Taiwan was once a province of China, but for only a brief period: 1887 to 1895, and the era laid the foundation for a separate identity in Taiwan.
Two hundred years earlier, in 1644, the Qing Dynasty under Manchu rule had come to power in Beijing, driving out the Ming Dynasty rulers. But at the time, Taiwan was under Dutch colonial rule through the Dutch United East India Company.
In April 1661, Ming warlord Cheng Cheng-kung (鄭成功, also known as Koxinga) — himself being on the run from the Qing invaders — crossed over to Taiwan with some 400 ships and 25,000 men, and after a nine-month siege of Zeelandia, a Dutch fortress in present-day Tainan, took control of the area.
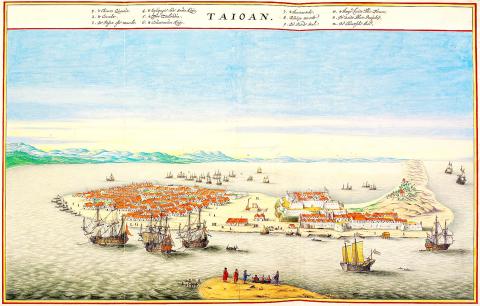
Photo courtesy of Wikemedia Commons
The rule of Koxinga’s family didn’t last long: in 1683 his grandson, Cheng Ke-shuang (鄭克塽), was defeated in a battle on the outlying island of Penghu (the Pescadores) by the famed admiral Shih Lang (施琅), the first official to rule Taiwan on behalf of the Qing. Then for 200 years, Taiwan was ruled from Fujian Province in a turbulent period known to have an “uprising every three years and a rebellion every five,” as one Qing official stated at the time.
GLOBAL TRADE
During these 200 years, Taiwan became a quiet backwater, with very little interaction with the global economy. This changed in the 1850s, when the advent of the steamship made it possible for Western nations to travel far and wide. In the mid 1850s, US Admiral Perry and his “Black Ships” were in the area and even proposed to Washington to make Taiwan an American trading hub, in part to counter the influence of the other Western nations expanding into the region: France, England and Germany.
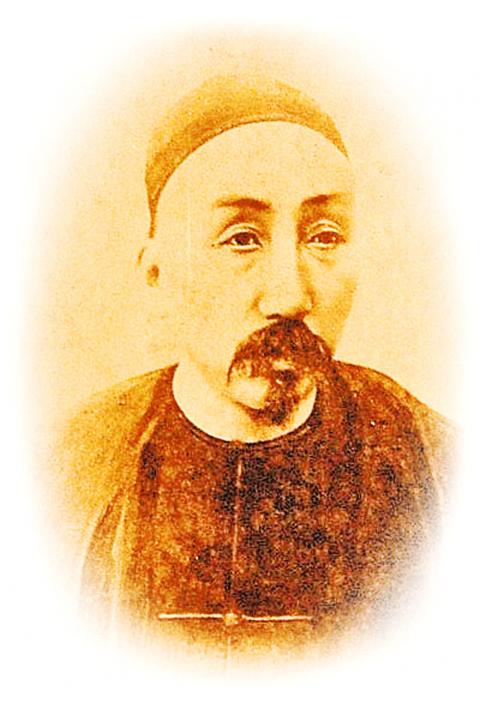

Photo courtesy of Wikemedia Commons
In the early 1870s Japan made military incursions into the area in order to punish local pirates, while from 1884 to 1885 France briefly occupied northern Taiwan. The Japanese expansion and the French episode convinced the Qing court in Beijing that it was necessary to pay more attention to Taiwan, and governor Liu Ming-chuan (劉銘傳) was asked by the Court to prepare to make Taiwan a province in its own right.
Liu’s first order of business was to try to bring the Aboriginal population under his control: from 1885 through 1887 he conducted three major military campaigns but lost one-third of his men, while in the end only one-third of Aboriginal areas were under his control. Still, in 1887 Taiwan was officially declared a province of China, and Liu was made its first governor.
MODERNIZATION
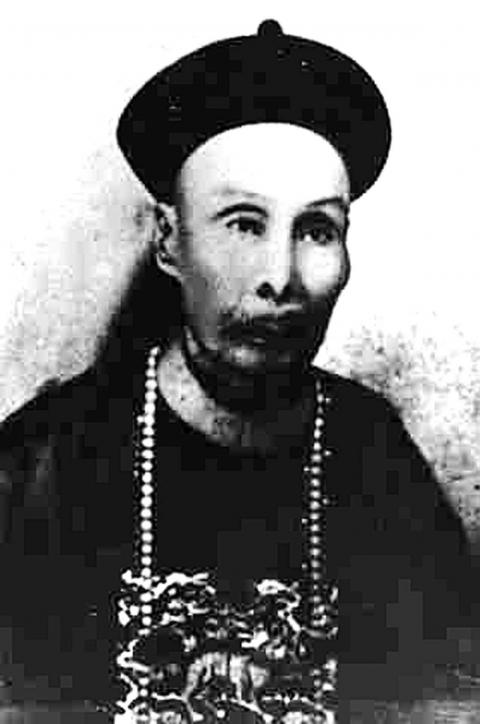

