Two National Chiao Tung University professors on Tuesday said they have developed a new technique that significantly reduces the time and money required to carry out virus genome sequencing, which is expected to speed up the process and cut the cost of developing vaccines and anti-viral drugs.
The technique can be used in the fields of genome research, preventive medicine and the development of personalized medicine, in which medical treatment is customized on the basis of the patient’s genetic code, the researchers said.
The technique cuts down the time it takes to sequence a virus’ genome to one hour instead of one day, and reduces the cost of the process from US$5,000 to about US$500, said Steven Huang (黃國華), a professor at the university’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering.
The research, conducted by Huang and Chen Yu-shiun (陳昱勳), a professor at the school’s Department of Biology Science and Technology, is to be published in the journal Nature Nanotechnology this month.
Huang said current sequencing techniques require the use of fluorescence and other external aids to enable the reading of polymerase synthesis, but his and Chen’s method requires no external aids and reduces the error rate to nearly zero.
Huang said he has applied for a patent for the sequencing technique that is pending approval, adding that he expects the new method will replace the current methods because it is more affordable, accurate and faster.

The Taipei Summer Festival is to begin tomorrow at Dadaocheng Wharf (大稻埕), featuring four themed firework shows and five live music performances throughout the month, the Taipei Department of Information and Tourism said today. The festival in the city’s Datong District (大同) is to run until Aug. 30, holding firework displays on Wednesdays and the final Saturday of the event. The first show is scheduled for tomorrow, followed by Aug. 13, 20 and 30. To celebrate the 30th anniversary of Disney Pixar's movie Toy Story, the festival has partnered with Walt Disney Co (Taiwan) to host a special themed area on

BE CAREFUL: The virus rarely causes severe illness or death, but newborns, older people and those with medical conditions are at risk of more severe illness As more than 7,000 cases of chikungunya fever have been reported in China’s Guangdong Province this year, including 2,892 new cases last week, the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) yesterday said it is monitoring the situation and considering raising the travel notice level, which might be announced today. The CDC issued a level 1 travel notice, or “watch,” for Guangdong Province on July 22, citing an outbreak in Foshan, a manufacturing hub in the south of the province, that was reported early last month. Between July 27 and Saturday, the province reported 2,892 new cases of chikungunya, reaching a total of 7,716

Aftershocks from a magnitude 6.2 earthquake that struck off Yilan County at 3:45pm yesterday could reach a magnitude of 5 to 5.5, the Central Weather Administration (CWA) said. Seismological Center technical officer Chiu Chun-ta (邱俊達) told a news conference that the epicenter of the temblor was more than 100km from Taiwan. Although predicted to measure between magnitude 5 and 5.5, the aftershocks would reach an intensity of 1 on Taiwan’s 7-tier scale, which gauges the actual effect of an earthquake, he said. The earthquake lasted longer in Taipei because the city is in a basin, he said. The quake’s epicenter was about 128.9km east-southeast
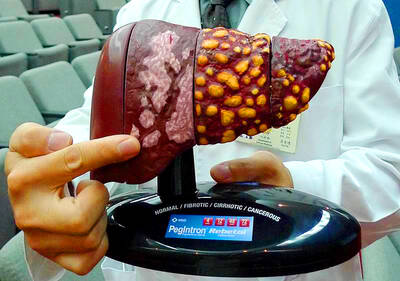
STAY VIGILANT: People should reduce the risk of chronic liver inflammation by avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, smoking and eating pickled foods, the physician said A doctor last week urged people to look for five key warning signs of acute liver failure after popular producer-turned-entertainer Shen Yu-lin (沈玉琳) was reportedly admitted to an intensive care unit for fulminant hepatitis. Fulminant hepatitis is the rapid and massive death of liver cells, impairing the organ’s detoxification, metabolic, protein synthesis and bile production functions, which if left untreated has a mortality rate as high as 80 percent, according to the Web site of Advancing Clinical Treatment of Liver Disease, an international organization focused on liver disease prevention and treatment. People with hepatitis B or C are at higher risk of