African populations have been revealed to share Neanderthal ancestry for the first time, in findings that add a new twist to the tale of ancient humans and our closest known relatives.
Previously it was believed that only non-African populations carried Neanderthal genes due to interbreeding that took place after a major human migration out of Africa and across the globe about 60,000 years ago. The latest findings suggest human and Neanderthal lineages are more closely intertwined than once thought and point to far earlier interbreeding events, about 200,000 years ago.
“Our results show this history was much more interesting and there were many waves of dispersal out of Africa, some of which led to admixture between modern humans and Neanderthals that we see in the genomes of all living individuals today,” said Joshua Akey, an evolutionary biologist at Princeton University and senior author of the research.
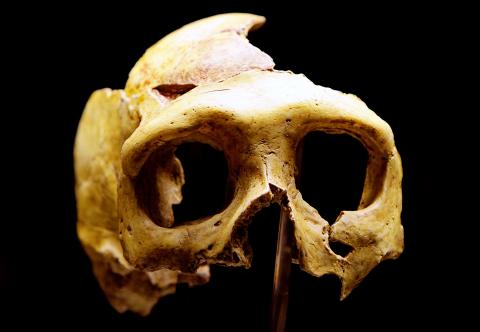
Photo: Reuters
照片:路透
The study suggests living Europeans and Asians carry about 1 percent Neanderthal DNA, compared with on average 0.3 percent for those of African ancestry. Akey and colleagues believe that this Neanderthal DNA arrived in Africa with ancient Europeans whose ancestors — over many generations — had left Africa, met and mated with Neanderthals and then returned to Africa and mixed with local populations.
“An important aspect of our study is that it highlights humans, and hominins, were moving in and out of Africa for hundreds of thousands of years and occasionally admixing,” said Akey. “These back-to-Africa migrations, largely from ancestors of contemporary Europeans, carried Neanderthal sequences with them, and through admixture, contributed to the Neanderthal ancestry we detect in African individuals today.”
The increasingly fine-grained details of our ancestors’ migration patterns and intimate encounters with other types of human are coming into focus thanks to the advent of sophisticated computational genetics techniques. These statistical methods allow scientists to line up the Neanderthal genome side by side with that of ancient modern humans and DNA from different living populations and figure out whether the different lineages have been steadily diverging or whether there are blips where large chunks of DNA were exchanged at certain time points.
The latest comparison highlights previously unnoticed ancient human genes in the Neanderthal genome, apparently acquired from interbreeding events dating to about 200,000 years ago. This suggests an early group of humans travelled from Africa to Europe or Asia, where they encountered Neanderthal populations and left a faint imprint on their genome that could still be detected more than 100,000 years later.
The paper also highlights the relative lack of genetics research in African populations, despite modern humans having first emerged on the continent and despite African populations today being more diverse genetically than the inhabitants of the rest of the world combined. “To more fully understand human genomic variation and human evolutionary history, it is imperative to comprehensively sample individuals from all regions of the world, and Africa remains one of the most understudied regions,” said Akey.
It is not known whether all African populations, some of whose roots stretch into the deep past, share this Neanderthal heritage. KhoeSan (bushmen) and Mbuti (central African pygmy) populations, for instance, appear to have split off from other groups more than 100,000 years ago. The findings are published in the journal Cell.
(The Guardian)
非洲的人類族群首度被科學家揭露帶有尼安德塔人的血統。這項發現為古代人類和尼安德塔人──與我們血緣最相近的親戚物種──之間的故事,帶來新的轉折。
先前,學界普遍認為只有非洲以外的族群帶有尼安德塔人的基因,這是因為人類大約在六萬年前發生過一次大型的「源出非洲」遷徙,散播到全球各地,而後與尼安德塔人異種交配。最新的研究結果顯示,人類和尼安德塔人的譜系比科學家先前認為的還要緊密相繫,並且指向更早以前──大約在二十萬年前──就出現過異種交配。
普林斯頓大學的演化生物學家、也是該篇研究的資深作者約書亞‧阿奇表示:「我們研究的結果顯示,這段歷史其實更為有趣。其實歷史上曾經發生過好幾波源出非洲的向外擴散,其中幾次造成現代人類與尼安德塔人混血,也就是我們今日在所有現代人類個體的基因組中所看到的現象。」
這份研究指出,相較於祖先來自非洲的現代人,身上平均帶有百分之零點三的尼安德塔DNA,現代歐洲人和亞洲人則帶有百分之一的尼安德塔DNA。阿奇和他的同事認為,這個尼安德塔DNA和古老的歐洲人一起抵達非洲,而這些歐洲人的祖先──在好幾個世代以前──從非洲離開,遇到尼安德塔人,並與他們交配,然後回到非洲,再與當地人口混血。
阿奇指出:「我們的研究其中一項重要的層面在於,它點出人類,以及其他古代人類亞族,在數十萬年間不斷地移入移出非洲,並且偶爾發生混血的情形。」他補充說:「這些回到非洲的移民,主要來自於當代歐洲人的祖先,他們身上帶有尼安德塔人的基因序列,並且經由混血,導致我們今日在非洲人身上探測到的尼安德塔血統。」
多虧了精密電腦計算基因學技術的來臨,關於我們祖先的遷徙模式,以及與其他人種的親密接觸,愈來愈細緻的細節逐漸變得清晰。這些統計學方法讓科學家能夠將尼安德塔人和古現代人的基因組並列,進行對比,也能夠對照今日不同人類族群的DNA,判斷這些相異的譜系是否一直持續產生分歧,又或者是否有跡象顯示某些時間點曾經出現大塊的DNA交換。
最新的基因組對比,凸顯出先前不曾被注意到的古人類基因存在於尼安德塔人的基因組中,明顯來自於距今約二十萬年的雜交事件。這項發現顯示,曾有早期人類族群從非洲前往歐洲或亞洲,在當地遇到尼安德塔人族群,並在後者基因組中留下淺淺的印記,在超過十萬年後的今天仍然可以探測得到。
該篇論文也點出,儘管現代人類最初發源於非洲大陸,而且今日非洲人類族群的遺傳多樣性遠高於世界其他地區居民的總和,目前學界對於當地族群的基因研究仍顯得相對缺乏。阿奇指出:「如果要更全盤了解人類基因組的變異,以及人類演化的歷史,廣泛對世界各地區的人類個體進行採樣是絕對必要的,而非洲目前仍然是研究最為不足的地區之一。」
目前仍不清楚是否所有非洲族群──其中有些族群的根源延續自遙遠的過去──共同擁有這項「尼安德塔遺產」。舉例而言,非洲的「科伊桑族」(亦稱布須曼人)以及「姆巴提人」(非洲中部的一支矮黑人),似乎在超過十萬年前就已經和其他人類族群在演化上分道揚鑣了。該篇研究刊登於期刊《細胞》上。
(台北時報章厚明譯)

