The Czech Republic’s experience in making high-end instruments and assisting European Space Agency (ESA) missions makes Prague and Taipei complementary partners in the field of aerospace, especially as Taiwan aims to develop scientific instruments for a lunar orbiter, Taiwanese scientists say.
While the US and France have been the nation’s major foreign partners in space technology development over the past three decades, a Czech delegation’s visit to Taiwan last week might usher in new opportunities.
The National Space Organization (NSPO) plans to sign memorandums of understanding with the Czech Academy of Sciences’ (CAS) Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Charles University’s Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, and the Czech Technical University in Prague’s Institute of Experimental and Applied Physics.
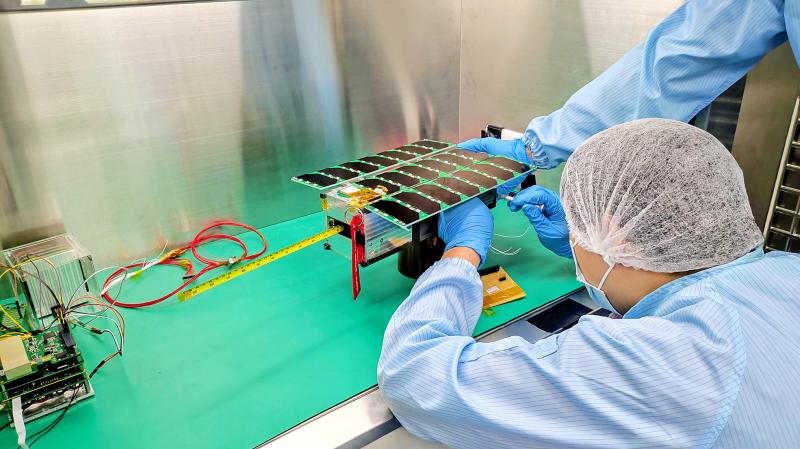

Photo courtesy of National Central University Department of Space Science and Engineering
It is the first time that the NSPO plans to sign such agreements with Czech institutions, while individual Taiwanese and Czech scientists have sustained ties for years.
Taiwan’s world-leading research on ionospheric observations is appealing for Czech scientists, while their high-end engineering technology cultivated during the former Soviet Union is valuable for Taiwan, said Liu Jann-yenq (劉正彥), a professor at National Central University (NCU) department of space science and engineering.
His team has worked with the Institute of Atmospheric Physics under the CAS for nearly eight years, said Liu, who is also a member of the Central Europe Task Force at the Ministry of Science and Technology’s Center for Global Affairs and Science Engagement.
The team has developed a network of ionospheric observation stations using high-frequency Doppler sounders deployed in Hsinchu, Miaoli, Chiayi, Nantou, Yilan, Hualien and Taitung counties, he said.
The sounders transmit and receive radio signals to analyze ionospheric disruptions, which can influence radio communications and global positioning systems on Earth, he said.
Taiwan and the Czech Republic are also looking forward to more cooperation in the development of artificial satellites, he said.
The department in December plans to launch a cubesat for ionospheric observations, he added.
The Ionospheric Dynamics Explorer and Attitude Subsystem Satellite (IDEASSat) weighs nearly 4.5kg and has been completely developed, manufactured, and assembled by the department’s faculty and students, he said.
His team would share the data collected by IDEASSat with their Czech collaborators, as they can help download and analyze them, he said.
The cubesat would be launched by US company SpaceX on a rideshare launch brokered by ISILaunch in the Netherlands and HelioX Cosmos in Taiwan, a project funded by the NSPO, he added.
Other Taiwanese and Czech researchers are working on proposals to develop scientific payloads on a spacecraft that would orbit the moon, a mission announced by the NSPO.
The NSPO earlier this year made a call soliciting scientific payloads to be installed on a lunar orbiter as part of the nation’s third space technology development program, which began last year and would run through 2028.
The payloads can weigh up to 3kg and need to withstand drastic radiation and temperature changes during the cislunar cruise and in lunar orbit, and the flight models of the payloads would be delivered by the first quarter of 2024, according to an NSPO announcement last month.
The spacecraft, with a planned dry mass of 150kg, would be sent to an orbit 100km above the moon, the announcement said, without naming the maker of the spacecraft.
Asked about the NSPO’s call, department director Chao Chi-kuang (趙吉光) said the department plans to develop an instrument to measure electromagnetic parameters on the lunar surface to deepen scientists’ understanding of the moon’s mantle.
Chao’s team has developed an Advanced Ionospheric Probe that was installed on Taiwan’s own Formosat-5 satellite, which was launched on a SpaceX Falcon 9 in 2017.
The department also aims to work with Charles University to develop an instrument to measure solar particles, he said.
Chao said he initially had reservations about the NSPO’s call, given Taiwan’s lack of experience in making instruments that can resist higher cosmic radiation outside the Earth’s magnetic field.
Nonetheless, he became more interested in it after building ties with Charles University, Chao said.
While the Czech Republic does not have a national agency similar to the NSPO, its Czech Space Alliance — an association of aerospace firms — is part of the ESA supply chain and has more experience in making instruments to explore other planets, he said.
Deepening ties with Czech institutions and the country’s space industry would allow Taiwan to save time on lunar exploration, as it attempts to move from Earth-centered observations to missions targeting other planets, Chao said.
The moon’s rich reserves of helium-3, a potential nuclear fuel, are worth investigating, and the moon can be regarded as a logistics station for missions to Mars, he added.
Gilbert Pi (畢可為), an NCU graduate working at Charles University’s Faculty of Mathematics and Physics, helped connect NCU and the NSPO to the faculty.
Pi said he had visited Prague several times while studying under his NCU adviser Shue Jih-hong (許志浤), who maintains close ties with the Czech faculty.
Having become a project researcher there after three years of postdoctoral research, Pi said he enjoys being part of the Space Physics Group led by professor Zdenek Nemecek, adding that he is the only non-European member of the team.
Their group has developed instruments for missions led by the ESA and Russia, and is glad to share its experience with Taiwan, he said.
Taiwan’s third space program also attracts many Czech institutions, he added.
In addition to the moon exploration project, Taiwan’s third space program also involves the development of six high-resolution optical remote sensing satellites, two super-high-resolution remote sensing satellites and two synthetic aperture radar satellites.
Professor Loren Chang (張起維) said he represented the department last week in a meeting with the members of the Czech Space Alliance at a trade forum during their visit to Taiwan with Czech Senate President Milos Vystrcil.
Some Czech companies specializing in satellite navigation systems or infrared sensors have expressed an interest in the department’s satellite development as well as research on the impact of ionospheric disruptions on communications, Chang said.
Asked about the lunar exploration project, Deputy Minister of Science and Technology Shieh Dar-bin (謝達斌) said a major hurdle is the loss of satellite or spacecraft communications on the far side of the moon, so advancing communications, materials, engine combustion and autocontrol technologies would be necessary to develop a lunar orbiter.
The ministry could help gather experts for the NSPO’s lunar exploration project, while foreign resources, such as a planned SpaceX lunar lander, would be part of its considerations as well, he said.

