The US Navy would start fielding an anti-ship version of its Tomahawk cruise missile on destroyers by late September in what US Fleet Forces Command Admiral Daryl Caudle sees as a “game-changer” against a numerically superior Chinese fleet.
An anti-ship version of the US’ best-known non-nuclear missile, which is currently used for land attack, would greatly increase the service’s lethality, Caudle said.
“The more fungible you make a weapon, the more utility it has for different circumstances,” he said.
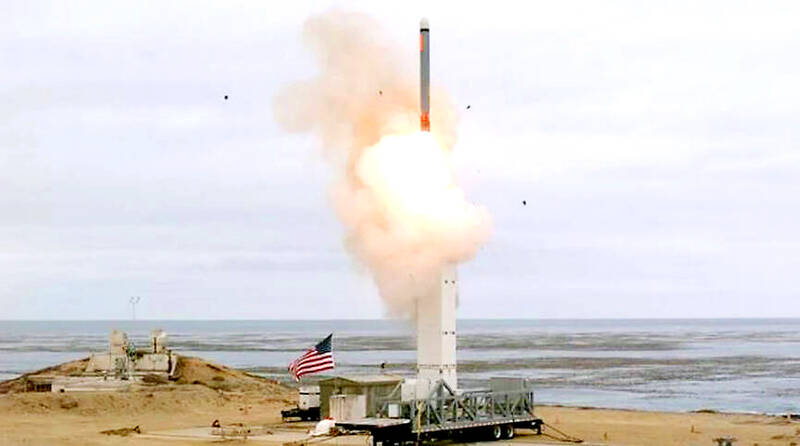

Photo: Screengrab from Defense Visual Information Distribution Service’s Web site
Fielding a new seaborne version of the Tomahawk would add to a growing US arsenal of ship-attack weapons, such as the new Long-Range Anti-Ship Missile, complementing submarine-launched torpedoes in the event of conflict in Asia.
Building it for submarine and destroyer launch would “make it a very high-utility weapon,” he said.
The navy plans to start fielding the new missiles on destroyers by Sept. 30 and make them available for submarine deployments between April and June next year once they complete testing, Tomahawk deputy program manager Chip Whipkey said.
The service is looking to purchase as many as 1,302 Maritime Strike Tomahawks from RTX Corp.
The schedule for outfitting the new maritime strike missile on destroyers fits roughly within the Pentagon’s plan to field thousands of drones in the Indo-Pacific region to counter China. That is known as the Replicator program, which the military aims to deploy on a large scale in August.
The navy’s growing arsenal also uses artificial intelligence algorithms on its submarine sonar systems “to help distinguish man-made noise sources from biological sources” such as fish, Caudle said.
China’s projected massive naval increase has fixated lawmakers intent on pouring billions into US warship construction to boost the navy’s roughly 300 inventory.
The US estimates that China’s fleet of more than 370 ships, including submarines and aircraft carriers, would grow to 435 by 2030.
Still, Caudle urged caution in launching into a “shipbuilding arms race,” saying the focus should be on US capabilities per vessel.
“It’s tempting to get in a shipbuilding arms race where we really are trying to go tit-for-tat, where we’re judging the value of combat power of a naval force by the numbers,” he said. “I don’t think that’s a good strategy.”
“A better strategy is to build high-end, highly capable, large payload volume ships like we have,” Caudle said, citing Arleigh Burke-class guided-missile destroyers and the US fleet submarines aircraft carriers.
A projected increase in China’s fleet comes with challenges, including more munitions purchases and crew, he said.
“You have to crew all those ships. You have to sustain all those ships. You’ve got to have a place for them to moor” and have housing for the crew, he said. “So it’s not just buying ships.”

The Central Election Commission has amended election and recall regulations to require elected office candidates to provide proof that they have no Chinese citizenship, a Cabinet report said. The commission on Oct. 29 last year revised the Measures for the Permission of Family-based Residence, Long-term Residence and Settlement of People from the Mainland Area in the Taiwan Area (大陸地區人民在台灣地區依親居留長期居留或定居許可辦法), the Executive Yuan said in a report it submitted to the legislature for review. The revision requires Chinese citizens applying for permanent residency to submit notarial documents showing that they have lost their Chinese household record and have renounced — or have never
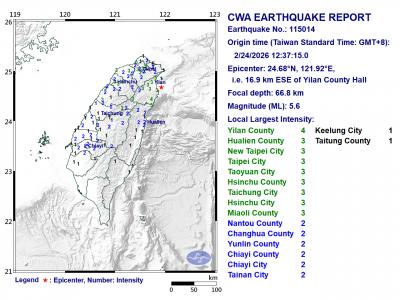
A magnitude 5.6 earthquake struck off the coast of Yilan County at 12:37pm today, with clear shaking felt across much of northern Taiwan. There were no immediate reports of damage. The epicenter of the quake was 16.9km east-southeast of Yilan County Hall offshore at a depth of 66.8km, Central Weather Administration (CWA) data showed. The maximum intensity registered at a 4 in Yilan County’s Nanao Township (南澳) on Taiwan’s seven-tier scale. Other parts of Yilan, as well as certain areas of Hualien County, Taipei, New Taipei City, Taoyuan, Hsinchu County, Taichung and Miaoli County, recorded intensities of 3. Residents of Yilan County and Taipei received

Taiwan has secured another breakthrough in fruit exports, with jujubes, dragon fruit and lychees approved for shipment to the EU, the Ministry of Agriculture said yesterday. The Animal and Plant Health Inspection Agency on Thursday received formal notification of the approval from the EU, the ministry said, adding that the decision was expected to expand Taiwanese fruit producers’ access to high-end European markets. Taiwan exported 126 tonnes of lychees last year, valued at US$1.48 million, with Japan accounting for 102 tonnes. Other export destinations included New Zealand, Hong Kong, the US and Australia, ministry data showed. Jujube exports totaled 103 tonnes, valued at

BIG SPENDERS: Foreign investors bought the most Taiwan equities since 2005, signaling confidence that an AI boom would continue to benefit chipmakers Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co’s (TSMC, 台積電) market capitalization swelled to US$2 trillion for the first time following a 4.25 percent rally in its American depositary receipts (ADR) overnight, putting the world’s biggest contract chipmaker sixth on the list of the world’s biggest companies by market capitalization, just behind Amazon.com Inc. The site CompaniesMarketcap.com ranked TSMC ahead of Saudi Aramco and Meta Platforms Inc. The Taiwanese company’s ADRs on Tuesday surged to US$385.75 on the New York Stock Exchange, as strong demand for artificial intelligence (AI) applications led to chip supply constraints and boost revenue growth to record-breaking levels. Each TSMC ADR represents