Sisters Mimi and Nikki have battled Thailand’s tropical climate, chased off elephants from their vineyards and won over a skeptical public to their award-winning wine. Now they’re taking on the “unfair” booze laws critics say benefit the kingdom’s billionaire booze monopolies.
Rows of Syrah, Viognier and Chenin Blanc grapes stretch across the 40-acre GranMonte Estate in the foothills of Khao Yai National Park.
The elevated terrain, three hours outside of Bangkok, provides unexpectedly fertile ground for grapes and an escape from city life, complete with a rust-colored guesthouse that could be pulled straight from a Tuscany tourism advert. As they snap selfies in between the vines, visitors run into Nikki Lohitnavy, 33, who studied enology in Australia and now steers the science behind each bottle.
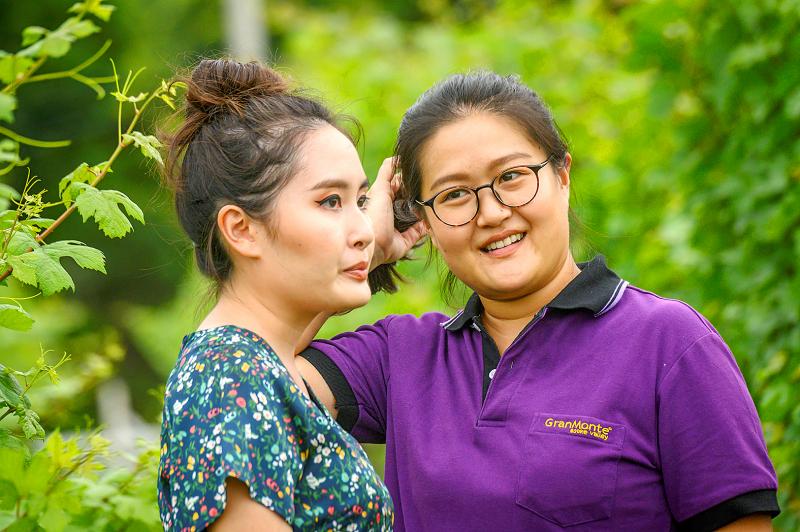

