A digital reconstruction of a million-year-old skull suggests humans may have diverged from our ancient ancestors 400,000 years earlier than previously thought and in Asia not Africa, a new study said yesterday.
The findings are based on a reconstruction of a crushed skull discovered in China in 1990, and have the potential to resolve the longstanding “Muddle in the Middle” of human evolution, researchers said.
The skull, labelled Yunxian 2, was previously thought to belong to a human forerunner called Homo erectus.
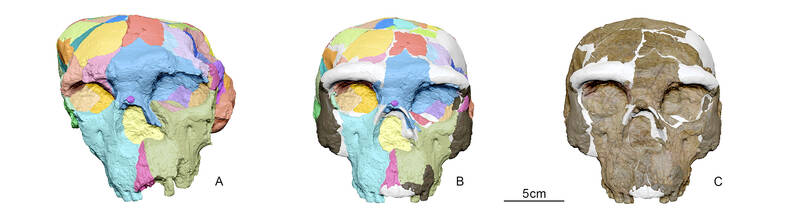
Photo: Reuters
But modern reconstruction technologies used by a group of researchers found features that are closer to species previously thought to have existed only later in human evolution, including the recently discovered Homo longi and our own Homo sapiens.
“This changes a lot of thinking,” said Chris Stringer, an anthropologist at the Natural History Museum, London, who was part of the research team.
“It suggests that by one million years ago, our ancestors had already split into distinct groups, pointing to a much earlier and more complex human evolutionary split than previously believed,” he added.
If the findings are correct, it suggests there could have been much earlier members of other early hominins, including Neanderthals and our own Homo sapiens line.
But it also “muddies the waters” on longstanding assumptions that early humans dispersed from Africa, said Michael Petraglia, director of Griffith University’s Australian Research Centre of Human Evolution, who was not involved in the study.
“There’s a big change potentially happening here, where east Asia is now playing a very key role in hominin evolution,” he said.
The research, published in the journal Science, used advanced CT scanning, structure light imaging and virtual reconstruction techniques to model a complete Yunxian 2.
The scientists relied in part on another similar skull to shape their model, and then compared it to over 100 other specimens.
The resulting model “shows a distinctive combination of traits,” the study said, some of them similar to Homo erectus, including a projecting lower face.
But other aspects, including its apparently larger brain capacity, are closer to Homo longi and Homo sapiens, the researchers said.
“Yunxian 2 may help us resolve what’s been called the ‘Muddle in the Middle,’ the confusing array of human fossils from between 1 million and 300,000 years ago,” Stringer said in a press release.
Much about human evolution remains debated, and Petraglia said the study’s findings were “provocative” though grounded in solid work.
“It’s sound, but I think the jury’s still out. I think there will be a lot of questions raised,” he said.
The findings are only the latest in a string of recent research that has complicated what we thought we know about our origins.
Homo longi, also known as “Dragon Man,” was itself only named as a new species and close human relative in 2021.
The authors said their work illustrates the complexity of our shared history.
“Fossils like Yunxian 2 show just how much we still have to learn about our origins,” said Stringer.

Dec. 8 to Dec. 14 Chang-Lee Te-ho (張李德和) had her father’s words etched into stone as her personal motto: “Even as a woman, you should master at least one art.” She went on to excel in seven — classical poetry, lyrical poetry, calligraphy, painting, music, chess and embroidery — and was also a respected educator, charity organizer and provincial assemblywoman. Among her many monikers was “Poetry Mother” (詩媽). While her father Lee Chao-yuan’s (李昭元) phrasing reflected the social norms of the 1890s, it was relatively progressive for the time. He personally taught Chang-Lee the Chinese classics until she entered public

Last week writer Wei Lingling (魏玲靈) unloaded a remarkably conventional pro-China column in the Wall Street Journal (“From Bush’s Rebuke to Trump’s Whisper: Navigating a Geopolitical Flashpoint,” Dec 2, 2025). Wei alleged that in a phone call, US President Donald Trump advised Japanese Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi not to provoke the People’s Republic of China (PRC) over Taiwan. Wei’s claim was categorically denied by Japanese government sources. Trump’s call to Takaichi, Wei said, was just like the moment in 2003 when former US president George Bush stood next to former Chinese premier Wen Jia-bao (溫家寶) and criticized former president Chen

Politics throughout most of the world are viewed through a left/right lens. People from outside Taiwan regularly try to understand politics here through that lens, especially those with strong personal identifications with the left or right in their home countries. It is not helpful. It both misleads and distracts. Taiwan’s politics needs to be understood on its own terms. RISE OF THE DEVELOPMENTAL STATE Arguably, both of the main parties originally leaned left-wing. The Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT) brought together radicals, dissidents and revolutionaries devoted to overthrowing their foreign Manchurian Qing overlords to establish a Chinese republic. Their leader, Sun Yat-sen

Late one night in April 2020, towards the start of the COVID lockdowns, Shanley Clemot McLaren was scrolling on her phone when she noticed a Snapchat post by her 16-year-old sister. “She’s basically filming herself from her bed, and she’s like: ‘Guys you shouldn’t be doing this. These fisha accounts are really not OK. Girls, please protect yourselves.’ And I’m like: ‘What is fisha?’ I was 21, but I felt old,” she says. She went into her sister’s bedroom, where her sibling showed her a Snapchat account named “fisha” plus the code of their Paris suburb. Fisha is French slang for