For almost 500 years, the arch that connects the largest Gothic cathedral in the world with its Renaissance sacristy has offered visitors a sumptuous, if little glimpsed — and even less studied — vision of religious bounty.
The 68 beautifully carved plates of food that adorn the archway in Seville’s cathedral offer rather more than bread and wine.
There are pigs’ trotters and wild strawberries, aubergines, clams and oysters. There are peaches, radishes, a skinned hare with a knife by its side, a squirrel served on a bed of hazelnuts and a plate of lemons across which a small snake slithers. There are also cakes and biscuits, and, more exotically, a dish of peppers newly imported from Mexico, which had fallen to Hernan Cortes and his men just over a decade before the carvers set to work.
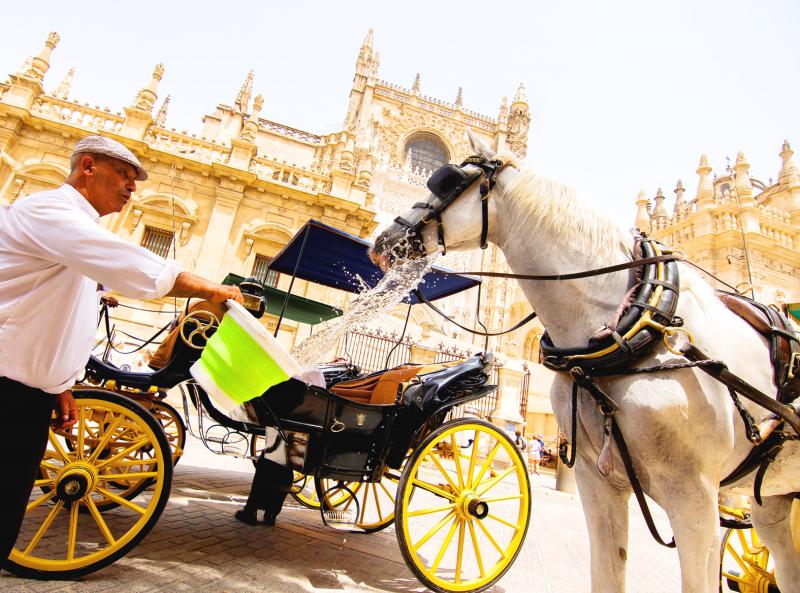

Photo: EPA-EFE
The plates, which are all too often obscured when the huge wooden doors of the sacristy are open, are the subject of a new book by a Spanish art historian who has spent the past 11 years trying to unpick the secrets and meanings of the cathedral’s stone buffet.
“People don’t really see the carvings because of the doors and because they’re too busy looking at the sacristy dome, but the carvings have been there for 500 years and have never been properly studied,” Juan Clemente Rodriguez Estevez said. “They’ve gone unnoticed apart from being seen as a bit of a novelty.”
The arch, which was carved between 1533 and 1535, provides what Rodriguez calls a “snapshot of a seminal moment.”
Its still-life carvings are chapters in the social, religious, economic and cultural history of Seville and Spain as a whole, he said.
The Americas were a fresh and lucrative discovery, the end of the seven-century Reconquista, which culminated in the expulsion of the Jews, was a mere four decades distant, and the Reformation was sweeping Europe.
Contemporary theologians and mystics focused on the importance of the eucharist and sought to portray communion as “a great feast to which everyone was invited,” said Rodriguez, who teaches at the University of Seville.
His book, The Universal Banquet: Art and Food in Renaissance Seville, examines how food was used to strengthen Catholic identity, employed as an image of the abundant joys of the afterlife, and even deployed as a bridge between Europe and the Americas.
Pork, unsurprisingly, features three times among the 68 plates, but olive oil — a staple of Andalucia since Roman times — is curiously absent. Rodriguez’s theory is that it might have been left out on the orders of Baltasar del Rio, a bishop who was instrumental in the arch’s creation.
Despite making a name for himself in the church in both Rome and Seville, Del Rio was from a family of conversos — Jewish converts to Catholicism — and his father was judged by the Inquisition at the end of the 15th century.
Mindful of his roots, the bishop might have chosen to exclude oil because it was used by Jews, who like Muslims — but unlike Catholics — did not fry their food in pig fat.
“Being a converso, Del Rio would have had to be very careful about the foods that were represented in the arch. They all needed to be really Catholic, but there are some foods that have a Jewish influence, such as the aubergines,” Rodriguez said. “Aubergines came to Europe through Islam, and came to be prized by Muslims and Jews alike. I think the presence of aubergines shows how normalized they had become by then.”
The bread at the center of the arch could also be a reference to Del Rio’s decision to found a brotherhood to help feed Seville’s poor.
“There was a terrible famine in 1521 and he ordered cheap wheat to be bought so that the poor would be provided with bread when wheat prices rose. If you look at the middle of the arch, you can see the loaves of bread,” Rodriguez said.
The peppers, which he had taken for strawberries until one of the botanists he consulted set him straight, are the only crop from the Americas.
“There aren’t more foods from there because it was still early days,” he said. “At that time, corn was mainly used as animal feed and the potato hadn’t arrived in Spain because the conquest of Peru took place in the 1530s, so the ships from Peru were only beginning to arrive.”
The traffic was not all one way.
The Augustinian friars who followed the Dominicans and the Franciscans to the Americas built three churches in Mexico in the 1560s whose doorways were decorated with plates of food, Rodriguez said.
The aim was to celebrate the eucharist and to help explain the importance of communion to a conquered people who were not familiar with bread and wine.
Rodriguez is delighted with the fruit of his more than a decade’s research, and keen to stress that he owes a huge debt to the botanists, zoologists and other experts he consulted on his physical and intellectual travels.
“I couldn’t have written the book if it wasn’t for the decades of work by researchers who have helped us understand food in a cultural context,” he said. “All I would have seen was a load of plates. When I started looking at the arch, I saw a window on to the 16th century, but I wasn’t quite sure what was on the other side.”

