A circle of deep shafts has been discovered near the world heritage site of Stonehenge, to the astonishment of archeologists, who have described it as the largest prehistoric structure ever found in the UK.
Four thousand five hundred years ago, the Neolithic peoples who constructed Stonehenge, a masterpiece of engineering, also dug a series of shafts aligned to form a circle spanning 2km in diameter.
The structure appears to have been a boundary guiding people to a sacred area, because Durrington Walls, one of the UK’s largest henge monuments, is located precisely at its center.
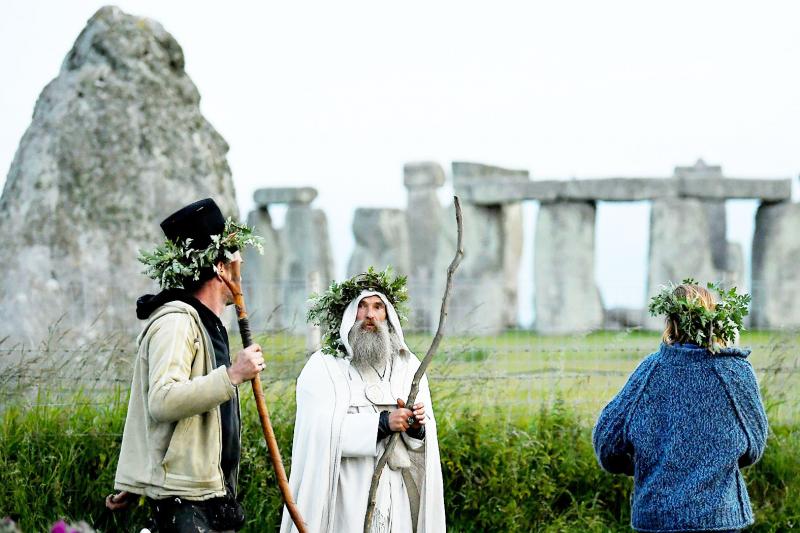

Photo: Reuters
The site is 3km northeast of Stonehenge on Salisbury Plain, near Amesbury, Wiltshire.
“This is an unprecedented find of major significance within the UK. Key researchers on Stonehenge and its landscape have been taken aback by the scale of the structure and the fact that it hadn’t been discovered until now so close to Stonehenge,” said Vincent Gaffney, a leading archeologist on the project.
The Durrington Shafts discovery, announced yesterday, is all the more extraordinary because it offers the first evidence that the early inhabitants of Britain, mainly farming communities, had developed a way to count. Constructing something of this size with such careful positioning of its features could only have been done by tracking hundreds of paces.
The shafts are vast, each more than 5m deep and 10m in diameter. About 20 have been found and there might have been more than 30. About 40 percent of the circle is no longer available for study as a consequence of modern development.
“The size of the shafts and circuit surrounding Durrington Walls is currently unique. It demonstrates the significance of Durrington Walls Henge, the complexity of the monumental structures within the Stonehenge landscape, and the capacity and desire of Neolithic communities to record their cosmological belief systems in ways, and at a scale, that we had never previously anticipated,” Gaffney said.
“I can’t emphasize enough the effort that would have gone in to digging such large shafts with tools of stone, wood and bone,” he added.
However, then these are the same people who also built Stonehenge, dragging bluestones to the site from southwest Wales about 241km away.
While Stonehenge was positioned in relation to the solstices, Gaffney said the newly discovered circular shape suggests a “huge cosmological statement and the need to inscribe it into the earth itself.”
“Stonehenge has a clear link to the seasons and the passage of time, through the summer solstice. But with the Durrington Shafts, it’s not the passing of time, but the bounding by a circle of shafts, which has cosmological significance,” he added.
The boundary might have guided people toward a sacred site within its center or warned against entering it.
As the area around Stonehenge is among the world’s most-studied archeological landscapes, the discovery is all the more unexpected.
Having filled naturally over millennia, the shafts — although enormous — had been dismissed as natural sinkholes and dew ponds. The latest technology — including geophysical prospection, ground-penetrating radar and magnetometry — showed them as geophysical anomalies and revealed their true significance.
“We are starting to see things we could never see through standard archeology, things we could not imagine,” Gaffney said.
Based at the University of Bradford, he is the co-principal investigator of the Stonehenge Hidden Landscape project, which has been surveying tens of kilometers of landscape across Salisbury Plain.
Archeologists are now joining the dots and seeing this massive pattern, he said.
Coring of the shafts has provided crucial radiocarbon dates to more than 4,500 years ago, making the boundary contemporary with Stonehenge and Durrington Walls.
The boundary also appears to have been laid out to include an earlier prehistoric monument, the Larkhill causewayed enclosure, built more than 1,500 years before the henge at Durrington.
Struck flint and unidentified bone fragments were recovered from the shafts, but archeologists can only speculate how those features were once used.
“What we’re seeing is two massive monuments with their territories. Other archeologists, including Michael Parker Pearson at University College London, have suggested that while Stonehenge, with its standing stones, was an area for the dead, Durrington, with its wooden structures, was for the living,” Gaffney said.
While numerous ancient civilizations had counting systems, the evidence lies primarily in texts in various forms that they left behind, he added.
The planning involved in contracting a prehistoric structure of this size must have involved a tally or counting system, he said.
Positioning each shaft would have involved pacing more than 800m from the henge outward.
The research has involved a consortium of archeologists, led by the University of Bradford, and including the universities of Birmingham and St Andrews, in an international collaboration with the Ludwig Boltzmann Institute for Archaeological Prospection and Virtual Archaeology at the University of Vienna.
Henry Chapman, professor of archeology at Birmingham University, described it as “an incredible new monument,” and Richard Bates, a geoscientist at St Andrews University, said it offered “an insight to the past that shows an even more complex society than we could ever imagine.”