Photo courtesy of Wikemedia Commons
Once in office, Liu started an extensive process of modernization. He felt constrained by the old capital Tainan — too many small winding streets —and proposed to move the capital to Taichung, where he laid out a grid for a modern city and started to build many new buildings, city walls, gates and imperial offices. However, cost overruns put a halt to the project.
Still, in the next few years Taiwan went through a period of frantic modernization: a modern telegraph line connected north and south, electric streetlights started to line the streets, a taxicab service with rickshaws was initiated and a modern railroad was built between Keelung, Taipei and Hsinchu. With the help of European trading houses, Taiwan became a major trading hub again, exporting tea, camphor, sugar and rice.
The renewed interaction with the West put Taiwan on the map again for Europe and also for the young American republic. Small European communities sprouted in Tainan and Taipei: traders and missionaries, who set up schools, clinics and hospitals. Missionary Thomas Barclay in Tainan set up the first ever printing press, and started publishing Presbyterian Taiwan Church News.
Much of this new vitality and innovation was possible as Taiwanese were frontiersmen and pioneers, much more open to innovation than tradition-bound Chinese officialdom in Beijing.
DISTINCT IDENTITY
Liu also tolerated dissent and his policies started to attract intellectuals from China, escaping the oppressive atmosphere under the late Qing dynasty rule. The mix of these intellectuals and local gentry brought about a flourishing culture of art and literature. It resulted in the birth of a local identity that saw itself as distinct from China. This also formed the powerbase for the subsequent Formosa Republic.
But Liu’s policies and expansion created resentment and jealousy at the Qing Court. In 1891 he was recalled to China, and retired to Anhui Province. He was succeeded by Shao Yu-lien (邵友濂), who was governor until 1894. Shao’s major achievement was the definitive move of the capital from Tainan. However, the eventual destination was Taipei, which had become the center of political activity.
INCOMPETENCE
Shao’s rule was mostly known for its rampant corruption and ineffective government. He stopped or reversed many of the new modernization projects and innovations started by his predecessor. He was ordered to prepare Taiwan for defense against Japan, but purchased old and useless weapons, pocketing the difference. To his credit, he did bring in the famous “Black Flag” Liu, who would later play a major role in the Formosa Republic.
The ineffectual Shao was replaced by governor Tang Ching-sung (唐景崧), who had fought against the French in the South. Tang had fought together with “Black Flag” general Liu Yung-fu, who received the command of some 100,000 soldiers.
TREATY OF SHIMONOSEKI
However, war had broken out between China and Japan over control over Korea. China lost and under the 1895 Treaty of Shimonoseki, it ceded Taiwan to Japan.
The treaty was signed on behalf of the Qing government by viceroy Li Hongzhang (李鴻章). Under its provisions, China recognized the independence of Korea, ceded Taiwan and Penghu in perpetuity to Japan, paid a huge war indemnity and opened port-cities to trade.
Back in Taiwan, the treaty came as a total surprise. Neither the population nor officials had been consulted. On May 23, 1895, Governor Tang was convinced by local gentry to declare an independent Formosa Republic, the first independent republic in Asia. A new government was inaugurated on May 25, 1895.
While during this brief interlude of eight years, Taiwan was indeed ruled as a province of China, at the same time the era established a more solid basis for a separate Taiwanese identity: a multicultural mix of the Aboriginal, Hakka and Hokkien heritages.
The earlier settlers were frontiersmen who had mainly engaged in agriculture and local trade. Along with the gentry, they had always had an independent streak, fighting off foreign control on numerous occasions. The intelligentsia and literati who arrived during the late 1880s did so to escape the stifling climate in Beijing under the Manchu rulers. The combination proved to be a powerful mix, which laid the basis for both the Formosa Republic and the early resistance against the Japanese.
Gerrit van der Wees is a former Dutch diplomat. From 1980 through 2016 he served as the editor of Taiwan Communique.

It’s a good thing that 2025 is over. Yes, I fully expect we will look back on the year with nostalgia, once we have experienced this year and 2027. Traditionally at New Years much discourse is devoted to discussing what happened the previous year. Let’s have a look at what didn’t happen. Many bad things did not happen. The People’s Republic of China (PRC) did not attack Taiwan. We didn’t have a massive, destructive earthquake or drought. We didn’t have a major human pandemic. No widespread unemployment or other destructive social events. Nothing serious was done about Taiwan’s swelling birth rate catastrophe.

Words of the Year are not just interesting, they are telling. They are language and attitude barometers that measure what a country sees as important. The trending vocabulary around AI last year reveals a stark divergence in what each society notices and responds to the technological shift. For the Anglosphere it’s fatigue. For China it’s ambition. For Taiwan, it’s pragmatic vigilance. In Taiwan’s annual “representative character” vote, “recall” (罷) took the top spot with over 15,000 votes, followed closely by “scam” (詐). While “recall” speaks to the island’s partisan deadlock — a year defined by legislative recall campaigns and a public exhausted

In the 2010s, the Communist Party of China (CCP) began cracking down on Christian churches. Media reports said at the time that various versions of Protestant Christianity were likely the fastest growing religions in the People’s Republic of China (PRC). The crackdown was part of a campaign that in turn was part of a larger movement to bring religion under party control. For the Protestant churches, “the government’s aim has been to force all churches into the state-controlled organization,” according to a 2023 article in Christianity Today. That piece was centered on Wang Yi (王怡), the fiery, charismatic pastor of the

Hsu Pu-liao (許不了) never lived to see the premiere of his most successful film, The Clown and the Swan (小丑與天鵝, 1985). The movie, which starred Hsu, the “Taiwanese Charlie Chaplin,” outgrossed Jackie Chan’s Heart of Dragon (龍的心), earning NT$9.2 million at the local box office. Forty years after its premiere, the film has become the Taiwan Film and Audiovisual Institute’s (TFAI) 100th restoration. “It is the only one of Hsu’s films whose original negative survived,” says director Kevin Chu (朱延平), one of Taiwan’s most commercially successful