It should have been a perfect day for Vincent Petit, finishing up an afternoon gallop on a wide expanse of beach along a pastel-colored bay. Instead, he and his mount were sucked into a hole of noxious black sludge.
The horse died within seconds, the rider lost consciousness and a dirty secret on the Brittany coast reverberated across France — decaying green algae was fouling some of its best beaches.
A report ordered by the government after the accident found concentrations of hydrogen sulfide gas emitted by the rotting algae were as high as 1,000 parts per million on the beach where the horse died — an amount that “can be fatal in several minutes.”
There had been signs of a crisis for years in this idyllic corner of Brittany. But scaring away tourists was in no one’s interest, including the farming industry — the region’s economic backbone — whose nitrate-packed fertilizers power algae blooms.
So, while tongues wagged, folks whispered and acrimony grew, an official hush prevailed. It took the death of the horse to bring the problem into the open.
Decaying ulva algae threatens other beaches around France and the world, from the US to China, experts say. Last year, the Chinese government brought in the army to remove the slimy growths so the Olympic sailing competition could be held.
In Brittany’s Cote d’Armor region, conditions are perfect for its spread — sunlight, shallow waters and flat beaches. Chemical and natural fertilizers like pig excrement, loaded with nitrates and phosphorous, have saturated the land, spilling into rivers and the ocean, feeding the algae that then proliferate.
Harmless while in water, the algae form dangerous gases — notably hydrogen sulfide, with its characteristic rotten-egg smell — when they wash up on land and decay. A white crust forms and traps the gases, which are released when stepped on or otherwise disturbed.
Over time, putrefied algae turns sand into a black silt muck, sometimes containing pockets of poison gas.
On July 28, Petit, a 28-year-old researcher in a state-run virology lab, had just finished riding his thoroughbred Sir Glitter, a retired racehorse, on the Saint-Michel-en-Greves beach, when the two were suddenly mired in muck as he led the horse on foot in search of a place to cross a stream running through the sand.
“The horse and I slid in,” said Petit, who is also trained in veterinary studies. “A horse in that situation is in an enormous panic, but he didn’t have time to struggle.”
Petit said he watched horrified as his horse stopped breathing and died within about 30 seconds, then he himself passed out. Petit was pulled from the mire by a bulldozer shovel after a man who witnessed the accident gave the alert.
While locals are aware of the perils posed by the silt traps that lurk under the sand around streams that feed from the beach into the ocean, Petit did not sense the danger until the ground gave way and he and his horse were sucked into the noxious ooze up to the man’s chest.
Police initially ruled the horse suffocated, but an autopsy showed the animal died of an acute pulmonary edema with symptoms “compatible with gaseous intoxication in a brutal manner,” Petit said, quoting the report, which he paid for.

FRUSTRATIONS: One in seven youths in China and Indonesia are unemployed, and many in the region are stuck in low-productivity jobs, the World Bank said Young people across Asia are struggling to find good jobs, with many stuck in low-productivity work that the World Bank said could strain social stability as frustrations fuel a global wave of youth-led protests. The bank highlighted a persistent gap between younger and more experienced workers across several Asian economies in a regional economic update released yesterday, noting that one in seven young people in China and Indonesia are unemployed. The share of people now vulnerable to falling into poverty is now larger than the middle class in most countries, it said. “The employment rate is generally high, but the young struggle to

STEPPING UP: Diminished US polar science presence mean opportunities for the UK and other countries, although China or Russia might also fill that gap, a researcher said The UK’s flagship polar research vessel is to head to Antarctica next week to help advance dozens of climate change-linked science projects, as Western nations spearhead studies there while the US withdraws. The RRS Sir David Attenborough, a state-of-the-art ship named after the renowned British naturalist, would aid research on everything from “hunting underwater tsunamis” to tracking glacier melt and whale populations. Operated by the British Antarctic Survey (BAS), the country’s polar research institute, the 15,000-tonne icebreaker — boasting a helipad, and various laboratories and gadgetry — is pivotal to the UK’s efforts to assess climate change’s impact there. “The saying goes

ENERGY SHIFT: A report by Ember suggests it is possible for the world to wean off polluting sources of power, such as coal and gas, even as demand for electricity surges Worldwide solar and wind power generation has outpaced electricity demand this year, and for the first time on record, renewable energies combined generated more power than coal, a new analysis said. Global solar generation grew by a record 31 percent in the first half of the year, while wind generation grew 7.7 percent, according to the report by the energy think tank Ember, which was released after midnight yesterday. Solar and wind generation combined grew by more than 400 terawatt hours, which was more than the increase in overall global demand during the same period, it said. The findings suggest it is
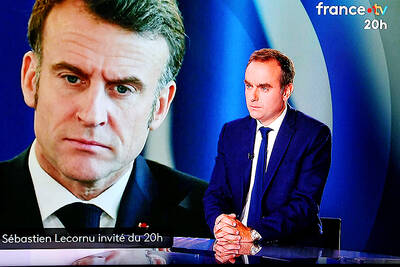
TICKING CLOCK: A path to a budget agreement was still possible, the president’s office said, as a debate on reversing an increase of the pension age carries on French President Emmanuel Macron yesterday was racing to find a new prime minister within a two-day deadline after the resignation of outgoing French Prime Minister Sebastien Lecornu tipped the country deeper into political crisis. The presidency late on Wednesday said that Macron would name a new prime minister within 48 hours, indicating that the appointment would come by this evening at the latest. Lecornu told French television in an interview that he expected a new prime minister to be named — rather than early legislative elections or Macron’s resignation — to resolve the crisis. The developments were the latest twists in three tumultuous