Rifle-toting soldiers patrolled the streets and armored vehicles guarded intersections in Mongolia’s capital yesterday, the start of a four-day state of emergency triggered by riots over alleged election fraud in which at least five people died.
Mongolian President Nambaryn Enkhbayar declared the emergency after rock-throwing protesters clashed with police on Tuesday as they mobbed the headquarters of the ruling Mongolian People’s Revolutionary Party (MPRP) and set it on fire.
He also issued a decree that imposed an overnight curfew and allowed police to use force in dealing with demonstrators.
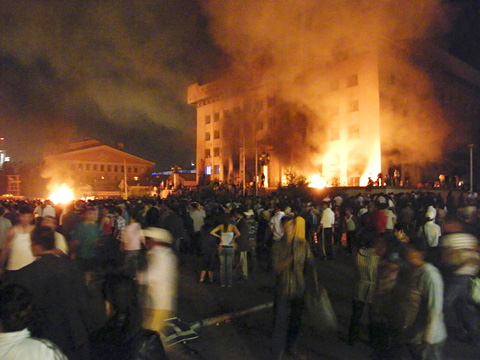
PHOTO: AP
A small group of people gathered yesterday afternoon in Ulan Bator’s main square next to the charred party headquarters, but dispersed after police using megaphones threatened to use force.
Montsame, Mongolia’s national news agency, said on its Web site that five people had died in Tuesday’s violence, in which officers used tear gas, rubber bullets and water cannons to beat back rioters wielding bricks and iron rods. The report did not say how they died.
Citing Munkhorgil, the minister of justice and home affairs, Montsame said 220 people were injured, including a Japanese reporter. While there were about 8,000 protesters, only about a quarter participated in the violence, it said.
A foreign ministry official who would not give her name because she was not authorized to speak to the media said about 1,000 people had been detained.
State television, the only station allowed to broadcast since the protests, showed two bleeding young men running into a hospital and said they later died.
The station showed burned and overturned cars and the charred four-story MPRP building. It said looters grabbed paintings from an art gallery and televisions from government offices during the protests.
“Police will use necessary force to crack down on criminals who are looting private and government property,” said Munkhorgil, the justice minister, who like many Mongolians uses only one name.
Early yesterday, armored vehicles blocked intersections near the MPRP building and groups of soldiers stood guard, rifles at the ready. Others patrolled the streets, but there were no immediate signs of tension. Shops were open and tourists wandered freely.
Preliminary results showed that the MPRP — the former Communists who governed the country when it was a Soviet satellite — won 46 seats in the 76-seat parliament, called the Great Hural.
Official results are to be announced on July 10.
Fraud allegations were vague and originally centered on two districts in Ulan Bator that were awarded to the ruling party but were contested by two popular members of the Civic Movement party.
Protesters later called the entire election into question, with opposition Democrats saying their party won the poll.
Voters stood in long lines on Sunday to cast their ballots in an election that focused on how to share the country’s mineral wealth.
Many hoped the vote would improve their lives in the landlocked, mostly poor country sandwiched between China and Russia.
The MPRP has long been dogged by allegations of corruption and official misconduct and is unpopular in the capital.
The president, a MPRP member, acknowledged the protesters’ complaints but appealed for calm.
The speaker of the parliament called a meeting to address the allegations, but it was not known when it would take place. Many members live in rural areas and will have to travel back to the capital.
Protesters also attacked the General Election Commission offices on Tuesday night, demanding that officials resign over the alleged voting irregularities.
Mongolia is struggling to modernize its nomadic, agriculture-based economy.
The government says per capita income is US$1,500 a year in the country of about 3 million people spread across an area about three times the size of Spain.
The two main political parties focused their campaigns on how to tap recently discovered mineral deposits — including copper, gold and coal — but disagreed over whether the government or private sector should hold a majority stake.
Mongolia has also been trying to have a more significant role in international politics.
In 2006, it hosted its first multinational peacekeeping training exercises. It also has sent troops to Iraq and Afghanistan to help shore up the US presence in those countries.
The moves are part of its burgeoning friendship with the US, in marked contrast with the cautious attitudes toward Washington of others in the region, notably in Beijing and Moscow.
In 2005, US President George W. Bush made the first visit to the country by a serving US president.
Meanwhile, in Taiwan, Ministry of Foreign Affairs spokesman Henry Chen (陳銘政) said yesterday that no Taiwanese had been harmed during the ongoing unrest in Mongolia.
ADDITIONAL REPORTING BY JENNY W. HSU

MISINFORMATION: The generated content tends to adopt China’s official stance, such as ‘Taiwan is currently governed by the Chinese central government,’ the NSB said Five China-developed artificial intelligence (AI) language models exhibit cybersecurity risks and content biases, an inspection conducted by the National Security Bureau (NSB) showed. The five AI tools are: DeepSeek, Doubao (豆包), Yiyan (文心一言), Tongyi (通義千問) and Yuanbao (騰訊元寶), the bureau said, advising people to remain vigilant to protect personal data privacy and corporate business secrets. The NSB said it, in accordance with the National Intelligence Services Act (國家情報工作法), has reviewed international cybersecurity reports and intelligence, and coordinated with the Ministry of Justice Investigation Bureau and the National Police Agency’s Criminal Investigation Bureau to conduct an inspection of China-made AI language

LIMITS: While China increases military pressure on Taiwan and expands its use of cognitive warfare, it is unwilling to target tech supply chains, the report said US and Taiwan military officials have warned that the Chinese People’s Liberation Army (PLA) could implement a blockade within “a matter of hours” and need only “minimal conversion time” prior to an attack on Taiwan, a report released on Tuesday by the US Senate’s China Economic and Security Review Commission said. “While there is no indication that China is planning an imminent attack, the United States and its allies and partners can no longer assume that a Taiwan contingency is a distant possibility for which they would have ample time to prepare,” it said. The commission made the comments in its annual

‘TROUBLEMAKER’: Most countries believe that it is China — rather than Taiwan — that is undermining regional peace and stability with its coercive tactics, the president said China should restrain itself and refrain from being a troublemaker that sabotages peace and stability in the Indo-Pacific region, President William Lai (賴清德) said yesterday. Lai made the remarks after China Coast Guard vessels sailed into disputed waters off the Senkaku Islands — known as the Diaoyutai Islands (釣魚台) in Taiwan — following a remark Japanese Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi made regarding Taiwan. Takaichi during a parliamentary session on Nov. 7 said that a “Taiwan contingency” involving a Chinese naval blockade could qualify as a “survival-threatening situation” for Japan, and trigger Tokyo’s deployment of its military for defense. Asked about the escalating tensions

DISPUTE: A Chinese official prompted a formal protest from Tokyo by saying that ‘the dirty head that sticks itself out must be cut off,’ after Takaichi’s Taiwan remarks Four armed China Coast Guard vessels yesterday morning sailed through disputed waters controlled by Japan, amid a diplomatic spat following Japanese Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi’s comments on Taiwan. The four ships sailed around the Senkaku Islands — known as the Diaoyutai Islands (釣魚台) to Taiwan, and which Taiwan and China also claim — on Saturday before entering Japanese waters yesterday and left, the Japan Coast Guard said. The China Coast Guard said in a statement that it carried out a “rights enforcement patrol” through the waters and that it was a lawful operation. As of the end of last month,