Wildlife conservationists are expected to push for new trade restrictions to protect fast-disappearing animals and plants, while lobbyists try to free up commerce in some species at international talks starting yesterday in Bangkok.
The two-week conference brings together thousands of delegates from the 166 countries that have signed the UN Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora, or CITES.
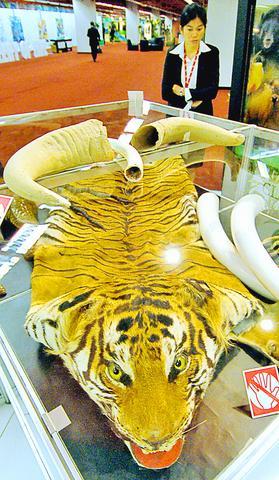
PHOTO: AP
The voluntary agreement, introduced in 1975, is meant to protect about 30,000 animals and plants, some of which are threatened with extinction due to commercial trade. About 50 proposals are expected to be submitted during the meeting to legitimize or block trade in some species.
Environmentalists say wildlife sales generate billions of dollars annually, making it the world's third-largest illicit enterprise after drug trafficking and illegal arms sales.
About 150 activists protested outside the conference hall yesterday, demanding the return of Thai elephants sold to zoos abroad and Indonesian orangutans allegedly smuggled into Thailand for use in boxing matches to entertain tourists at a local wildlife park.
Namibia is expected to propose lifting a 1989 ban on the sale of ivory that would allow it to sell tusks, ivory trinkets and goods made from the hair and skin of elephants that had died naturally or were culled under government-supervised programs.
Kenya and several West and Central African nations have opposed the idea, calling for a 20-year extension of the current moratorium.
Kenya is also lobbying for a global ban on trade in lion trophies and skins, arguing that the animals have declined sharply in number due to hunting, loss of habitat and lack of prey.
Australia and Madagascar are expected to call for tighter restrictions on trade in great white sharks -- the massive ocean predator that has increasingly become the prey of traders and trophy hunters seeking its jaws, teeth, skin and meat. The US has backed the proposal.
Meanwhile, activists have denounced a proposal by Japan to allow some populations of minke whales to be hunted for scientific purposes. Japan is among a few countries that have continued to hunt the mammals despite a 1986 ban on commercial whaling that largely halted the practice.
Thailand will ask delegates to outlaw trade of the Irrawaddy dolphin, which is native to freshwater habitats in Southeast Asia and is sought after by zoos, particularly in Japan and Singapore, for its pleasing appearance and ability to perform tricks.
While Thailand has made strides in cracking down on illicit wildlife trade in recent years, the country remains a hub for the sale and export of protected species due to corruption and weak law enforcement. Bangkok will ask for greater latitude in selling farm-grown orchids, a lucrative export. Wild specimens of the flower have been over-harvested worldwide because of their popularity among collectors, according to the UN.
Among the aquatic species set to be debated at the conference is the humphead wrasse, a Pacific reef fish considered a delicacy in some countries.
Proposals to protect the ramin timber tree, the Chinese yew and other medicinal plants, as well as an array of bird, turtle, crocodile and rhinoceros species will also be considered.

Tens of thousands of Filipino Catholics yesterday twirled white cloths and chanted “Viva, viva,” as a centuries-old statue of Jesus Christ was paraded through the streets of Manila in the nation’s biggest annual religious event. The day-long procession began before dawn, with barefoot volunteers pulling the heavy carriage through narrow streets where the devout waited in hopes of touching the icon, believed to hold miraculous powers. Thousands of police were deployed to manage crowds that officials believe could number in the millions by the time the statue reaches its home in central Manila’s Quiapo church around midnight. More than 800 people had sought

DENIAL: Pyongyang said a South Korean drone filmed unspecified areas in a North Korean border town, but Seoul said it did not operate drones on the dates it cited North Korea’s military accused South Korea of flying drones across the border between the nations this week, yesterday warning that the South would face consequences for its “unpardonable hysteria.” Seoul quickly denied the accusation, but the development is likely to further dim prospects for its efforts to restore ties with Pyongyang. North Korean forces used special electronic warfare assets on Sunday to bring down a South Korean drone flying over North Korea’s border town. The drone was equipped with two cameras that filmed unspecified areas, the General Staff of the North Korean People’s Army said in a statement. South Korea infiltrated another drone

COMMUNIST ALIGNMENT: To Lam wants to combine party chief and state presidency roles, with the decision resting on the election of 200 new party delegates next week Communist Party of Vietnam General Secretary To Lam is seeking to combine his party role with the state presidency, officials said, in a move that would align Vietnam’s political structure more closely to China’s, where President Xi Jinping (習近平) heads the party and state. Next week about 1,600 delegates are to gather in Hanoi to commence a week-long communist party congress, held every five years to select new leaders and set policy goals for the single-party state. Lam, 68, bade for both top positions at a party meeting last month, seeking initial party approval ahead of the congress, three people briefed by

Cambodia’s government on Wednesday said that it had arrested and extradited to China a tycoon who has been accused of running a huge online scam operation. The Cambodian Ministry of the Interior said that Prince Holding Group chairman Chen Zhi (陳志) and two other Chinese citizens were arrested and extradited on Tuesday at the request of Chinese authorities. Chen formerly had dual nationality, but his Cambodian citizenship was revoked last month, the ministry said. US prosecutors in October last year brought conspiracy charges against Chen, alleging that he had been the mastermind behind a multinational cyberfraud network, used his other businesses to launder