The landscape around the west coast of Ireland is breathtaking enough to wipe years off furrowed brows.
But it is not the rugged Irish scenery that has changed the face of the beauty industry. It is a pristine-looking glass-walled factory set in 12 hectares outside the picturesque town of Westport in County Mayo, which produces the entire world’s supply of Botox.
Kylie Minogue has admitted using it, as have Geri Halliwell, Courteney Cox and Jennifer Aniston, but it is no longer just celebrities looking to iron out the wrinkles in their foreheads.
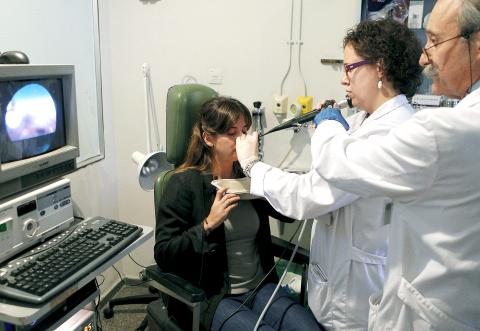
Photo: EPA
Since it began production in 1990, the factory has pumped out more than 26 million phials of the chemical otherwise known as Botulinum toxin A, generating US$500 million a year for the pharmaceutical firm Allergan. Last year, at the height of the recession, the company reported 8 percent earnings growth.
What makes investors “rather ecstatic,” chief executive David Pyott said, is that Allergan has grown from a company that relied on “purely reimbursed” business from hospitals and clinics to one that includes a booming cash business of private clients who use Botox and other medical aesthetic treatments under the Allergan umbrella, including dermal-fillers, breast implants and gastric bands. The wealthy always want to look beautiful.
“Even in the depths of the recession, the first half of 2009, the world market [for Botox] only declined 9 percent,” Pyott said. “In the recession what’s happened is men have spread out their treatments [from every three months to four months] and women have fewer things done.”
The Botulinum toxin, which is produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum, works by temporarily paralyzing key muscles in the forehead. Pyott, 55, a Scot with a smooth-looking forehead, leads by example and uses it himself.
But it isn’t the beauty treatment that has the company so confident about future growth. It is all its other less sexy applications for Botox — 20 of them in total, including the recently approved application as a preventative medicine for chronic migraine — that opens up another potential goldmine.
There are an estimated 700,000 migraine sufferers in the UK alone reporting chronic head pain — dizziness, nausea and headaches can put someone out of action for up to two days at a time. The chronic form is defined as someone who has 15 headache days a month, of which at least eight are migraine.
Analysts reckon that the migraine breakthrough could generate revenue of between US$400 million and US$1 billion by 2015 — almost double the company’s turnover.
Allergan employs 800 staff in Westport, but the production of Botox is now so automated that it only requires the direct labor of 80 people. That’s about US$625,000 revenue per employee.
“The Botox story is an amazing story and what’s really unusual is that the best may still be to come,” said Pyott, a Glasgow-born lawyer who has been chief executive since 1998.
“Right now our revenues are split 50:50 between cosmetic and therapeutic. But five years from now 70 percent of our sales may come from therapeutic, and that’s not because the use of Botox will decline,” he said.
Pyott lists off some of the other Botox applications in the pipeline.
“It always starts in a severe population,” he said, referring to two future therapeutic applications: controlling weak bladders in multiple sclerosis sufferers and crash victims with spinal cord injuries.
This is currently in clinical trials as is another weak bladder condition, affecting women over the age of 50.
Many of the discoveries of the use of Botox are by accident. It was discovered that it could erase wrinkles in 1987 after an eye specialist injecting patients to correct crossed eyes reported that a patient’s frown had disappeared.
Another cosmetic application, which was approved in 2008 by the US Food and Drug Administration, was born from an eye-drop product that Allergan makes. Patients reported that one side-effect was longer and fuller eyelashes. Back in the laboratory, Allergan came up with Latisse, which has now been approved in the US and is undergoing clinical trials in Europe.
For Ireland, which is in the throes of one of the worst recessions in the eurozone, the Botox story is important.
One of the reasons that Allergan set up shop in Westport 33 years ago was relocation aid and low corporate tax, which now stands at just 12.5 percent. European Commissioner for Economic and Financial Affairs Olli Rehn recently suggested that this might have to be increased if Ireland was to reduce its gargantuan budget deficit.
But Pyott is unperturbed by the threat of rising taxes.
“We have long assumed the rate would go up a couple of points,” he said.
Having studied EU law, he said Brussels could huff and puff, but “at the end of the day, it’s a matter of national sovereignty.”
He is also optimistic about the overall recovery of European markets comparison with those in the US.
“Here and there, there are patches of gloom, but here in our company we really see no big issues at all,” he said.
“We look at all the statistics very carefully and in fact, looking at the recovery of our markets, particularly those that are cash paid, there is no sign of the infamous ‘double dip.’ In fact, I would say most European markets are recovering and growing more quickly than those in the United States,” he said.

