The US Federal Reserve’s move to match its historic low in interest rates along with a downbeat economic outlook suggests the central bank is girding for more actions to stave off a crippling deflationary threat, analysts said.
The Fed cut its key lending rate a half point on Wednesday to 1 percent in the latest action to ease a credit crisis that is strangling the US economy, but also noted that “downside risks to growth remain” for the world’s biggest economy.
“It is clear that the Fed has moved from a defensive, case-by-case crisis management approach in the summer months to an offensive and comprehensive attack on the deflationary forces in the economy,” said Brian Bethune, chief US economist at IHS Global Insight.

PHOTO: AFP
Bethune predicts the Fed will bring the federal funds rate below the previously unthinkable level of 1 percent despite fears of a Japanese-style deflation threat that is unresponsive to monetary policy.
He said the Fed is likely to cut another 50 basis points on Dec. 16, which would be the lowest since the inception of the funds rate in 1954.
The economist said Fed chairman Ben Bernanke has made it clear he will use all tools at his disposal to break the grip of a worldwide credit crunch.
“The Fed has broadened and amplified its response to the escalation of the financial crisis and the recessionary forces now gaining momentum in the economy.
“In the month of October, the Fed slashed interest rates by 100 basis points, and also committed to close to US$2 trillion of additional short-term lending in the next few months,” he said. “That is a massive commitment to unlocking the credit markets.”
In 2003 and 2004, the Fed did not go below 1 percent amid concerns about how low rates could hurt small investors and money market funds.
But Peter Kretzmer, senior economist at Bank of America, pointed out that the latest statement “said nothing that would indicate technical issues preventing it from lowering rates further.”
The cut in the federal funds rate, which impacts on a number of other borrowing rates, followed an emergency half-point cut on Oct. 8 coordinated with other central banks to help fight a worldwide credit crunch.
“The pace of economic activity appears to have slowed markedly, owing importantly to a decline in consumer expenditures,” said the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) after the unanimous decision widely expected by financial markets.
Some analysts said the glum tone of the statement suggested the Fed could cut rates further, but would likely await the impact of its actions because of potential dangers of lowering its base rate below 1 percent — the level in 2003 and 2004 that likely fueled the US housing boom-and-bust cycle.
The statement “opens the door to more easing if incoming data continue to deteriorate,” said Aaron Smith, an analyst at Moody’s Economy.com.
Cary Leahey, senior economist at Decision Economics, said the FOMC “was reluctant to lower rates further than 1.0 percent but they did say that downside risks remain.”
This suggests “they want to wait till the next meeting before cutting again,” he said.
“The Fed doesn’t want to be caught in a trap of leaving rates too low too long.” Leahey said. “There is also a feeling they want to keep their powder dry.”

SECURITY: As China is ‘reshaping’ Hong Kong’s population, Taiwan must raise the eligibility threshold for applications from Hong Kongers, Chiu Chui-cheng said When Hong Kong and Macau citizens apply for residency in Taiwan, it would be under a new category that includes a “national security observation period,” Mainland Affairs Council (MAC) Minister Chiu Chui-cheng (邱垂正) said yesterday. President William Lai (賴清德) on March 13 announced 17 strategies to counter China’s aggression toward Taiwan, including incorporating national security considerations into the review process for residency applications from Hong Kong and Macau citizens. The situation in Hong Kong is constantly changing, Chiu said to media yesterday on the sidelines of the Taipei Technology Run hosted by the Taipei Neihu Technology Park Development Association. With

CARROT AND STICK: While unrelenting in its military threats, China attracted nearly 40,000 Taiwanese to over 400 business events last year Nearly 40,000 Taiwanese last year joined industry events in China, such as conferences and trade fairs, supported by the Chinese government, a study showed yesterday, as Beijing ramps up a charm offensive toward Taipei alongside military pressure. China has long taken a carrot-and-stick approach to Taiwan, threatening it with the prospect of military action while reaching out to those it believes are amenable to Beijing’s point of view. Taiwanese security officials are wary of what they see as Beijing’s influence campaigns to sway public opinion after Taipei and Beijing gradually resumed travel links halted by the COVID-19 pandemic, but the scale of
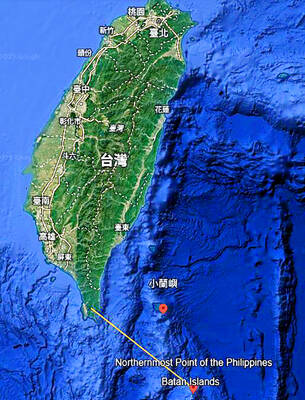
A US Marine Corps regiment equipped with Naval Strike Missiles (NSM) is set to participate in the upcoming Balikatan 25 exercise in the Luzon Strait, marking the system’s first-ever deployment in the Philippines. US and Philippine officials have separately confirmed that the Navy Marine Expeditionary Ship Interdiction System (NMESIS) — the mobile launch platform for the Naval Strike Missile — would take part in the joint exercise. The missiles are being deployed to “a strategic first island chain chokepoint” in the waters between Taiwan proper and the Philippines, US-based Naval News reported. “The Luzon Strait and Bashi Channel represent a critical access

Pope Francis is be laid to rest on Saturday after lying in state for three days in St Peter’s Basilica, where the faithful are expected to flock to pay their respects to history’s first Latin American pontiff. The cardinals met yesterday in the Vatican’s synod hall to chart the next steps before a conclave begins to choose Francis’ successor, as condolences poured in from around the world. According to current norms, the conclave must begin between May 5 and 10. The cardinals set the funeral for Saturday at 10am in St Peter’s Square, to be celebrated by the dean of the College