When 55-year-old Chiu was diagnosed with breast cancer last September, she was told that after undergoing surgery and chemotherapy, she could better battle a reoccurrence of the cancer by taking a new target-therapy drug called Herceptin. However, she could not afford to pay for the drug because it would cost her NT$1 million a year.
Chiu said her doctor, knowing she couldn’t afford the drug, suggested she take fewer doses, because “less is still better than none at all.”
“My doctor told me that some people are on a NT$500,000 plan, and there are a few people using the NT$350,000 plan,” said Chiu, a mother of two whose husband regularly needs dialysis to cleanse his kidneys.
“But even if I had that much money [NT$350,000], I would save it for living expenses,” she said.
Her two children have already started working, but they each have their own families and Chiu said she did not want to burden them with her “luxury drug.”
“I wouldn’t want to spend my entire savings [on Herceptin]. I still need it for my day-to-day expenses and for my family,” she said. “So when I heard how much the drug costs, I couldn’t even open my mouth to tell my family about it.”
“I didn’t have NT$350,000, and even if I did, I would save it for my family. If I could choose again, I would still save it for my family,” she said lowering her head, hairless from the chemotherapy, to look at her hands.
With less than NT$100,000 in her bank account, she told herself, “I’ll see where life takes me.”
But her cancer reappeared. Early this year, the cancer spread to her bones, and in July, to her liver.
Because the cancer was now so widespread, she finally qualified for coverage under the National Health Insurance (NHI) system for Herceptin treatment in August.
“I watched as the drug entered my body, drop by drop, and I thought, does this drug mean I still have hope, or does it mean I am nearing the end?” she said.
Chiu is one of the more than 6,000 women affected by breast cancer each year in Taiwan.
Breast cancer is the only form of cancer that has been medically proven to be effectively treated with target therapy drugs, said Wang Cheng-hsu (王正旭), president of the Hope Society for Cancer Care.
In target therapy, the chemotherapy targets the molecules that feed tumor growth and allows tumors to spread, which not only effectively prevents cancer recurrence, but also decreases the side effects of conventional chemotheraphy.
Large-scale clinical trials have proven that Herceptin can effectively reduce the recurrence of breast cancer by 36 percent to 52 percent, and reduce the mortality rate by 33 percent to 41 percent, said Chang Hsieh-kun, an attending physician of Chang Gung Memorial Hospital’s medical oncology division and internal medicine department.
But NHI only covers Herceptin for patients whose cancer has metastasized to other parts of the body.
In the UK, Germany, Canada and other developed countries, the governments fully cover the use of Herceptin both for early breast cancer treatment and metastatic breast cancer, while only metastatic breast cancer is reimbursed in Taiwan, Chang said.
“This means that a cancer patient has to wait until the cancer gets really bad in order to receive treatment,” Chang said.
While it might appear to be a greater burden on the NHI to fund target therapy drugs like Herceptin for early stage breast cancer, the contrary is true, he said.
“If we wait until the cancer spreads, the money [for Herceptin] still has to be spent eventually, but if we can stop cancer before it spreads, not only will this benefit cancer patients, but also decrease the social costs involved in caring for them,” he said.
“It’s actually cheaper [for the government] to pay for the drug in early stages of cancer,” Chang said.
Breast cancer is one cancer that is usually detected fairly early, which means patients have the chance to benefit from target therapy drugs before it’s too late, Wang said.
Chiu, like many other cancer patients, is angry that she had to wait until her cancer invaded other parts of her body to receive Herceptin treatment.
“If I was told that there is no cure for my sickness, then at least I could be reassured that this was a problem which could not be solved and I couldn’t do anything about it,” Chiu said.
“Instead I was told that there was a solution, but the solution was too expensive … How is that supposed to make me feel?” she said.
Many patients have to choose between using up their life savings to battle their cancer or giving up.
“Many patients say to me, ‘Should I be glad that my cancer hasn’t spread yet, or feel unlucky because the NHI doesn’t cover my drug?’” Wang said.
Even though cancer is the No. 1 cause of death in Taiwan, killing about 35,000 people annually, only 6 percent of the national health expenditure is spent on cancer treatment, the Bureau of National Health Insurance (BNHI) said in a 2004 report.
The Hope Society for Cancer Care has urged the bureau to speed up the approval process for cancer drugs.
It takes an average of 13.27 months for a drug to go from obtaining marketing approval to the bureau approving it for coverage, Wang said.
Some drugs can take four to six years.
“How can cancer patients wait that long?” Wang said.
BNHI spokesperson Huang Sui-fang (黃穗芬) said that a certain amount of time is needed for a drug to go through the approval process because the bureau must invite experts to meet and discuss whether the drug should be covered under the NHI program.

The manufacture of the remaining 28 M1A2T Abrams tanks Taiwan purchased from the US has recently been completed, and they are expected to be delivered within the next one to two months, a source said yesterday. The Ministry of National Defense is arranging cargo ships to transport the tanks to Taiwan as soon as possible, said the source, who is familiar with the matter. The estimated arrival time ranges from late this month to early next month, the source said. The 28 Abrams tanks make up the third and final batch of a total of 108 tanks, valued at about NT$40.5 billion

Two Taiwanese prosecutors were questioned by Chinese security personnel at their hotel during a trip to China’s Henan Province this month, the Mainland Affairs Council (MAC) said yesterday. The officers had personal information on the prosecutors, including “when they were assigned to their posts, their work locations and job titles,” MAC Deputy Minister and spokesman Liang Wen-chieh (梁文傑) said. On top of asking about their agencies and positions, the officers also questioned the prosecutors about the Cross-Strait Joint Crime-Fighting and Judicial Mutual Assistance Agreement, a pact that serves as the framework for Taiwan-China cooperation on combating crime and providing judicial assistance, Liang
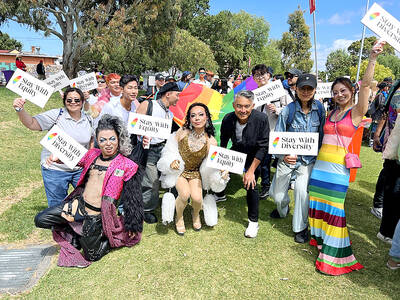
A group from the Taiwanese Designers in Australia association yesterday represented Taiwan at the Midsumma Pride March in Melbourne. The march, held in the St. Kilda suburb, is the city’s largest LGBTQIA+ parade and the flagship event of the annual Midsumma Festival. It attracted more than 45,000 spectators who supported the 400 groups and 10,000 marchers that participated this year, the association said. Taiwanese Designers said they organized a team to march for Taiwan this year, joining politicians, government agencies, professionals and community organizations in showing support for LGBTQIA+ people and diverse communities. As the first country in Asia to legalize same-sex

MOTIVES QUESTIONED The PLA considers Xi’s policies toward Taiwan to be driven by personal considerations rather than military assessment, the Epoch Times reports Chinese President Xi Jinping’s (習近平) latest purge of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army (PLA) leadership might have been prompted by the military’s opposition to plans of invading Taiwan, the Epoch Times said. The Chinese military opposes waging war against Taiwan by a large consensus, putting it at odds with Xi’s vision, the Falun Gong-affiliated daily said in a report on Thursday, citing anonymous sources with insight into the PLA’s inner workings. The opposition is not the opinion of a few generals, but a widely shared view among the PLA cadre, the Epoch Times cited them as saying. “Chinese forces know full well that