A preclearance service to facilitate entry for people traveling to select airports in Japan would be available from Thursday next week to Feb. 25 at Taiwan Taoyuan International Airport, Taoyuan International Airport Corp (TIAC) said on Tuesday. The service was first made available to Taiwanese travelers throughout the winter vacation of 2024 and during the Lunar New Year holiday. In addition to flights to the Japanese cities of Hakodate, Asahikawa, Akita, Sendai, Niigata, Okayama, Takamatsu, Kumamoto and Kagoshima, the service would be available to travelers to Kobe and Oita. The service can be accessed by passengers of 15 flight routes operated by
Chinese spouse and influencer Guan Guan’s (關關) residency permit has been revoked for repeatedly posting pro-China videos that threaten national security, the National Immigration Agency confirmed today. Guan Guan has said many controversial statements in her videos posted to Douyin (抖音), including “the red flag will soon be painted all over Taiwan” and “Taiwan is an inseparable part of China,” and expressing hope for expedited reunification. The agency last year received multiple reports alleging that Guan Guan had advocated for armed reunification. After verifying the reports, the agency last month issued a notice requiring her to appear and explain her actions. Guan

GIVE AND TAKE: Blood demand continues to rise each year, while fewer young donors are available due to the nation’s falling birthrate, a doctor said Blood donors can redeem points earned from donations to obtain limited edition Formosan black bear travel mugs, the Kaohsiung Blood Center said yesterday, as it announced a goal of stocking 20,000 units of blood prior to the Lunar New Year. The last month of the lunar year is National Blood Donation Month, when local centers seek to stockpile blood for use during the Lunar New Year holiday. The blood demand in southern Taiwan — including Tainan and Kaohsiung, as well as Chiayi, Pingtung, Penghu and Taitung counties — is about 2,000 units per day, the center said. The donation campaign aims to boost
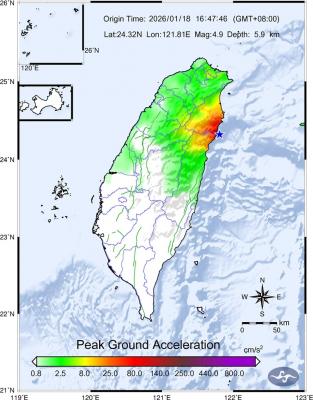
The Central Weather Administration (CWA) said a magnitude 4.9 earthquake that struck off the coast of eastern Taiwan yesterday was an independent event and part of a stress-adjustment process. The earthquake occurred at 4:47pm, with its epicenter at sea about 45.4km south of Yilan County Hall at a depth of 5.9km, the CWA said. The quake's intensity, which gauges the actual effects of a temblor, was highest in several townships in Yilan and neighboring Hualien County, where it measured 4 on Taiwan's seven-tier intensity scale, the CWA said. Lin Po-yu (林柏佑), a division chief at the CWA's Seismological Center, told a news conference