Mexico City wants to turn one of the planet’s biggest and messiest waste management systems into the greenest in Latin America, if not the developing world.
A newly formed Waste Commission is working to build four state-of-the-art processing centers in the next four years to recycle, compost or burn for energy 85 percent of Mexico City’s trash — compared with about 6 percent recycled today. If it works, it would put this sprawling, polluted metropolis in a league with San Francisco, the Netherlands and other top recyclers, and first among developing cities, where the recycling rates mostly hover around 10 percent.
“The whole concept of recycling is very new in Latin America,” said Atiliano Savino, president of the International Solid Waste Association.
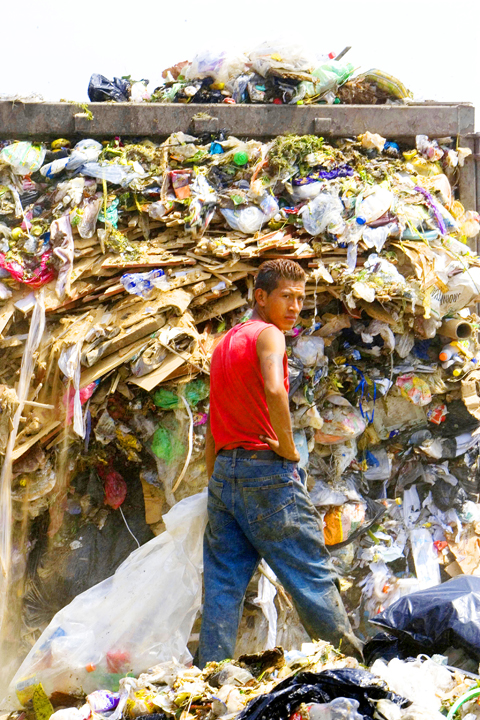

PHOTO: AP
While many places are good at recycling one thing, such as aluminum, Savino said he had never seen a city revamp its recycling program on this scale in so little time. US and European cities that now have recycling rates of more than 50 percent began decades ago.
NO CHOICE
But Mexico City has no choice. The federal government proposed to close the city’s main landfill this month, saying the 50 million-tonne dump has become too full and leaches contamination. Scientists dispute that and the closing has been delayed by a city appeal in federal court for an extension. Yet waste management officials know that soon much of Latin America’s largest metro area will be forced into expensive, temporary alternatives for dumping trash.
It will take more than technology to recycle most of the 12,500 tonnes of trash the mega-city produces daily. As in much of the developing world, Mexico City residents aren’t accustomed to separating their garbage.
But Fernando Menendez, the dapper, silver-haired Waste Commission director, says naysayers need only look at the success of his other major environmental project. No one thought he could get Mexico City residents out of their cars to cut air pollution, either. But his Hoy No Circula campaign now idles at least 1.6 million cars a week.
“Nobody has ever done anything like this,” Menendez said of shutting down what he calls the world’s biggest landfill. “But it has to work. There’s no other option.”
The Bordo Poniente dump was built on a dry lake bed on the northeast edge of the city in part to handle the rubble from the devastating 1985 earthquake. It now takes about 700 truckloads of unsorted rubbish a day.
SORTING TRASH
The city has required residents to sort trash since 2003, but without providing the infrastructure to handle it. Ninety percent of garbage trucks lack separate compartments for organic and inorganic waste. Thirteen transfer stations are supposed to process waste separately. But on a recent afternoon at a mid-sized center, three men were shoveling tree branches into a pit with plastic foam cups.
That’s where the enterprising informal economy takes over. Mexico City’s garbage workers union officially employs 17,000 and at least 8,000 more unofficially. Paid drivers and so-called volunteers make extra cash collecting “tips” from customers and selling aluminum and cardboard from their routes. Some union members rake in as much as three times their wage.
Meanwhile, just outside the Bordo Poniente, garbage pickers, including some children, sift through waste on fast-moving conveyer belts with their bare hands in a foul and dangerous open-air pit.
The Waste Commission plans to replace the ad-hoc system with new processing centers — about 180 million pesos (US$13 million) apiece — that by 2012 will recycle 20 percent of Mexico City’s garbage, compost 20 percent more and burn another 45 percent for energy.
As of November, only one center, in the rural southern delegation of Tlahuac, had been approved. Menendez says he is negotiating with private investors to finance the other three, while the Tlahuac center will be paid for with public funds.
The government also will harvest methane gas from the Bordo for energy to power the subway and light homes.

Yemen’s separatist leader has vowed to keep working for an independent state in the country’s south, in his first social media post since he disappeared earlier this month after his group briefly seized swathes of territory. Aidarous al-Zubaidi’s United Arab Emirates (UAE)-backed Southern Transitional Council (STC) forces last month captured two Yemeni provinces in an offensive that was rolled back by Saudi strikes and Riyadh’s allied forces on the ground. Al-Zubaidi then disappeared after he failed to board a flight to Riyadh for talks earlier this month, with Saudi Arabia accusing him of fleeing to Abu Dhabi, while supporters insisted he was

The Chinese Embassy in Manila yesterday said it has filed a diplomatic protest against a Philippine Coast Guard spokesman over a social media post that included cartoonish images of Chinese President Xi Jinping (習近平). Philippine Coast Guard spokesman Jay Tarriela and an embassy official had been trading barbs since last week over issues concerning the disputed South China Sea. The crucial waterway, which Beijing claims historic rights to despite an international ruling that its assertion has no legal basis, has been the site of repeated clashes between Chinese and Philippine vessels. Tarriela’s Facebook post on Wednesday included a photo of him giving a

Syrian President Ahmed al-Sharaa on Sunday announced a deal with the chief of Kurdish-led forces that includes a ceasefire, after government troops advanced across Kurdish-held areas of the country’s north and east. Syrian Kurdish leader Mazloum Abdi said he had agreed to the deal to avoid a broader war. He made the decision after deadly clashes in the Syrian city of Raqa on Sunday between Kurdish-led forces and local fighters loyal to Damascus, and fighting this month between the Kurds and government forces. The agreement would also see the Kurdish administration and forces integrate into the state after months of stalled negotiations on
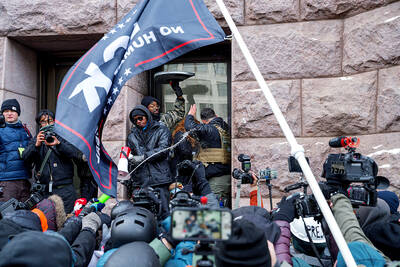
‘MOBILIZED’: While protesters countered ICE agents, Minnesota Governor Tim Walz activated the state’s National Guard to ‘support the rights of Minnesotans’ to assemble Hundreds of counterprotesters drowned out a far-right activist’s attempt to hold a small rally in support of US President Donald Trump’s latest immigration crackdown in Minneapolis, Minnesota, on Saturday, as the governor’s office announced that National Guard troops were mobilized and ready to assist law enforcement, although not yet deployed to city streets. There have been protests every day since the US Department of Homeland Security (DHS) ramped up immigration enforcement in the Twin Cities of Minneapolis and Saint Paul by bringing in more than 2,000 federal officers. Conservative influencer Jake Lang organized an anti-Islam, anti-Somali and pro-US Immigration and Customs Enforcement