When Kuo Wen-hsi started learning the ancient art of making Chinese ink brushes six decades ago, he had no idea that one day his business would boom because of customers who can't even write.
But as Taiwan's birth rate plunges to worringly low levels, so-called “fetal hair brushes” made of a baby's hair are in massive demand from better-off parents to commemorate the birth of their newborns.
The baby trade forms the core business for Kuo's once-ailing small shop in Taipei that is stocked with hundreds of the products waiting to be delivered across the country.

PHOTOS: AFP
“In the past only government officials and rich families ordered a fetal hair brush to commemorate the birth of a baby because such a tailor-made brush is more expensive,” says Kuo.
“Now many younger parents have two salaries and fewer children so they are more willing to spend money on pampering their kids,” adds Kuo, 73, who struggled to keep his family tradition alive through the hard times.
The ink brush has been widely used by officials, scholars and students to write, practice calligraphy or paint for thousands of years.

Its popularity diminished with the advent of fountain pens and later ballpoint pens in the last five decades or so.
“Even though very few people were buying ink brushes during that time, I did not consider switching to a new profession because the elders in my family wished me to continue our trade,” recalls the modest, soft-spoken Kuo.
Born into a family of calligraphy brush-makers, Kuo inherited the business just in time to witness the downturns, seeing trade plummet 80 percent from a peak of 5,000 brushes a day.
For a while Kuo had to work part-time selling furniture to support his shop but his persistence eventually paid off, thanks to an old product catching on amid the new social phenomenon of record low birth rates.
Taiwan's fertility rate fell to an all-time low last year, as the average number of children that a woman gave birth to dropped to 0.91 from 0.96 in 2004, according to statistics from the interior ministry.
A total of 206,400 babies were born last year, down 5.2 percent from the previous year, the ministry said.
Kuo's biggest customers now are aged between 12 days and 18 months.
The only requirement is that they never have a haircut so the fetal hair remains intact to make the special brushes.
Kuo takes all the hair from the baby's head, shaving it off in his shop or at the customer's home. The size of the brushes depends on the amount of hair.
A set consists of three to five fetal hair brushes, two name chops and a stamp pad that costs between NT$3,500 and NT$56,800 and is sold in a wooden box carved with the baby's footprints, according to Kuo.
Part of the umbilical cord is preserved inside the name chops aimed at bringing fortune to the baby, as traditionally the cord is a sign of wealth, he says.
The most expensive brushes Kuo ever sold were a NT$100,000 set made of jade.
A basic calligraphy brush sold in bookstores or stationary shops costs some NT$50.
“The fetal hair brush is the biggest opportunity for brush-makers as popular demand for this product helps revive our trade, and now there are some 200 shops offering the souvenir brush,” says Kuo.
The niche market is apparently lucrative as Kuo's shop boasts a monthly revenue of up to NT$1 million.
He also has Taiwanese customers living in Japan, the US, Australia and elsewhere who found his services on the Internet and returned to order the brush.
“The fetal hair brush is valuable to keep and it is also very practical,” said housewife Tsai Pao-chen, who took her one-year-old son to Kuo's shop to make the brush.
“I like to practice calligraphy and it would be very interesting if my son can use the brush made of his own hair to learn calligraphy in the future,” Tsai said.

Late last month Philippines Foreign Affairs Secretary Theresa Lazaro told the Philippine Senate that the nation has sufficient funds to evacuate the nearly 170,000 Filipino residents in Taiwan, 84 percent of whom are migrant workers, in the event of war. Agencies have been exploring evacuation scenarios since early this year, she said. She also observed that since the Philippines has only limited ships, the government is consulting security agencies for alternatives. Filipinos are a distant third in overall migrant worker population. Indonesia has over 248,000 workers, followed by roughly 240,000 Vietnamese. It should be noted that there are another 170,000

Hannah Liao (廖宸萱) recalls the harassment she experienced on dating apps, an experience that left her frightened and disgusted. “I’ve tried some voice-based dating apps,” the 30-year-old says. “Right away, some guys would say things like, ‘Wanna talk dirty?’ or ‘Wanna suck my d**k?’” she says. Liao’s story is not unique. Ministry of Health and Welfare statistics show a more than 50 percent rise in sexual assault cases related to online encounters over the past five years. In 2023 alone, women comprised 7,698 of the 9,413 reported victims. Faced with a dating landscape that can feel more predatory than promising, many in
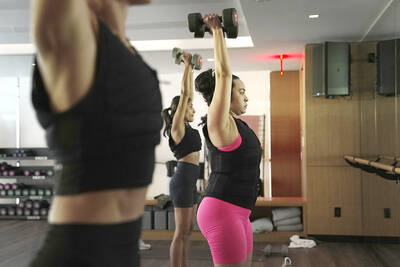
“This is one of those rare bits of TikTok fitness advice with a lot of truth behind it,” says Bethan Crouse, performance nutritionist at Loughborough University. “Sometimes it’s taken a bit too literally, though! You see people chugging protein drinks as they’re scanning out of their gym.” Crouse recommends the athletes she works with consume 20-30g of protein within 30-60 minutes of finishing a resistance training session. “The act of exercising our muscles increases the breakdown of muscle proteins,” she says. “In order to restore, or hopefully improve them — and get gains such as increased muscle mass or strength —
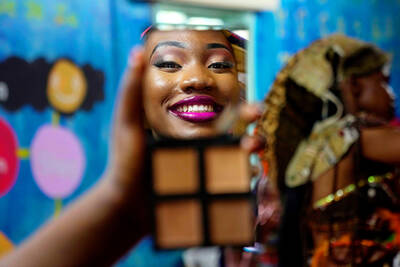
“Far from being a rock or island … it turns out that the best metaphor to describe the human body is ‘sponge.’ We’re permeable,” write Rick Smith and Bruce Lourie in their book Slow Death By Rubber Duck: The Secret Danger of Everyday Things. While the permeability of our cells is key to being alive, it also means we absorb more potentially harmful substances than we realize. Studies have found a number of chemical residues in human breast milk, urine and water systems. Many of them are endocrine disruptors, which can interfere with the body’s natural hormones. “They can mimic, block