Photo: AFP
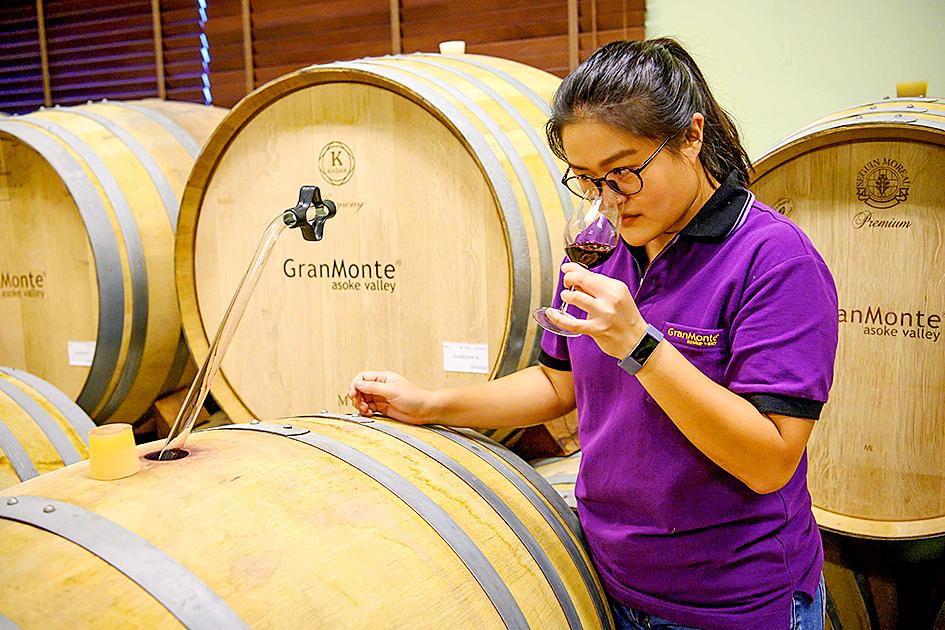
She painstakingly experiments with grape varieties to see how they respond to the climate — it takes at least six years to see if a decent wine will emerge from the ground.
The plot of land was once a cornfield, but their father Visooth transformed the terrain into trellised vines and as a teenager Nikki joined him in the fields.
Younger sister Mimi was not interested in the viticulture, but today, she heads the label’s marketing, calling it her “mission to put Thai wine into the market.” The kingdom’s wine remains an outlier — grapes grown in warmer temperatures tend to produce tannic wines, something that seasoned drinkers eschew. But after more than two decades in business, GranMonte is gaining recognition especially for its progress in tropical viticulture.
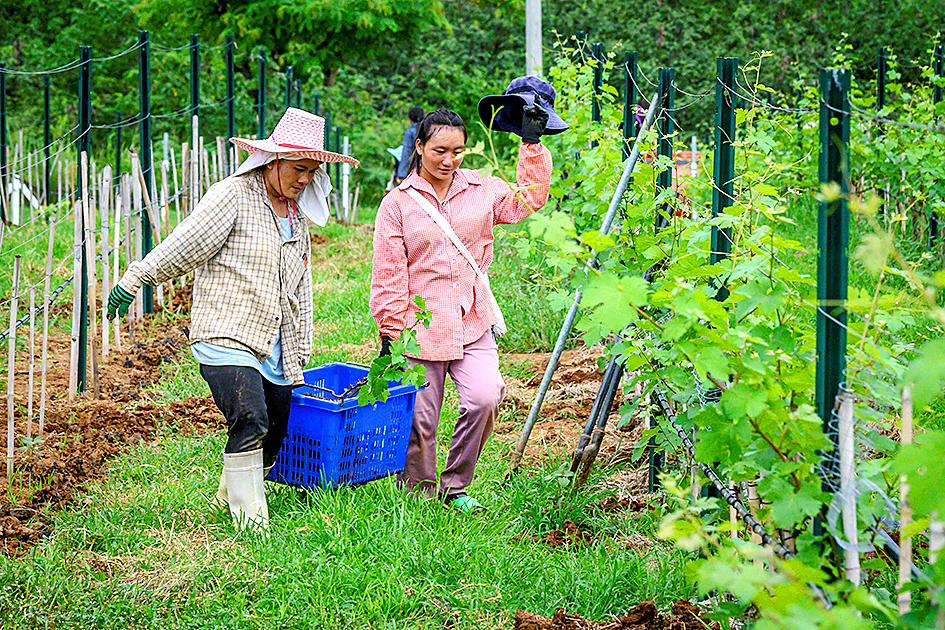

Photo: AFP
“Winemakers around the world want to know what we do here because the climate is changing so they have to adapt to warmer temperatures and higher rainfall in their regions too,” Nikki said.
Its proximity to a national park also poses an unusual pest control issue as hungry elephants occasionally trespass through their vineyard, prompting calls from the sisters to rangers for help.
QUE SYRAH SERA

Warning: Excessive consumption of alcohol can damage your health.
Photo: AFP
Despite the gains, the long term future of the GranMonte wines is clouded by the kingdom’s heavily restrictive booze laws.
Thailand has a strange relationship with alcohol. A devoutly Buddhist kingdom, it also has the highest alcohol consumption rate in Southeast Asia, according to the WHO.
A web of rules, including high import taxes on alcohol, hefty fines for breaches and a licensing culture where bars require friends at local police stations, can make drinking a complicated business.