MONEY GRAB: People were rushing to collect bills scattered on the ground after the plane transporting money crashed, which an official said hindered rescue efforts A cargo plane carrying money on Friday crashed near Bolivia’s capital, damaging about a dozen vehicles on highway, scattering bills on the ground and leaving at least 15 people dead and others injured, an official said. Bolivian Minister of Defense Marcelo Salinas said the Hercules C-130 plane was transporting newly printed Bolivian currency when it “landed and veered off the runway” at an airport in El Alto, a city adjacent to La Paz, before ending up in a nearby field. Firefighters managed to put out the flames that engulfed the aircraft. Fire chief Pavel Tovar said at least 15 people died, but
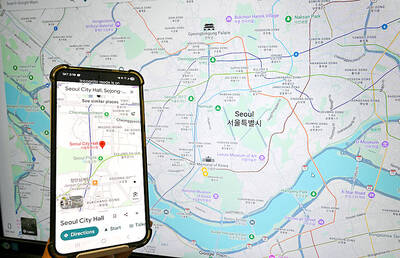
South Korea would soon no longer be one of the few countries where Google Maps does not work properly, after its security-conscious government reversed a two-decade stance to approve the export of high-precision map data to overseas servers. The approval was made “on the condition that strict security requirements are met,” the South Korean Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport said. Those conditions include blurring military and other sensitive security-related facilities, as well as restricting longitude and latitude coordinates for South Korean territory on products such as Google Maps and Google Earth, it said. The decision is expected to hurt Naver and Kakao

LIKE FATHER, LIKE DAUGHTER: By showing Ju-ae’s ability to handle a weapon, the photos ‘suggest she is indeed receiving training as a successor,’ an academic said North Korea on Saturday released a rare image of leader Kim Jong-un’s teenage daughter firing a rifle at a shooting range, adding to speculation that she is being groomed as his successor. Kim’s daughter, Ju-ae, has long been seen as the next in line to rule the secretive, nuclear-armed state, and took part in a string of recent high-profile outings, including last week’s military parade marking the closing stages of North Korea’s key party congress. Pyongyang’s official Korean Central News Agency (KCNA) released a photo of Ju-ae shooting a rifle at an outdoor shooting range, peering through a rifle scope

Australian Prime Minister Anthony Albanese yesterday said he did not take his security for granted, after he was evacuated from his residence for several hours following a bomb threat sent to a Chinese dance group. Albanese was evacuated from his Canberra residence late on Tuesday following the threat, and returned a few hours later after nothing suspicious was found. The bomb scare was among several e-mails threatening Albanese sent to a representative of Shen Yun, a classical Chinese dance troupe banned in China that is due to perform in Australia this month, a spokesperson for the group said in a statement. The e-mail