As demand for clean energy rises around the world, the US' high-tech hub is looking to squeeze more money out of silicon.
Engineers and entrepreneurs in Silicon Valley are taking advantage of their expertise in computer chips to design and manufacture electricity-generating solar cells that they hope will be increasingly competitive with traditional energy sources such as coal and natural gas. Most solar cells and chips are made from the same raw material from which the valley gets its name.
"We're in the very early stages of a long build-out in solar technology," said Erik Straser, who heads the "cleantech" practice at the Menlo Park venture capital firm Mohr Davidow Ventures. "The potential is really enormous."

PHOTO: AP
Despite technological advances since the first photovoltaic cells were invented 50 years ago, solar is still two to three times more expensive than fossil fuels in the US and relies on government subsidies to compete.
But improving technology, falling costs, rising prices for fossil fuels, concerns about the electric grid's stability and worries about global warming are all raising interest in solar energy. The industry is expected to grow from US$11 billion last year to US$51 billion in 2015, according to a projection by Clean Edge Inc, a market research firm focused on clean technology.
And that's why Silicon Valley is getting involved.
This month, Applied Materials Inc, a Santa Clara company that manufactures chipmaking equipment, announced plans to sell tools for producing solar cells. The company projects the market for such gear will triple to US$3 billion over the next four years.
The company's equipment can be retooled for silicon solar wafers, while another of its technologies -- for making flat-panel displays -- can be applied to "thin film" solar cells sprayed onto glass and other flat surfaces.
"By lowering the cost and increasing the volumes, we think that solar power will become much more affordable in more places in the world," chief technology officer Mark Pinto said.
Cypress Semiconductor Corp of San Jose was one of the first Silicon Valley chipmakers to cross over into the solar sector.
Four years ago, Cypress founder T.J. Rodgers convinced his board to buy a majority stake in solar cell-maker SunPower Corp, founded by his former Stanford University classmate Richard Swanson.
Rodgers argued that Cypress' manufacturing technology could be used to reduce costs and expand production of SunPower's cells.
Cypress' investment is paying off. SunPower raised US$146 million when it went public last year, making it one of last year's most successful initial public offerings. Revenue has increased from about US$10 million in 2004 to a projected US$230 million next year, SunPower CEO Tom Werner said.
"The semiconductor and solar industries are very similar," Werner said. "It's just that the solar industry hasn't gotten to the same scale as the semiconductor industry."
Solar's expansion in Silicon Valley won't necessarily create lots of manufacturing jobs in the San Francisco Bay Area. Production primarily takes place in low-cost countries, mostly in Asia.
Only about 100 of SunPower's 1,300 employees work at its San Jose headquarters; the rest work at a new manufacturing plant in the Philippines.
Silicon Valley venture capitalists are also taking an interest in solar, part of their growing interest in companies that develop environmentally friendly technologies.
About US$1.4 billion in venture capital was invested in cleantech ventures during the first six months of this year, and US$1.6 billion was invested last year, according to the Cleantech Venture Network.
About one-third of that money was invested in Silicon Valley, said Carl Guardino, who heads the Silicon Valley Leadership Group.
"We all realize that green is gold," Guardino said.
"Venture capitalists are betting with their wallets that cleantech will play a significant role in Silicon Valley," he said.
So many valley companies, venture capitalists and entrepreneurs are rushing into the burgeoning solar industry that it's inviting comparisons to the early expansion of the microchip industry more than two decades ago.
"If there's anywhere in the world that can push the envelope on solar, it might very well be Silicon Valley," Clean Edge co-founder Ron Pernick said.
But the valley's rush to solar isn't without risk. The solar industry must first bring down costs significantly to persuade homeowners and businesses to install solar systems onsite rather than just buy electricity from the local utility.
The industry also faces a worldwide shortage of polysilicon created by the rapid expansion of solar. This year, for the first time, the solar industry is expected to consume more silicon than the computer chip industry.
Some valley solar startups are moving beyond silicon. Miasole of San Jose and Nanosolar Inc of Palo Alto are developing thin-film solar cells made from alternative materials like copper and selenium. Nanosolar has raised US$100 million in venture funding and plans to build what it says will be the world's largest solar-cell factory.

NATIONAL SECURITY THREAT: An official said that Guan Guan’s comments had gone beyond the threshold of free speech, as she advocated for the destruction of the ROC China-born media influencer Guan Guan’s (關關) residency permit has been revoked for repeatedly posting pro-China content that threatens national security, the National Immigration Agency said yesterday. Guan Guan has said many controversial things in her videos posted to Douyin (抖音), including “the red flag will soon be painted all over Taiwan” and “Taiwan is an inseparable part of China,” while expressing hope for expedited “reunification.” The agency received multiple reports alleging that Guan Guan had advocated for armed reunification last year. After investigating, the agency last month issued a notice requiring her to appear and account for her actions. Guan Guan appeared as required,
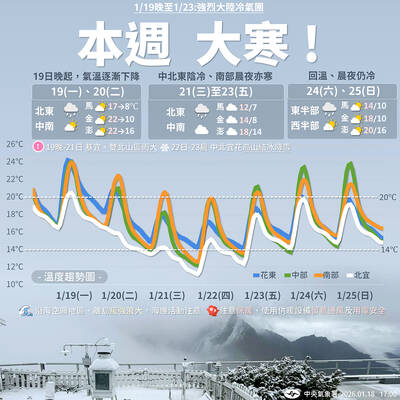
A strong cold air mass is expected to arrive tonight, bringing a change in weather and a drop in temperature, the Central Weather Administration (CWA) said. The coldest time would be early on Thursday morning, with temperatures in some areas dipping as low as 8°C, it said. Daytime highs yesterday were 22°C to 24°C in northern and eastern Taiwan, and about 25°C to 28°C in the central and southern regions, it said. However, nighttime lows would dip to about 15°C to 16°C in central and northern Taiwan as well as the northeast, and 17°C to 19°C elsewhere, it said. Tropical Storm Nokaen, currently

PAPERS, PLEASE: The gang exploited the high value of the passports, selling them at inflated prices to Chinese buyers, who would treat them as ‘invisibility cloaks’ The Yilan District Court has handed four members of a syndicate prison terms ranging from one year and two months to two years and two months for their involvement in a scheme to purchase Taiwanese passports and resell them abroad at a massive markup. A Chinese human smuggling syndicate purchased Taiwanese passports through local criminal networks, exploiting the passports’ visa-free travel privileges to turn a profit of more than 20 times the original price, the court said. Such criminal organizations enable people to impersonate Taiwanese when entering and exiting Taiwan and other countries, undermining social order and the credibility of the nation’s

‘SALAMI-SLICING’: Beijing’s ‘gray zone’ tactics around the Pratas Islands have been slowly intensifying, with the PLA testing Taiwan’s responses and limits, an expert said The Ministry of National Defense yesterday condemned an intrusion by a Chinese drone into the airspace of the Pratas Islands (Dongsha Islands, 東沙群島) as a serious disruption of regional peace. The ministry said it detected the Chinese surveillance and reconnaissance drone entering the southwestern parts of Taiwan’s air defense identification zone early yesterday, and it approached the Pratas Islands at 5:41am. The ministry said it immediately notified the garrison stationed in the area to enhance aerial surveillance and alert levels, and the drone was detected in the islands’ territorial airspace at 5:44am, maintaining an altitude outside the effective range of air-defense weaponry. Following