The COP27 summit of nearly 200 countries agreed on Sunday to set up a “loss and damage” fund to support poorer countries that are being ravaged by climate impacts, overcoming decades of resistance from wealthy nations whose historic emissions have fueled climate change.
Pakistan’s climate minister Sherry Rehman, who was part of the campaign by developing nations to win the commitment at the two-week UN summit in Egypt, hailed the landmark decision as “downpayment on climate justice.”
However, the text of the agreement leaves open a number of crucial details to be worked out next year and beyond, including who would contribute to the fund and who would benefit.
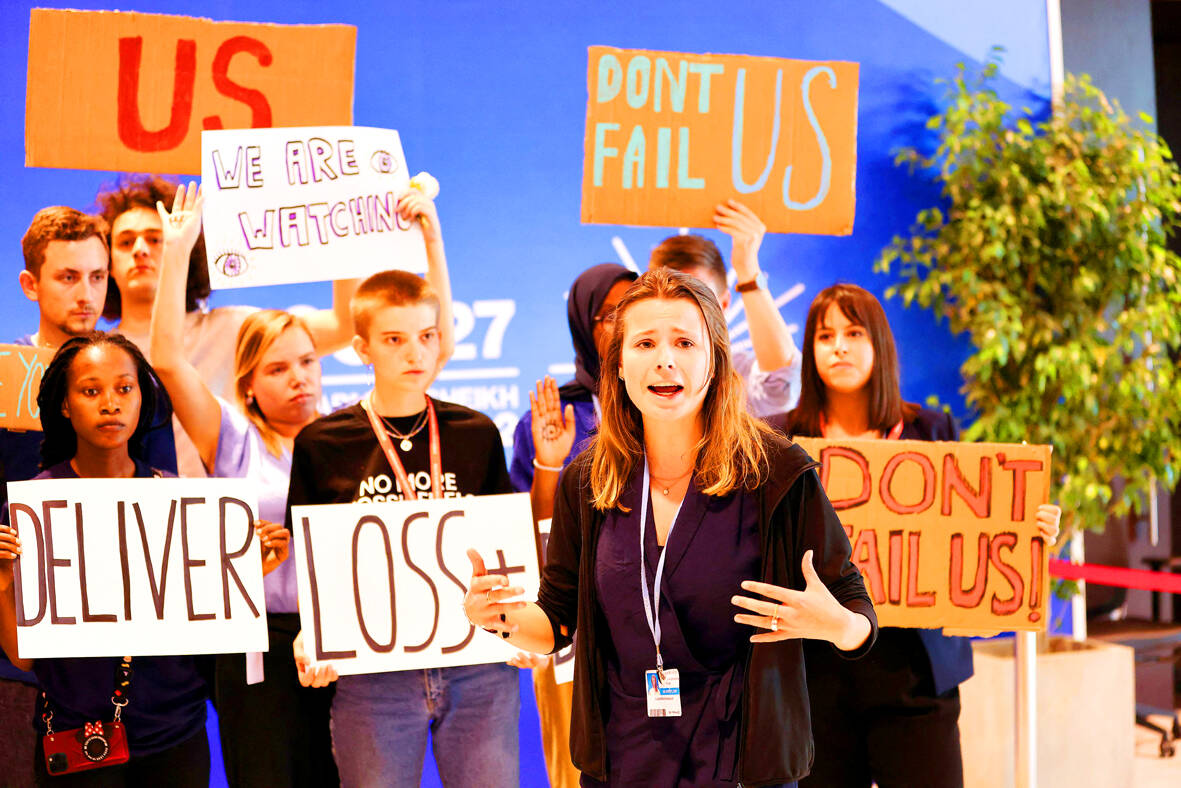
Photo: Reuters 照片:路透
Here is what you need to know about the agreement:
WHAT IS ‘LOSS AND DAMAGE’?
In UN climate talks, “loss and damage” refers to costs incurred from climate-fueled weather extremes or impacts, like rising sea levels.
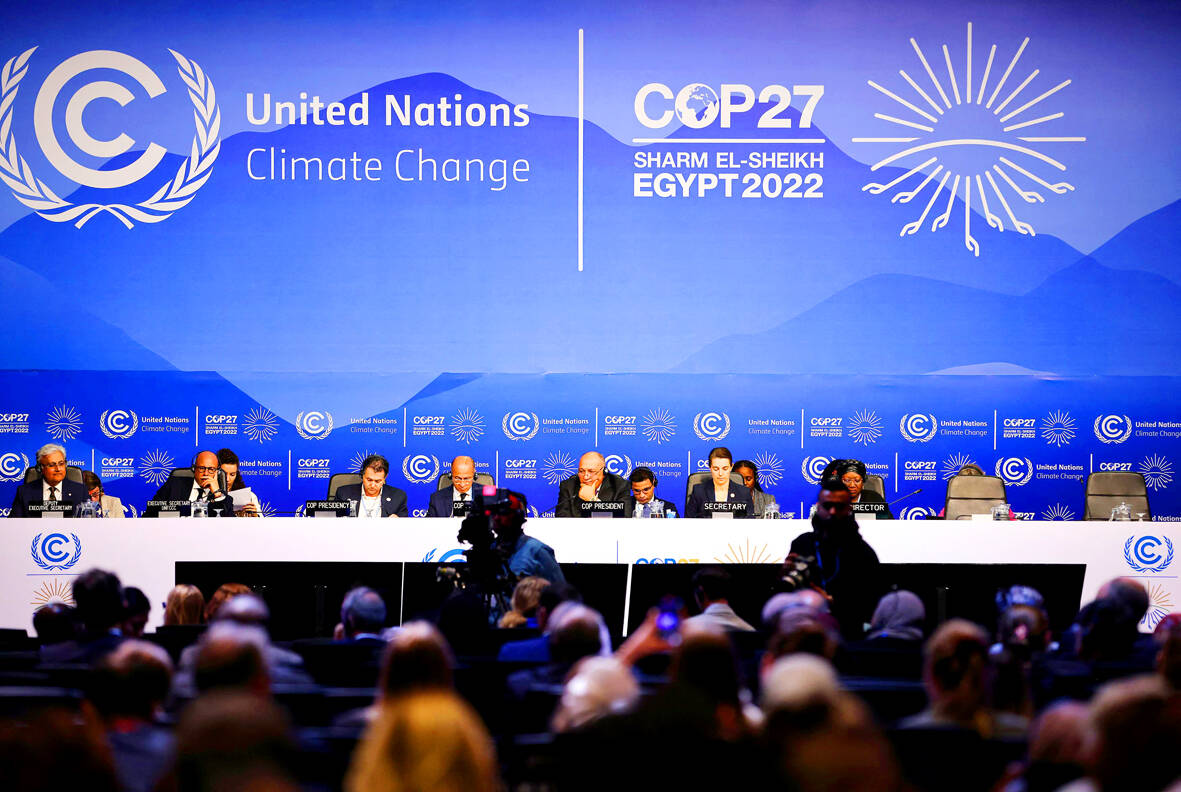

