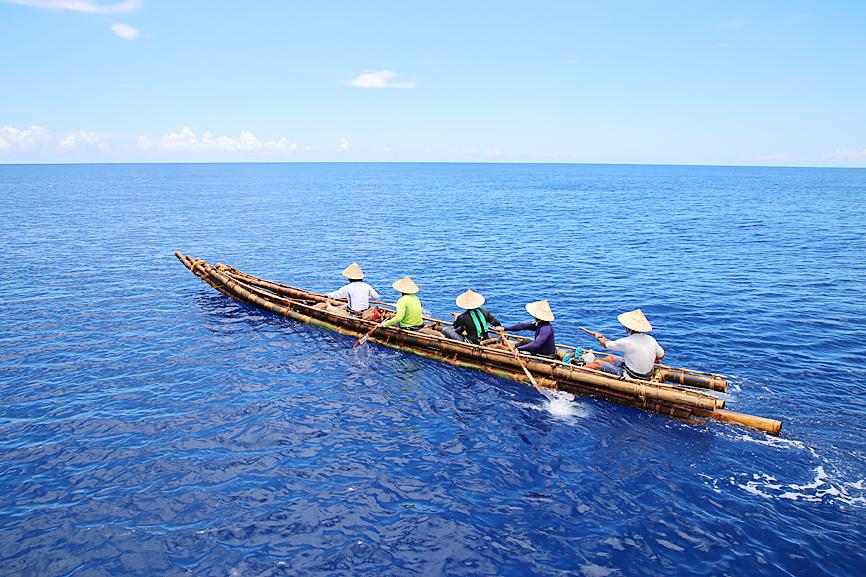

Photo courtesy of University of Tokyo professor Yousuke Kaifu
While some of them are believed to have migrated from Taiwan to the Ryukyu Islands, it has been unclear whether their voyages were made by chance or choice.
“I had been seeking a good way to demonstrate the intentionality of the sea crossings, but had no idea what to do. Then, I ... came across the idea of using the tracking buoys,” Kaifu wrote in an e-mail to the Taipei Times.
Kaifu, with the help of Jan Sen (詹森), a professor at National Taiwan University’s Institute of Oceanography, and former technician Kuo Tien-hsia (郭天俠), analyzed data of the movements of 138 satellite-tracked buoys that drifted past the Philippines, Taiwan and Japan from 1989 to 2017.
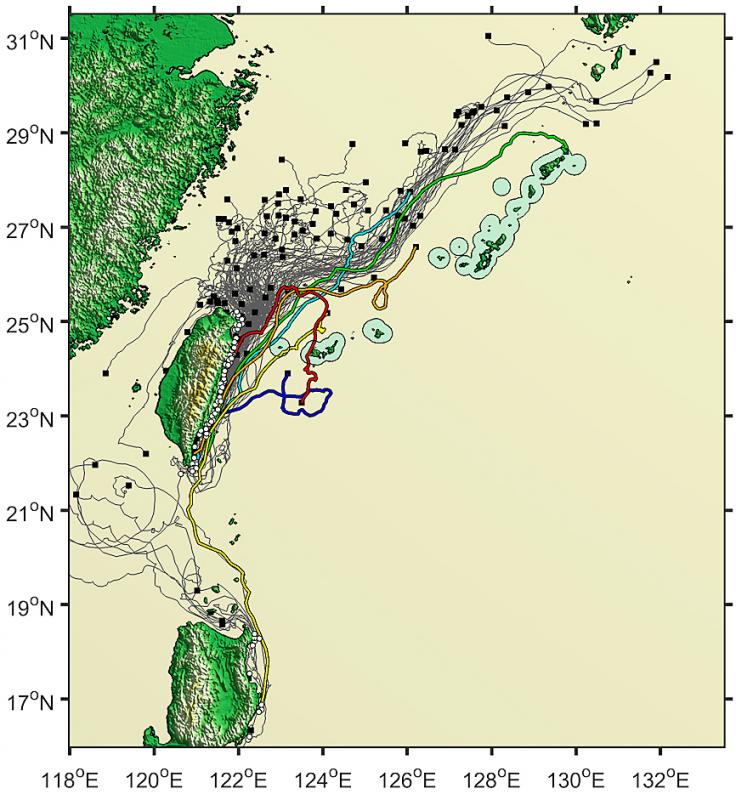
Photo courtesy of former National Taiwan University technician Kuo Tien-hsia
The methodology was predicated on some evidence showing that the Kuroshio’s flow remained unchanged over the past 100,000 years, the team said.
Of the 122 buoys that drifted past Taiwan, 114 were carried northward by the Kuroshio, and of these, only three came within 20km of the central and southern Ryukyu Islands, the researchers found.
This usually happened under severe weather conditions, such as typhoons and northeasterly monsoons, they found.
Of the 16 buoys that drifted past the Philippine main island of Luzon, only one drifted toward the Ryukyu Islands, they found.
The ancient sailors could not have reached the Ryukyu Islands through random drifting, whereas bad weather conditions, although occasionally bringing some buoys closer to the islands, are unlikely to have been used by the ancient seafarers, Jan said.
Yonaguni Island, the westernmost of the Ryukyu Islands, is in good weather conditions visible from some mountains in eastern Taiwan, he added.
The movements of the buoys, originally deployed by the US-led Surface Velocity Program, show the possible routes of ancient voyages, Jan said, adding that their method can be described as “mining old data for a new application.”
Asked if there were conditions unfavorable for survival in Taiwan that prompted the Paleolithic people to move, Kaifu said that if there were such conditions, people might have sought to relocate within Taiwan.
“You really do not have to go to that remote island, but they did,” Kaifu said. “I think that is human nature.”
“It must be a one-way trip. The Kuroshio current is too strong to come back, even if they plan a round trip,” he added.
In July last year, a team of five paddled from Taitung to Yonaguni Island in a logboat, covering the 225km in 45 hours.
Kaifu said he seeks to document the research in further academic papers, books and films, including a short film that would be screened in Tokyo this month.
Asked if the migration from Taiwan was the first known sea crossing to Japan, Kaifu said that ancient populations also crossed the sea from the Korean Peninsula, adding that the first residents of the Ryukyu Islands were not necessarily the ancestors of modern Japanese.
“This project is to highlight a part of interesting human histories, not to applaud someone. I do not want to be nationalistic in my anthropological studies,” he said.

