Japanese people are the least satisfied with their sex and romantic lives, closely followed by South Koreans, a global survey by a French research firm showed.
The two Asian rivals are grappling with a similar demographic crisis with their chronically — and dangerously, as authorities warn — low birthrates.
The poll of 31 countries, conducted by Paris-headquartered Ipsos, showed this week that just 37 percent of Japanese respondents derive satisfaction from sex and romance, versus the 76 percent of top-ranked Indians and Mexicans.

Photo: Bloomberg
Similarly displeased are South Koreans, whose sexual satisfaction was the second worst at 45 percent.
In June, Japan’s health ministry described the nation’s birthrate as “critical” as it stood at 1.20 last year, hitting a record low for the eighth straight year.
However, Japan’s rate is still above that of South Korea, which has the world’s lowest at 0.72.
The poll also showed that South Koreans feel the least contentment from their “relationships with partners and spouses,” with Japanese faring the second worst.
Asked how much they “feel loved” in life, 51 percent of Japanese said so, again the worst of all, slightly outranked by South Koreans and Italians at 63 percent.
The discontentment is partly the result of “the personality of Japanese people who aren’t good at articulating their emotions and attitudes when it comes to romance,” Ipsos said.
Among efforts to boost Japan’s plunging birthrates is a dating app launched earlier this year by authorities in the capital Tokyo. Users are required to submit documentation proving they are legally single and sign a letter stating they are willing to get married.

THE TRAGEDY OF PUNCH: Footage of the seven-month-old Japanese macaque has gone viral online after he was rejected by his mother and formed a bond with a soft toy A baby monkey in Japan has captured hearts around the world after videos of him being bullied by other monkeys and rejected by his mother went viral last week. Punch, a Japanese macaque, was born in July last year at Ichikawa City Zoo. He has drawn international attention after zookeepers gave him a stuffed orangutan toy after he was abandoned by his mother. Without maternal guidance to help him integrate, Punch has turned to the toy for comfort. He has been filmed multiple times being dragged and chased by older Japanese macaques inside the enclosure. Early clips showed him wandering alone with
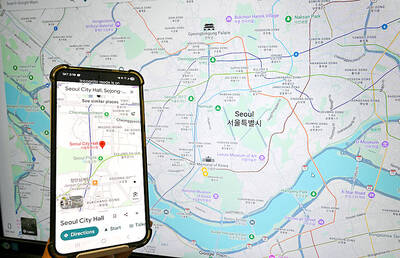
South Korea would soon no longer be one of the few countries where Google Maps does not work properly, after its security-conscious government reversed a two-decade stance to approve the export of high-precision map data to overseas servers. The approval was made “on the condition that strict security requirements are met,” the South Korean Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport said. Those conditions include blurring military and other sensitive security-related facilities, as well as restricting longitude and latitude coordinates for South Korean territory on products such as Google Maps and Google Earth, it said. The decision is expected to hurt Naver and Kakao

MONEY GRAB: People were rushing to collect bills scattered on the ground after the plane transporting money crashed, which an official said hindered rescue efforts A cargo plane carrying money on Friday crashed near Bolivia’s capital, damaging about a dozen vehicles on highway, scattering bills on the ground and leaving at least 15 people dead and others injured, an official said. Bolivian Minister of Defense Marcelo Salinas said the Hercules C-130 plane was transporting newly printed Bolivian currency when it “landed and veered off the runway” at an airport in El Alto, a city adjacent to La Paz, before ending up in a nearby field. Firefighters managed to put out the flames that engulfed the aircraft. Fire chief Pavel Tovar said at least 15 people died, but

Australian Prime Minister Anthony Albanese yesterday said he did not take his security for granted, after he was evacuated from his residence for several hours following a bomb threat sent to a Chinese dance group. Albanese was evacuated from his Canberra residence late on Tuesday following the threat, and returned a few hours later after nothing suspicious was found. The bomb scare was among several e-mails threatening Albanese sent to a representative of Shen Yun, a classical Chinese dance troupe banned in China that is due to perform in Australia this month, a spokesperson for the group said in a statement. The e-mail