Photo: Reuters Photo: Reuters
Climate funding so far has focused mostly on cutting carbon dioxide emissions in an effort to curb global warming, while about a third of it has gone toward projects to help communities adapt to future impacts.
Loss and damage funding is different, specifically covering the cost of damage that countries cannot avoid or adapt to.
But there is no agreement yet over what should count as “loss and damage” caused by climate change — which could include damaged infrastructure and property, as well as harder-to-value natural ecosystems or cultural assets.

Photo: AP 照片:美聯社
A report by 55 vulnerable countries estimated that their combined climate-linked losses over the last two decades totaled US$525 billion, or 20 percent of their collective GDP. Some research suggests that by 2030 such losses could reach US$580 billion per year.
WHO PAYS WHOM?
Vulnerable countries and campaigners in the past argued that rich countries that caused the bulk of climate change with their historical greenhouse gas emissions should pay.
The US and EU had resisted the argument, fearing spiraling liabilities, but changed their position during the COP27 summit. The EU has argued that China — the world’s second-biggest economy, but classified by the UN as a developing country — should also pay into it.
A few governments have made relatively small but symbolic funding commitments for loss and damage: Denmark, Belgium, Germany and Scotland, plus the EU. China has not committed any payment.
Also remaining to be worked out are the details on which countries or disasters qualify for compensation.
WHAT DOES THE COP27 AGREEMENT SAY?
The fund agreed upon at the UN summit in Egypt will be aimed at helping developing countries that are “particularly vulnerable” to climate change — language wanted by wealthy nations to ensure the money goes to the most urgent cases while also limiting the pool of potential recipients.
The deal lays out a roadmap for future decision-making, with recommendations to be made at next year’s UN climate summit for decisions including who would oversee the fund, how the money would be dispersed, and to whom.
The agreement calls for the funds to come from a variety of existing sources, including financial institutions, rather than relying on rich nations to pay in.
(Reuters)
參與《聯合國氣候變化框架公約》締約方大會第27次會議(COP27)的近兩百個國家,上週日同意設立「損失與損害」基金,以援助受氣候變化衝擊、慘遭蹂躪的較貧窮國家,克服了富裕國家數十年來的抵制,這些富國過去的碳排放助長了氣候變化。
巴基斯坦氣候部長雪莉‧雷曼,在為期兩週、在埃及舉行的聯合國峰會上為發展中國家發聲,讓大會做出此承諾,她稱讚此具有里程碑意義的決定是「氣候正義的頭期款」。
但該協議的內容有些關鍵細節並未釐清,有待明年及之後決定,包括該基金之出資者以及受益者。
以下為該協議之重點:
什麼是「損失及損害」?
在聯合國氣候談判中,「損失及損害」是指因受到氣候引發的極端天氣或衝擊──例如海平面上升──所影響,而產生的成本。
氣候資金到目前主要都集中在減少二氧化碳排放以遏制全球暖化,其中約三分之一用於幫助社群適應未來衝擊的計畫。
損失及損害資金則不同,它特別支付國家無法避免或無法調適因應的損害成本。
但是,對於何者該計入氣候變化所造成的「損失及損害」,目前尚未有一致看法──這可能包括受損的基礎設施與財產,以及更難以估價的自然生態系統或文化資產之破壞。
五十五個易受氣候變化衝擊的脆弱國家所做的一份報告估計,過去二十年他們與氣候相關的損失總計5,250億美元,佔其總GDP的20%。一些研究顯示,到了二○三○年,此類損失可能會達到每年5,800億美元。
誰該為誰買單?