Warning: Excessive consumption of alcohol can damage your health.
Photo: AFP
Then there’s the 2008 Alcoholic Beverage Control Act, a law forbidding the display of booze logos on their products, as well as any advertising that could “directly or indirectly appeal to people to drink.” It’s aimed at controlling consumption, but in effect clips the wings of small producers who do not possess the same reach to customers as established brands.
“I can’t show clearly a bottle of my wine, I can’t post on social media what the wine tastes like, or how or why it’s good,” says Mimi, who worries that their Web site might fall afoul of the law.
Critics say it has always been unevenly enforced, allowing booze giants to cement their brand recognition, spraying their logos via non-alcoholic drinks like soda water on giant billboards and public transport. The market leader —Thai Beverage — makes the ubiquitous Chang lager. The firm is owned by Sirivadhanabhakdi family, the kingdom’s third richest family with US$10.5 billion in wealth according to Forbes, and their portfolio includes massive downtown Bangkok real estate projects and hotels. Together with Boon Rawd Brewery — which produces Singha and Leo — the duopoly are unrivalled in reach and capital. Neither responded to multiple requests for comment. Thailand’s booze laws are uncharacteristically responsive to changes in drinking culture.
Online alcohol sales — which surged during the pandemic lockdown — are now in the regulators’ crosshairs, potentially closing down another revenue route for small alcohol producers. GranMonte lost 30 million baht (US$964,000) in three months during the shutdown — and Mimi says their recovery will be further hampered by new rules slated to ban all online booze sales.
MONOPOLY PLAYERS
But Nipon Chinanonwait, director of the Ministry of Health’s Alcohol Control Board, rejects criticism that established giants are given an unfair advantage.
“Both big and small companies face the same procedure,” he said, while the ministry insists the laws are there only to prevent underage drinking. The sisters have teamed up with dozens of small-scale craft brewers, importers and bars to petition the government to axe the advertising law, and to halt the impending online booze sales ban. “People cannot live like this,” said brewer Supapong Pruenglampoo, who hid his Sandport Brewing Facebook page from public view in fear of a crackdown.
“In these COVID times, (the fines) are impossible to pay,” he said. But in an unequal kingdom, any efforts to change the monopoly culture are bruising. It’s “a reflection of how Thailand operates,” says Mimi.
“The lawmaking, the enforcement and everything surrounding it is to benefit the small group of people holding most of the wealth in Thailand,” she said. As Nikki tastes their recent batch of Syrah grapes kept in imported barrels, she says the challenges to start were numerous. Now, they are working to stay on top.
“It’s our passion — we like it so we do it,” she says.

President William Lai (賴清德) yesterday delivered an address marking the first anniversary of his presidency. In the speech, Lai affirmed Taiwan’s global role in technology, trade and security. He announced economic and national security initiatives, and emphasized democratic values and cross-party cooperation. The following is the full text of his speech: Yesterday, outside of Beida Elementary School in New Taipei City’s Sanxia District (三峽), there was a major traffic accident that, sadly, claimed several lives and resulted in multiple injuries. The Executive Yuan immediately formed a task force, and last night I personally visited the victims in hospital. Central government agencies and the

Australia’s ABC last week published a piece on the recall campaign. The article emphasized the divisions in Taiwanese society and blamed the recall for worsening them. It quotes a supporter of the Taiwan People’s Party (TPP) as saying “I’m 43 years old, born and raised here, and I’ve never seen the country this divided in my entire life.” Apparently, as an adult, she slept through the post-election violence in 2000 and 2004 by the Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT), the veiled coup threats by the military when Chen Shui-bian (陳水扁) became president, the 2006 Red Shirt protests against him ginned up by
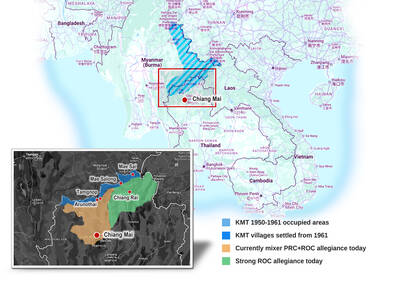
As with most of northern Thailand’s Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT) settlements, the village of Arunothai was only given a Thai name once the Thai government began in the 1970s to assert control over the border region and initiate a decades-long process of political integration. The village’s original name, bestowed by its Yunnanese founders when they first settled the valley in the late 1960s, was a Chinese name, Dagudi (大谷地), which literally translates as “a place for threshing rice.” At that time, these village founders did not know how permanent their settlement would be. Most of Arunothai’s first generation were soldiers

Among Thailand’s Chinese Nationalist Party (KMT) villages, a certain rivalry exists between Arunothai, the largest of these villages, and Mae Salong, which is currently the most prosperous. Historically, the rivalry stems from a split in KMT military factions in the early 1960s, which divided command and opium territories after Chiang Kai-shek (蔣介石) cut off open support in 1961 due to international pressure (see part two, “The KMT opium lords of the Golden Triangle,” on May 20). But today this rivalry manifests as a different kind of split, with Arunothai leading a pro-China faction and Mae Salong staunchly aligned to Taiwan.