LOUD AND PROUD Taiwan might have taken a drubbing against Australia and Japan, but you might not know it from the enthusiasm and numbers of the fans Taiwan might not be expected to win the World Baseball Classic (WBC) but their fans are making their presence felt in Tokyo, with tens of thousands decked out in the team’s blue, blowing horns and singing songs. Taiwanese fans have packed out the Tokyo Dome for all three of their games so far and even threatened to drown out home team supporters when their team played Japan on Friday. They blew trumpets, chanted for their favorite players and had their own cheerleading squad who dance on a stage during the game. The team struggled to match that exuberance on the field, with

Taiwanese paleontologists have discovered fossil evidence that pythons up to 4m long inhabited Taiwan during the Pleistocene epoch, reporting their findings in the international scientific journal Historical Biology. National Taiwan University (NTU) Institute of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology associate professor Tsai Cheng-hsiu (蔡政修) led the team that discovered the largest snake fossil ever found in Taiwan. The single trunk vertebra was discovered in Tainan at the Chiting Formation, dated to between 400,000 and 800,000 years ago in the Middle Pleistocene, the paper said. The area also produced Taiwan’s first avian fossil, as well as crocodile, mammoth, saber-toothed cat and rhinoceros fossils, it said. Discoveries

Taiwanese paleontologists have discovered fossil evidence that pythons up to 4m long inhabited Taiwan during the Pleistocene epoch, reporting their findings in the international scientific journal Historical Biology. National Taiwan University (NTU) Institute of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology associate professor Tsai Cheng-hsiu (蔡政修) led the team that discovered the largest snake fossil ever found in Taiwan. A single trunk vertebra was discovered in Tainan at the Chiting Formation, dated to between 800,000 to 400,000 years ago in the Middle Pleistocene, the paper said. The area also produced Taiwan’s first avian fossil, as well as crocodile, mammoth, sabre-toothed cat and rhinoceros fossils, it said. Discoveries

Whether Japan would help defend Taiwan in case of a cross-strait conflict would depend on the US and the extent to which Japan would be allowed to act under the US-Japan Security Treaty, former Japanese minister of defense Satoshi Morimoto said. As China has not given up on the idea of invading Taiwan by force, to what extent Japan could support US military action would hinge on Washington’s intention and its negotiation with Tokyo, Morimoto said in an interview with the Liberty Times (sister paper of the Taipei Times) yesterday. There has to be sufficient mutual recognition of how Japan could provide