A small bone that scientists had initially ignored has begun to yield secrets of the Neanderthal genome, launching a new way to learn about the stocky and muscular relative of modern humans, scientists say.
Genetic material from the bone has let researchers identify more than a million building blocks of Neanderthal DNA so far, and it should be enough to derive most of the creature's 3.3 billion blocks within the next two years, said researcher Svante Paabo.
"We're at the dawn of Neanderthal genomics," said gene specialist Edward Rubin of the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory in Berkeley, California.
Such research will "serve as a DNA time machine that will tell us about the biology and aspects of Neanderthals that we could never get" otherwise, Rubin said.
The Neanderthal data will shed light on what DNA changes helped produce modern humanity by revealing which changes appeared relatively late in human evolution, after the ancestors of Neanderthals and of humans split apart, scientists said.
Paabo, of the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany, and colleagues presented an initial analysis of Neanderthal DNA in this week's issue of the journal Nature. Rubin and his collaborators presented their own analysis in this week's issue of Science.
Both are based on DNA extracted from a bone that lay in a Croatian cave for 38,000 years.
"It's rather small and uninteresting and was thrown into a big box of uninformative bones" at a museum in Zagreb, Croatia, Paabo said.
It wasn't handled much, meaning that its DNA was not extensively contaminated by that of modern-day people, a major plus for the DNA work, he said. Only about four grams or less of the bone will be enough to get a rough draft of the Neanderthal genome.

Yemen’s separatist leader has vowed to keep working for an independent state in the country’s south, in his first social media post since he disappeared earlier this month after his group briefly seized swathes of territory. Aidarous al-Zubaidi’s United Arab Emirates (UAE)-backed Southern Transitional Council (STC) forces last month captured two Yemeni provinces in an offensive that was rolled back by Saudi strikes and Riyadh’s allied forces on the ground. Al-Zubaidi then disappeared after he failed to board a flight to Riyadh for talks earlier this month, with Saudi Arabia accusing him of fleeing to Abu Dhabi, while supporters insisted he was

The Chinese Embassy in Manila yesterday said it has filed a diplomatic protest against a Philippine Coast Guard spokesman over a social media post that included cartoonish images of Chinese President Xi Jinping (習近平). Philippine Coast Guard spokesman Jay Tarriela and an embassy official had been trading barbs since last week over issues concerning the disputed South China Sea. The crucial waterway, which Beijing claims historic rights to despite an international ruling that its assertion has no legal basis, has been the site of repeated clashes between Chinese and Philippine vessels. Tarriela’s Facebook post on Wednesday included a photo of him giving a
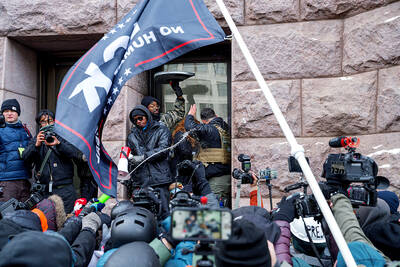
‘MOBILIZED’: While protesters countered ICE agents, Minnesota Governor Tim Walz activated the state’s National Guard to ‘support the rights of Minnesotans’ to assemble Hundreds of counterprotesters drowned out a far-right activist’s attempt to hold a small rally in support of US President Donald Trump’s latest immigration crackdown in Minneapolis, Minnesota, on Saturday, as the governor’s office announced that National Guard troops were mobilized and ready to assist law enforcement, although not yet deployed to city streets. There have been protests every day since the US Department of Homeland Security (DHS) ramped up immigration enforcement in the Twin Cities of Minneapolis and Saint Paul by bringing in more than 2,000 federal officers. Conservative influencer Jake Lang organized an anti-Islam, anti-Somali and pro-US Immigration and Customs Enforcement

NASA on Saturday rolled out its towering Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft as it began preparations for its first crewed mission to the Moon in more than 50 years. The maneuver, which takes up to 12 hours, would allow the US space agency to begin a string of tests for the Artemis 2 mission, which could blast off as early as Feb. 6. The immense orange and white SLS rocket, and the Orion vessel were slowly wheeled out of the Vehicle Assembly Building at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, and painstakingly moved 6.5km to Launch Pad 39B. If the