DIVIDED VIEWS: Although the Fed agreed on holding rates steady, some officials see no rate cuts for this year, while 10 policymakers foresee two or more cuts There are a lot of unknowns about the outlook for the economy and interest rates, but US Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell signaled at least one thing seems certain: Higher prices are coming. Fed policymakers voted unanimously to hold interest rates steady at a range of 4.25 percent to 4.50 percent for a fourth straight meeting on Wednesday, as they await clarity on whether tariffs would leave a one-time or more lasting mark on inflation. Powell said it is still unclear how much of the bill would fall on the shoulders of consumers, but he expects to learn more about tariffs
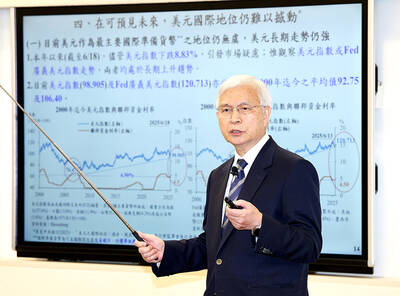
NOT JUSTIFIED: The bank’s governor said there would only be a rate cut if inflation falls below 1.5% and economic conditions deteriorate, which have not been detected The central bank yesterday kept its key interest rates unchanged for a fifth consecutive quarter, aligning with market expectations, while slightly lowering its inflation outlook amid signs of cooling price pressures. The move came after the US Federal Reserve held rates steady overnight, despite pressure from US President Donald Trump to cut borrowing costs. Central bank board members unanimously voted to maintain the discount rate at 2 percent, the secured loan rate at 2.375 percent and the overnight lending rate at 4.25 percent. “We consider the policy decision appropriate, although it suggests tightening leaning after factoring in slackening inflation and stable GDP growth,”

Meta Platforms Inc offered US$100 million bonuses to OpenAI employees in an unsuccessful bid to poach the ChatGPT maker’s talent and strengthen its own generative artificial intelligence (AI) teams, OpenAI CEO Sam Altman has said. Facebook’s parent company — a competitor of OpenAI — also offered “giant” annual salaries exceeding US$100 million to OpenAI staffers, Altman said in an interview on the Uncapped with Jack Altman podcast released on Tuesday. “It is crazy,” Sam Altman told his brother Jack in the interview. “I’m really happy that at least so far none of our best people have decided to take them

As they zigzagged from one machine to another in the searing African sun, the workers were covered in black soot. However, the charcoal they were making is known as “green,” and backers hope it can save impoverished Chad from rampant deforestation. Chad, a vast, landlocked country of 19 million people perched at the crossroads of north and central Africa, is steadily turning to desert. It has lost more than 90 percent of its forest cover since the 1970s, hit by climate change and overexploitation of trees for household uses such as cooking, officials say. “Green charcoal” aims to protect what