MONEY GRAB: People were rushing to collect bills scattered on the ground after the plane transporting money crashed, which an official said hindered rescue efforts A cargo plane carrying money on Friday crashed near Bolivia’s capital, damaging about a dozen vehicles on highway, scattering bills on the ground and leaving at least 15 people dead and others injured, an official said. Bolivian Minister of Defense Marcelo Salinas said the Hercules C-130 plane was transporting newly printed Bolivian currency when it “landed and veered off the runway” at an airport in El Alto, a city adjacent to La Paz, before ending up in a nearby field. Firefighters managed to put out the flames that engulfed the aircraft. Fire chief Pavel Tovar said at least 15 people died, but
South Korea would soon no longer be one of the few countries where Google Maps does not work properly, after its security-conscious government reversed a two-decade stance to approve the export of high-precision map data to overseas servers. The approval was made “on the condition that strict security requirements are met,” the South Korean Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport said. Those conditions include blurring military and other sensitive security-related facilities, as well as restricting longitude and latitude coordinates for South Korean territory on products such as Google Maps and Google Earth, it said. The decision is expected to hurt Naver and Kakao

Australian Prime Minister Anthony Albanese yesterday said he did not take his security for granted, after he was evacuated from his residence for several hours following a bomb threat sent to a Chinese dance group. Albanese was evacuated from his Canberra residence late on Tuesday following the threat, and returned a few hours later after nothing suspicious was found. The bomb scare was among several e-mails threatening Albanese sent to a representative of Shen Yun, a classical Chinese dance troupe banned in China that is due to perform in Australia this month, a spokesperson for the group said in a statement. The e-mail

LIKE FATHER, LIKE DAUGHTER: By showing Ju-ae’s ability to handle a weapon, the photos ‘suggest she is indeed receiving training as a successor,’ an academic said North Korea on Saturday released a rare image of leader Kim Jong-un’s teenage daughter firing a rifle at a shooting range, adding to speculation that she is being groomed as his successor. Kim’s daughter, Ju-ae, has long been seen as the next in line to rule the secretive, nuclear-armed state, and took part in a string of recent high-profile outings, including last week’s military parade marking the closing stages of North Korea’s key party congress. Pyongyang’s official Korean Central News Agency (KCNA) released a photo of Ju-ae shooting a rifle at an outdoor shooting range, peering through a rifle scope