Driving to work at his factory to the west of London last week, designer Steve Brooks had coronavirus on his mind. What could he make that would let him open a door without touching the handle?
“Everyone has to use their little finger or find the bit of the door that nobody’s touched,” said the designer and owner at DDB Ltd, a company which makes office furniture. So he produced a hook to do the job.
The so-called hygienehook is small enough to fit in a pocket and made from a non-porous material, which makes it easy to clean. It is one of hundreds of gadgets dreamt up in recent days and weeks to help prevent people from spreading the coronavirus.
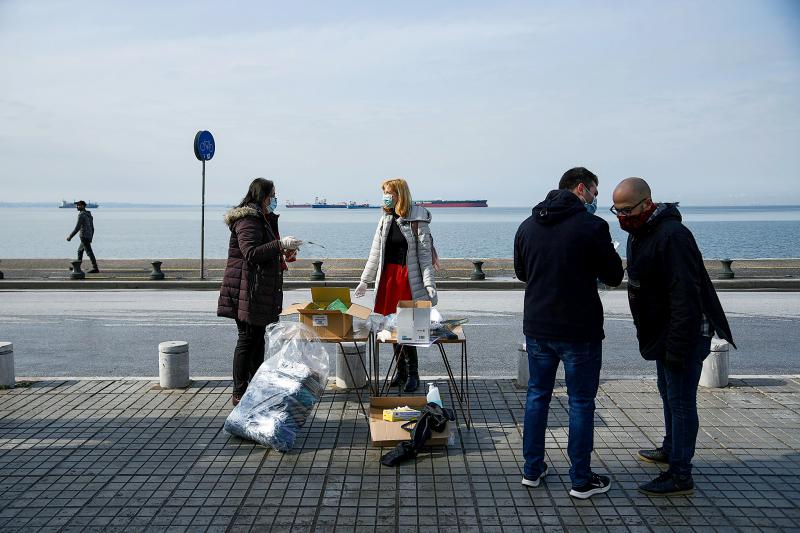

Photo: Reuters
From furniture makers to AI software developers, companies around the world are adapting existing products or inventing new ones to help fight the pandemic or just make life easier for those working from home, in hospitals or stuck in quarantine.
The flurry of innovation comes as companies from Ford and Airbus to luxury goods giant LVMH retool plants to make critical equipment like hand sanitizers, ventilators and masks.
In years gone by it was large companies like these, with the financial clout and factories, who typically had to be relied upon to move rapidly from designing a prototype to manufacturing the product.
A crucial difference now, though, is that 3D printing and high-tech software mean devices can be produced faster than ever by companies big and small.
“There is definitely a ton of people with 3D resources very willing to help,” said MacKenzie Brown, founder of California-based product design company CAD Crowd.
Two weeks ago, his company launched a month-long contest for practical devices for navigating the new coronavirus world.
About 65 entries have poured in, including a wrist-mounted disinfectant sprayer, half gloves for knuckle-pushing of buttons and a device that lets you open car doors without touching the handle, aimed at cab users.
As the pandemic makes people far more aware of hygiene, some new products may have a shelf life beyond the current crisis.
‘WE HAD THE ALGORITHM’
Startups are retooling their technology.
In Seattle, brothers Joseph and Matthew Toles and their friend Justin Ith, who own a young company called Slightly Robot, had developed a wristband after college aimed at reducing compulsive skin-picking, nail-biting and hair-pulling.
When their home city reported its first fatalities from the virus last month, they adapted the design to create a new smartband, the Immutouch, which buzzes when the wearer’s hand goes near their face.
“We had the algorithm, we had the software and the hardware. We’ve repurposed it for face-touching,” Matthew Toles said in an interview. “We made 350 devices and a Web site in one week and now it’s how fast can we ramp up.”
Romanian robotic software company UiPath has meanwhile found a way for nurses in the Mater Misericordiae University Hospital in the Irish capital Dublin to ditch time-consuming data entry and automate filing of virus test results. It hopes to replicate it in other hospitals.
Scylla, a US-based AI company that makes gun detection systems for schools and casinos, turned its sights on the virus when China, the original epicenter of the outbreak, reported its first cases three months ago.
It has re-deployed its AI analytics software to measure the temperature of a person’s forehead, sending out an alert if it detects a fever. Taking images from a thermal camera, the software can be used in public buildings like hospitals and airports, and corporate offices, chief technology officer Ara Ghazaryan said.
The government of a South American nation has placed an order for 5,000 licenses of Scylla’s system for its public buildings and transport system, Ghazaryan said. He declined to name the country.
WORLD WAR TWO INNOVATION
Global upheaval often spawns new products and innovation.
The current burst of creativity may eventually compare to that seen during World War II when companies, governments and scientists embarked on projects that had lasting consequences.
Technology used to help guide rockets eventually led to the first satellites and putting men on the moon.
“There’s no question that inventors will be coming up with hundreds, if not thousands, of new ideas,” said Kane Kramer, inventor and co-founder of the British Inventor’s Society. He first conceived the idea of downloading music and data in the late 1970s.
“Everyone’s downed tools and are only picking them up to fight the virus. It’s a global war.”
Many companies are donating their new wares or selling them at cost price. The CAD Crowd contest designs are free for download and use, for example. For some, though, the extra business could provide a financial cushion as other sources of income evaporate during the pandemic.
DDB designer Brooks near London has worked quickly.
Less than a week after his first design, four different models of the hook went on sale this week, selling at just under US$18.60 each. He is donating one hook for every one he sells.
Now Brooks is turning his creative eye to another gadget along similar lines.
“We’ve already had a request from the National Health Service in Wales about designing something for pushing a door.”

Taiwan has next to no political engagement in Myanmar, either with the ruling military junta nor the dozens of armed groups who’ve in the last five years taken over around two-thirds of the nation’s territory in a sprawling, patchwork civil war. But early last month, the leader of one relatively minor Burmese revolutionary faction, General Nerdah Bomya, who is also an alleged war criminal, made a low key visit to Taipei, where he met with a member of President William Lai’s (賴清德) staff, a retired Taiwanese military official and several academics. “I feel like Taiwan is a good example of

March 2 to March 8 Gunfire rang out along the shore of the frontline island of Lieyu (烈嶼) on a foggy afternoon on March 7, 1987. By the time it was over, about 20 unarmed Vietnamese refugees — men, women, elderly and children — were dead. They were hastily buried, followed by decades of silence. Months later, opposition politicians and journalists tried to uncover what had happened, but conflicting accounts only deepened the confusion. One version suggested that government troops had mistakenly killed their own operatives attempting to return home from Vietnam. The military maintained that the
Jacques Poissant’s suffering stopped the day he asked his daughter if it would be “cowardly to ask to be helped to die.” The retired Canadian insurance adviser was 93, and “was wasting away” after a long battle with prostate cancer. “He no longer had any zest for life,” Josee Poissant said. Last year her mother made the same choice at 96 when she realized she would not be getting out of hospital. She died surrounded by her children and their partners listening to the music she loved. “She was at peace. She sang until she went to sleep.” Josee Poissant remembers it as a beautiful

Before the last section of the round-the-island railway was electrified, one old blue train still chugged back and forth between Pingtung County’s Fangliao (枋寮) and Taitung (台東) stations once a day. It was so slow, was so hot (it had no air conditioning) and covered such a short distance, that the low fare still failed to attract many riders. This relic of the past was finally retired when the South Link Line was fully electrified on Dec. 23, 2020. A wave of nostalgia surrounded the termination of the Ordinary Train service, as these train carriages had been in use for decades