The UN yesterday unveiled its largest-ever scientific assessment on the dire state of the environment, but a crucial summary of its findings was torpedoed as nations feuded over fossil fuels.
The dispute over the Global Environment Outlook echoes a growing trend in consensus-based negotiations where oil-producing countries in particular are frustrating efforts to address pollution from fossil fuels and plastic.
The UN Environment Programme (UNEP) said it was the first time that countries had failed to produce a politically negotiated summary of the mammoth report, which is published roughly every five years and involves hundreds of scientists.

Photo: Bloomberg
“It’s regrettable,” UNEP executive director Inger Andersen said, but added that “the integrity of the report” remained above question.
Since first being published in 1997, UNEP’s flagship outlook reports have been accompanied by a summary for policymakers: a political statement, negotiated line by line, that distils the science into plain language for governments.
Under UN rules, this can only be approved by consensus, as it serves as a collective understanding of the latest science in a way policy leaders can act upon.
However, at a five-day meeting in late October to approve the summary, sharp divisions over the text made consensus impossible. Major oil producers Saudi Arabia and the US opposed references to phasing out fossil fuels, which are used to make plastic, and when burned are the primary driver of climate change, according to minutes of the meeting seen by AFP.
Other countries disagreed with language on gender, conflict and environmentally harmful subsidies, among other flashpoint issues, the minutes showed.
In a joint statement read as the negotiations closed, the EU, the UK and several other nations criticized “diversion attempts” during the talks, but did not name any country by name.
“It’s always the same story,” a French diplomat said of the “difficult discussions” that took place at UNEP headquarters in Nairobi.
Andersen said several countries “had significant disagreements,” but defended their right to dissent.
The US “actually was quite quiet and only spoke at the very end” to indicate their opposition, she added.
“That is what makes the United Nations the United Nations, and so we arrived where we did. But we certainly would like to hope that that doesn’t set a precedence for other processes,” she said.
The report, “A Future We Choose,” spans more than 1,200 pages and makes the case that investing in a cleaner planet could deliver trillions of dollars each year in additional economic growth.
Key to this would be “a total transformation of our energy system,” said report co-chair Robert Watson, who has helmed the UN’s expert scientific panels on climate change and biodiversity.
“We clearly have to eliminate the use of fossil fuels over the coming decades,” the British scientist told reporters.
However, this issue has stalled politically since countries agreed at the UN climate summit in Dubai in 2023 to move away from coal, gas and oil.
In October, pressure from the US helped delay a vote on an emissions price on global shipping, while negotiations for a world-first plastic treaty collapsed in August under opposition from oil-producing nations.
Last month’s UN COP30 climate summit ended with a watered-down deal after dozens of countries, including Saudi Arabia and coal producer India, opposed calls to advance a fossil fuel phaseout.
Watson said the world was “not moving fast enough by any stretch of the imagination to become sustainable” and progressive governments would need to take the lead.
“As our report says, the cost of action is less than the cost of inaction. But I have to say at this moment in time, multilateralism does seem to be in trouble,” he said.

MONEY GRAB: People were rushing to collect bills scattered on the ground after the plane transporting money crashed, which an official said hindered rescue efforts A cargo plane carrying money on Friday crashed near Bolivia’s capital, damaging about a dozen vehicles on highway, scattering bills on the ground and leaving at least 15 people dead and others injured, an official said. Bolivian Minister of Defense Marcelo Salinas said the Hercules C-130 plane was transporting newly printed Bolivian currency when it “landed and veered off the runway” at an airport in El Alto, a city adjacent to La Paz, before ending up in a nearby field. Firefighters managed to put out the flames that engulfed the aircraft. Fire chief Pavel Tovar said at least 15 people died, but

LIKE FATHER, LIKE DAUGHTER: By showing Ju-ae’s ability to handle a weapon, the photos ‘suggest she is indeed receiving training as a successor,’ an academic said North Korea on Saturday released a rare image of leader Kim Jong-un’s teenage daughter firing a rifle at a shooting range, adding to speculation that she is being groomed as his successor. Kim’s daughter, Ju-ae, has long been seen as the next in line to rule the secretive, nuclear-armed state, and took part in a string of recent high-profile outings, including last week’s military parade marking the closing stages of North Korea’s key party congress. Pyongyang’s official Korean Central News Agency (KCNA) released a photo of Ju-ae shooting a rifle at an outdoor shooting range, peering through a rifle scope
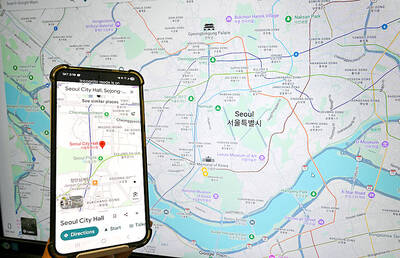
South Korea would soon no longer be one of the few countries where Google Maps does not work properly, after its security-conscious government reversed a two-decade stance to approve the export of high-precision map data to overseas servers. The approval was made “on the condition that strict security requirements are met,” the South Korean Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport said. Those conditions include blurring military and other sensitive security-related facilities, as well as restricting longitude and latitude coordinates for South Korean territory on products such as Google Maps and Google Earth, it said. The decision is expected to hurt Naver and Kakao

Australian Prime Minister Anthony Albanese yesterday said he did not take his security for granted, after he was evacuated from his residence for several hours following a bomb threat sent to a Chinese dance group. Albanese was evacuated from his Canberra residence late on Tuesday following the threat, and returned a few hours later after nothing suspicious was found. The bomb scare was among several e-mails threatening Albanese sent to a representative of Shen Yun, a classical Chinese dance troupe banned in China that is due to perform in Australia this month, a spokesperson for the group said in a statement. The e-mail