Western Europe has a new oldest face: the facial bones of an adult nicknamed “Pink” discovered in Spain are from a potential new member of the human family who lived more than 1.1 million years ago, scientists said Wednesday.
Until now, the oldest-known human species in Western Europe was the slender-faced Homo antecessor, dating back around 850,000 years.
But research published in the journal Nature “introduces a new actor in the history of human evolution in Europe,” lead study author Rosa Huguet of Spain’s University of Rovira i Virgili told a press conference.
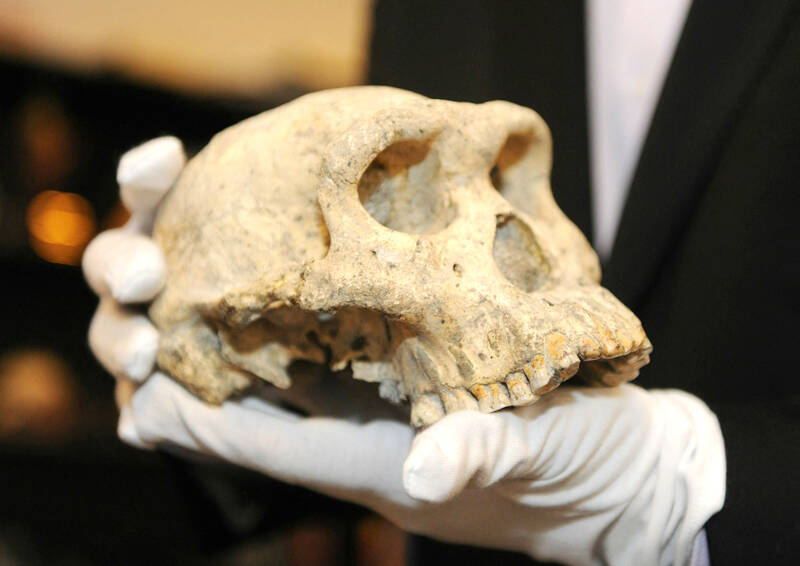
Photo: AFP
The fossilized upper jawbone and partial cheekbone of Pink were discovered at the Atapuerca archaeological site in northern Spain in 2022.
Since then, a team of Spanish scientists have been working to find out more about Pink, whose nickname is a reference to prog rock band Pink Floyd.
The bones were excavated from a layer of silt and red mud 16 meters deep at a site known as Sima del Elefante — or “elephant pit”.
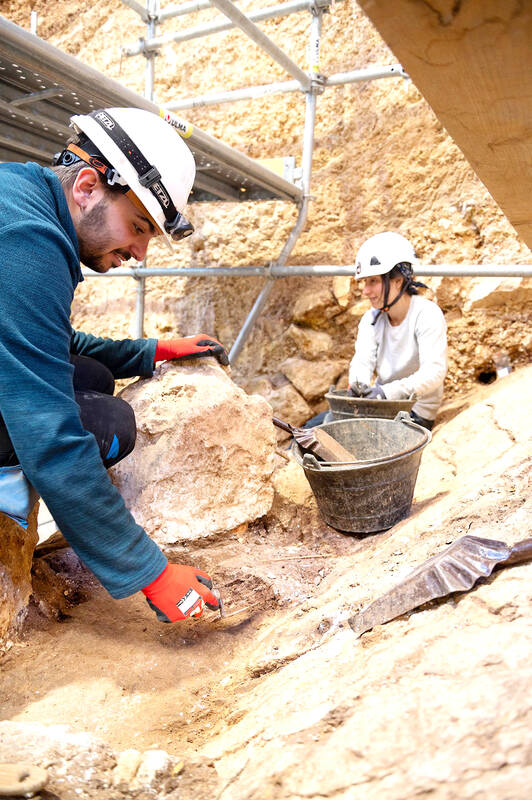