A: Just like the Democratic Party’s presidential candidate Kamala Harris, the Republican Party’s Donald Trump has received endorsements from some celebrities, including SpaceX founder Elon Musk. B: Plus, a new film, “The Apprentice,” about Trump’s rise was released recently. A: Isn’t it the same title as the reality TV series he hosted? B: Yeah, it was a competition reality show for jobseekers. A: My English teacher even uses it as supplemental material for English courses. A: 就像民主黨的賀錦麗,共和黨的唐納川普也獲得一些名人支持,例如SpaceX的創辦人伊隆馬斯克。 B: 關於川普崛起的電影《誰是接班人》最近也上映了。 A: 這不是跟他主持的電視實境秀同名嗎? B: 對啊,那是一群求職者的實境競賽秀。 A: 我的英文老師還拿它當英文課程的補充教材! (By Eddy Chang, Taipei Times/台北時報張聖恩)

Many patients with certain types of cancers suffer from damage to their blood cells due to the cancer itself or treatments like chemotherapy. To help rebuild healthy blood cells, patients often receive bone marrow transplants by using either pluripotent or hematopoietic stem cells. A bone marrow or stem cell transplant can speed up recovery and boost healthy blood cell production. There are primarily two types of bone marrow transplants: autologous and allogeneic. The former involves using the patient’s own stem cells, while the latter uses stem cells from a matching donor, usually a relative with a compatible human leukocyte

It’s won Oscars. Its television shows and K-pop stars dominate global charts. Its leading novelist just won the Nobel literature prize. How did South Korea become such a global cultural powerhouse? What is Hallyu? From the late 1990s, Korean dramas and K-pop idols started gaining traction in neighboring Asian countries like China and Japan, marking the start of Hallyu, or the Korean Wave. It wasn’t until Psy’s breakout hit “Gangnam Style” that Hallyu hit the West. In the decade that followed, “Babyshark” broke YouTube records, K-pop megastars BTS topped the charts, Bong Joon-ho’s “Parasite” won an Oscar, and Squid Game

在防疫期間,「超前部署」此一用語常見諸報章,成為台灣很夯的熱詞 (buzzword): 超前部署並非2020 年才出現的用語,以下為一些過去台灣政府官員曾使用「超前部署」的語境: 總統馬英九今天指出,八八風災帶來很大教訓,應落實災害防救工作……料敵從寬,禦敵從嚴,超前部署……2010 年 5 月 26 日,《中央社》 行政院副院長張善政……表示,蓮花颱風速度雖然減緩……料敵從嚴,並以超前部署為原則……2015 年 7 月 7 日,《新聞傳播處》 《今日科學》有篇文章 “Outbreak science: Infectious disease research leads to outbreak predictions” 就提到做好預判,有利政府防疫的「超前部署」: Infectious disease outbreaks, whether they be widespread like Influenza or fairly geographically restricted like Ebola, may be difficult to prevent . . . if we can forecast outbreak potential in time, public health officials and governments can preemptively prepare for a potential outbreak event. 傳染病爆發,無論是像流感那樣全面,或像伊波拉那種侷限某些地理區域,都很難預防— 然而,如果我們可以及時預知(疾病)爆發的可能,公衛當局和政府便可以為潛在的疫情爆發提前部署。 Science Daily, January 8, 2020 所以「超前部署」若是在「防災/防疫」的語境下,可譯為preemptive preparation 或 preemptive preparedness,如果用作動詞,可以說 preemptively prepare for (an outbreak, etc.)。 《世界雜誌》上有位作者提到 preemptive 和 preparation 的差異,她說 preemptive 的弦外之音是 heading off something undesirable(避凶/避災): “Preemptive” and “preparation” both refer to work done ahead