脆弱國家及運動人士以前主張,富裕國家過去所排放的溫室氣體,是導致氣候變化的一大因素,因此富國應為此付出代價。
美國和歐盟一直抗拒此論點,擔心會負債累累,但在COP27峰會期間改變了立場。歐盟認為,中國──世界第二大經濟體,但被聯合國列為發展中國家──也應為此付出代價。
一些國家的政府為損失及損害承諾了相對較小但具象徵意義的資助:丹麥、比利時、德國與蘇格蘭,以及歐盟。中國並未承諾支付任何款項。
仍有待確定的,是哪些國家或災害有獲賠償資格之細節。
COP27協議是怎麼說的?
在埃及舉行的聯合國峰會中商定的基金,旨在幫助「特別容易受到」氣候變化影響的發展中國家,這是富國屬意的措辭,以確保資金用於最緊急的情況,同時限制潛在受資助者的數量。
該協議為未來的決策制定了路線圖,並建議明年聯合國氣候峰會可做的相關決策,包括該基金該由誰來監督、資金將如何分配,以及分配給誰。
該協議要求資金來自各種既有來源,包括金融機構,而不是仰賴富裕國家來支付。
(台北時報林俐凱編譯)

In an effort to fight phone scams, British mobile phone company O2 has introduced Daisy, an AI designed to engage phone con artists in time-wasting conversations. Daisy is portrayed as a kindly British granny, exploiting scammers’ tendency to target the elderly. Her voice, based on a real grandmother’s for authenticity, adds to her credibility in the role. “O2” has distributed several dedicated phone numbers online to direct scammers to Daisy instead of actual customers. When Daisy receives a call, she translates the scammers’ spoken words into text and then responds to them accordingly through a text-to-speech system. Remarkably, Daisy

Bilingual Story is a fictionalized account. 雙語故事部分內容純屬虛構。 Emma had reviewed 41 resumes that morning. While the ATS screened out 288 unqualified, she screened for AI slop. She could spot it a mile away. She muttered AI buzzwords like curses under her breath. “Team player.” “Results-driven.” “Stakeholder alignment.” “Leveraging core competencies.” Each resume reeked of AI modeling: a cemetery of cliches, tombstones of personality. AI wasn’t just changing hiring. It was draining the humanity from it. Then she found it: a plain PDF cover letter. No template. No design flourishes. The first line read: “I once tried to automate my

Every May 1, Hawaii comes alive with Lei Day, a festival celebrating the rich culture and spirit of the islands. Initiated in 1927 by the poet Don Blanding, Lei Day began as a tribute to the Hawaiian custom of making and wearing leis. The idea was quickly adopted and officially recognized as a holiday in 1929, and leis have since become a symbol of local pride and cultural preservation. In Hawaiian culture, leis are more than decorative garlands made from flowers, shells or feathers. For Hawaiians, giving a lei is as natural as saying “aloha.” It shows love and

1. 他走出門,左右看一下,就過了馬路。 ˇ He walked outside, looked left and right, and crossed the road. χ He walked outside and looked left and right, crossed the road. 註︰並列連接詞 and 在這句中連接三個述語。一般的結構是 x, y, and z。x and y and z 是加強語氣的結構,x and y, z 則不可以。 2. 他們知道自己的弱點以及如何趕上其他競爭者。 ˇ They saw where their weak points lay and how they could catch up with the other competitors. χ They saw where their weak points lay and how to catch up with the other competitors. 註:and 一般連接同等成分,結構相等的單詞、片語或子句。誤句中 and 的前面是子句,後面是不定詞片語,不能用 and 連接,必須把不定詞片語改為子句,and 前後的結構才相等。 3. 她坐上計程車,直接到機場。 ˇ She took a cab, which took her straight to the airport. ˇ She took a cab and it took her straight