Photo: AFP
They were found less than 250 meters from where the fossils of Western Europe’s previous oldest human, Homo antecessor, were discovered nearly two decades ago.
But the title of oldest human in all of Europe is still held by the Dmanisi people — also called Homo georgicus — who lived up to 1.8 million years ago in what is now Georgia.
They were the first members of the human family, or hominins, known to have made it to Europe from Africa, the cradle of humanity. We modern Homo sapiens first showed up in Africa around 300,000 years ago — and took our time getting to Europe.
FACE VALUE
The Spanish researchers used 3D imaging techniques to flesh out Pink’s full face.
Homo antecessor had a “very modern” face which is “vertical and flat” similar to our own, said Maria Martinon-Torres, director of Spain’s National Research Center on Human Evolution.
But Pink’s face is more “projected forward and more robust,” the study co-author added.
This means it bears some similarities to the face of Homo erectus — but not enough that the scientists could confirm that Pink was a member of this important human ancestor.
So the scientists made up a new name for the possible species that Pink could belong to: Homo affinis erectus.
“This is the most honest proposal we can make with the evidence we have,” Martinon-Torres said.
From just a few face bones, the researchers could not determine Pink’s age or gender.
But by analyzing small stone tools and animals bones found at the site, they were able to get an idea of the environment Pink lived in.
It was a humid forest landscape, roamed by horses, ancient cattle, monkeys and even some hippos.
The area was a wildlife corridor with plenty of water, making it an “ideal” place for our ancient relatives to settle, Huguet said.
WHAT HAPPENED TO THEM?
The new discovery supports the hypothesis that early humans settled Europe going from east to west at least 1.4 million years ago, according to the Spanish researchers. If Pink is a representative of a previously unknown human species, it could have been a bridge between the Dmanisi hominins and Homo antecessors, they added.
But this raises another question: what became of these people?
Spanish paleoanthropologist Jose Maria Bermudez de Castro felt that Pink’s people likely did not survive a severe human “bottleneck” nearly 900,000 years ago thought to have been caused by global cooling.
“I think that Homo affinis erectus probably disappeared,” the study co-author said.
Future research will aim to shed light on these mysteries. The Spanish team has not yet reached the bottom of the elephant pit — nor other sites around it.
Jacques Poissant’s suffering stopped the day he asked his daughter if it would be “cowardly to ask to be helped to die.” The retired Canadian insurance adviser was 93, and “was wasting away” after a long battle with prostate cancer. “He no longer had any zest for life,” Josee Poissant said. Last year her mother made the same choice at 96 when she realized she would not be getting out of hospital. She died surrounded by her children and their partners listening to the music she loved. “She was at peace. She sang until she went to sleep.” Josee Poissant remembers it as a beautiful

For many centuries from the medieval to the early modern era, the island port of Hirado on the northwestern tip of Kyushu in Japan was the epicenter of piracy in East Asia. From bases in Hirado the notorious wokou (倭寇) terrorized Korea and China. They raided coastal towns, carrying off people into slavery and looting everything from grain to porcelain to bells in Buddhist temples. Kyushu itself operated a thriving trade with China in sulfur, a necessary ingredient of the gunpowder that powered militaries from Europe to Japan. Over time Hirado developed into a full service stop for pirates. Booty could

Lori Sepich smoked for years and sometimes skipped taking her blood pressure medicine. But she never thought she’d have a heart attack. The possibility “just wasn’t registering with me,” said the 64-year-old from Memphis, Tennessee, who suffered two of them 13 years apart. She’s far from alone. More than 60 million women in the US live with cardiovascular disease, which includes heart disease as well as stroke, heart failure and atrial fibrillation. And despite the myth that heart attacks mostly strike men, women are vulnerable too. Overall in the US, 1 in 5 women dies of cardiovascular disease each year, 37,000 of them

Before the last section of the round-the-island railway was electrified, one old blue train still chugged back and forth between Pingtung County’s Fangliao (枋寮) and Taitung (台東) stations once a day. It was so slow, was so hot (it had no air conditioning) and covered such a short distance, that the low fare still failed to attract many riders. This relic of the past was finally retired when the South Link Line was fully electrified on Dec. 23, 2020. A wave of nostalgia surrounded the termination of the Ordinary Train service, as these train carriages had been in use for decades