The delivery of organic compounds from stars to the solar system might have played an important role in the origin of life on Earth, an Academia Sinica researcher said yesterday.
In a review article published in British science journal Nature yesterday, author Kwok Sun (郭新), the director and distinguished research fellow of the Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Academia Sinica, summarized the evidence collected from recent infrared astronomy satellites showing that old stars can form complex organic compounds.
"No one had expected that complex organic compounds could be created in stars. In fact, theoretically, we still do not understand how it is possible," Kwok told the Taipei Times.
"But from our observations we have no doubt that these compounds are being made [in stars], and made on very short time lines," he added.
Given the availability of complex organic compounds in early Earth, life on the planet could have an easier start than previously believed. Kwok said that these organic compounds were probably incorporated in Earth during the formation of the solar system 4.5 billion years ago.
Using the technique of infrared spectroscopy, Kwok found that a chemical synthesis can occur rapidly in stars. In the research paper, Kwok argued that over a period of only several thousand years, small organic molecules with aliphatic structures are shown to have evolved into large, complex aromatic molecules. Since only a few thousand years are needed, differing levels of infrared spectra give the most direct evidence of a chemical synthesis in stars. Kwok said that most of these results were obtained from observations using the European Space Agency's Infrared Space Observatory satellites.
In the 1950s, many scientists were tasked with finding the origin of life. Around the world, the scientific community was examining what kind of environment would be needed to allow life to begin. Since the Miller-Urey experiment in 1953, most scientists have held the view that life on Earth was created from simple inorganic molecules. With a suitable energy source, such as lightning, and a hospitable environment, such as oceans, complex organic molecules such as sugars and amino acids are thought to have originated from methane, hydrogen, and ammonia. These organic molecules then formed what is believed to be the basis of life as we know it today.
However, in the past couple years, there has been a shift in the opinion of the scientific community that external delivery (for example, a collision by a meteorite into the earth) played a larger role in the origin of life than previously thought, Kwok said.
"Instead of life being created spontaneously from simple inorganic compounds, it now seems that the Earth had the advantage of having more complex ingredients at the starting point," Kwok said.
Kwok's main research interests have been old stars and infrared spectroscopy. The conclusions were made possible by comparing astronomical infrared spectroscopy with the laboratory analysis of meteorites, performed by scientists at the Washington University at St. Louis in the US.
"Clearly this is not the whole solution to the problem of origin of life or the existence of extraterrestrial life, but it does represent one small step in our understanding of how life began on Earth and how unique life is in the Galaxy," Kwok said.

The manufacture of the remaining 28 M1A2T Abrams tanks Taiwan purchased from the US has recently been completed, and they are expected to be delivered within the next one to two months, a source said yesterday. The Ministry of National Defense is arranging cargo ships to transport the tanks to Taiwan as soon as possible, said the source, who is familiar with the matter. The estimated arrival time ranges from late this month to early next month, the source said. The 28 Abrams tanks make up the third and final batch of a total of 108 tanks, valued at about NT$40.5 billion

Two Taiwanese prosecutors were questioned by Chinese security personnel at their hotel during a trip to China’s Henan Province this month, the Mainland Affairs Council (MAC) said yesterday. The officers had personal information on the prosecutors, including “when they were assigned to their posts, their work locations and job titles,” MAC Deputy Minister and spokesman Liang Wen-chieh (梁文傑) said. On top of asking about their agencies and positions, the officers also questioned the prosecutors about the Cross-Strait Joint Crime-Fighting and Judicial Mutual Assistance Agreement, a pact that serves as the framework for Taiwan-China cooperation on combating crime and providing judicial assistance, Liang
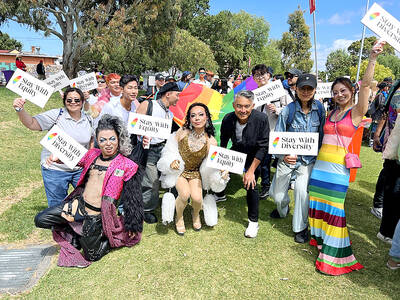
A group from the Taiwanese Designers in Australia association yesterday represented Taiwan at the Midsumma Pride March in Melbourne. The march, held in the St. Kilda suburb, is the city’s largest LGBTQIA+ parade and the flagship event of the annual Midsumma Festival. It attracted more than 45,000 spectators who supported the 400 groups and 10,000 marchers that participated this year, the association said. Taiwanese Designers said they organized a team to march for Taiwan this year, joining politicians, government agencies, professionals and community organizations in showing support for LGBTQIA+ people and diverse communities. As the first country in Asia to legalize same-sex

MOTIVES QUESTIONED The PLA considers Xi’s policies toward Taiwan to be driven by personal considerations rather than military assessment, the Epoch Times reports Chinese President Xi Jinping’s (習近平) latest purge of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army (PLA) leadership might have been prompted by the military’s opposition to plans of invading Taiwan, the Epoch Times said. The Chinese military opposes waging war against Taiwan by a large consensus, putting it at odds with Xi’s vision, the Falun Gong-affiliated daily said in a report on Thursday, citing anonymous sources with insight into the PLA’s inner workings. The opposition is not the opinion of a few generals, but a widely shared view among the PLA cadre, the Epoch Times cited them as saying. “Chinese forces know full well that