Iran has further increased its stockpile of uranium enriched to near weapons-grade levels, a confidential report on Monday by the UN’s nuclear watchdog said, the latest in Tehran’s attempts to steadily exert pressure on the international community.
Iran is seeking to have economic sanctions imposed over the nation’s controversial nuclear program lifted in exchange for slowing the program down. The program is under the guidance of Iranian Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, and that likely would not change in the wake of last week’s helicopter crash that killed Iran’s president and foreign minister.
The report by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) said that as of May 11, Iran had 142.1kg of uranium enriched up to 60 percent — an increase of 20.6kg since the last report by the UN agency in February.

Photo:AP
Uranium enriched at 60 percent purity is just a short, technical step away from weapons-grade levels of 90 percent.
By the IAEA’s definition, about 42kg of uranium enriched to 60 percent is the amount at which creating one atomic weapon is theoretically possible — if the material is enriched further, to 90 percent.
Iran’s overall stockpile of enriched uranium stood at 6,201.3kg, an increase of 675.8kg since the IAEA’s previous report.
Iran has maintained its nuclear program is for peaceful purposes only, but IAEA Director-General Rafael Mariano Grossi has previously warned that Tehran has enough uranium enriched to near-weapons-grade levels to make “several” nuclear bombs if it chose to do so.
He has acknowledged the UN agency cannot guarantee that none of Iran’s centrifuges might have been peeled away for clandestine enrichment.
Tensions have grown between Iran and the IAEA since 2018, when then-US president Donald Trump unilaterally withdrew the US from Tehran’s nuclear deal with world powers. Since then, Iran has abandoned all limits the deal put on its program and quickly stepped up enrichment.
Under the original nuclear deal, struck in 2015, Iran was allowed to enrich uranium only up to 3.67 percent purity, maintain a stockpile of about 300kg and use only very basic IR-1 centrifuges — machines that spin uranium gas at high speed for enrichment purposes.
Monday’s report also said that Tehran has not reconsidered its decision in September last year to bar IAEA inspectors from further monitoring its nuclear program, adding that it expects Iran “to do so in the context of the ongoing consultations between the agency and Iran.”
In the report, Grossi said he “deeply regrets” Iran’s decision to bar inspectors, and a reversal of that decision “remains essential to fully allow the agency to conduct its verification activities in Iran effectively.”
The deaths of then-Iranian president Ebrahim Raisi and then-minister of foreign affairs Hossein Amirabdollahian have triggered a pause in the IAEA’s talks with Tehran over improving cooperation, the report said.
Before the May 19 helicopter crash, Iran had agreed to hold technical negotiations with IAEA on May 20, following a visit by Grossi earlier in the month, but those meetings fell apart due to the crash.
Iran then sent a letter on Tuesday last week, saying its nuclear team wants to continue discussions in Tehran “on an appropriate date that will be mutually agreed upon,” the report said.
The report added that Iran has still not provided answers to the IAEA’s years-long investigation about the origin and current location of manmade uranium particles found at two locations — Varamin and Turquzabad — that Tehran has failed to declare as potential nuclear sites.

SECURITY: As China is ‘reshaping’ Hong Kong’s population, Taiwan must raise the eligibility threshold for applications from Hong Kongers, Chiu Chui-cheng said When Hong Kong and Macau citizens apply for residency in Taiwan, it would be under a new category that includes a “national security observation period,” Mainland Affairs Council (MAC) Minister Chiu Chui-cheng (邱垂正) said yesterday. President William Lai (賴清德) on March 13 announced 17 strategies to counter China’s aggression toward Taiwan, including incorporating national security considerations into the review process for residency applications from Hong Kong and Macau citizens. The situation in Hong Kong is constantly changing, Chiu said to media yesterday on the sidelines of the Taipei Technology Run hosted by the Taipei Neihu Technology Park Development Association. With

CARROT AND STICK: While unrelenting in its military threats, China attracted nearly 40,000 Taiwanese to over 400 business events last year Nearly 40,000 Taiwanese last year joined industry events in China, such as conferences and trade fairs, supported by the Chinese government, a study showed yesterday, as Beijing ramps up a charm offensive toward Taipei alongside military pressure. China has long taken a carrot-and-stick approach to Taiwan, threatening it with the prospect of military action while reaching out to those it believes are amenable to Beijing’s point of view. Taiwanese security officials are wary of what they see as Beijing’s influence campaigns to sway public opinion after Taipei and Beijing gradually resumed travel links halted by the COVID-19 pandemic, but the scale of
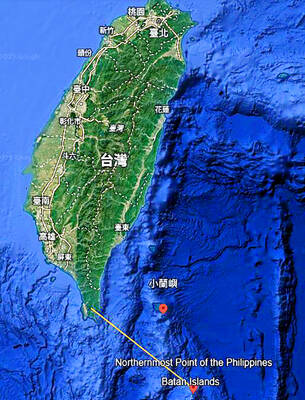
A US Marine Corps regiment equipped with Naval Strike Missiles (NSM) is set to participate in the upcoming Balikatan 25 exercise in the Luzon Strait, marking the system’s first-ever deployment in the Philippines. US and Philippine officials have separately confirmed that the Navy Marine Expeditionary Ship Interdiction System (NMESIS) — the mobile launch platform for the Naval Strike Missile — would take part in the joint exercise. The missiles are being deployed to “a strategic first island chain chokepoint” in the waters between Taiwan proper and the Philippines, US-based Naval News reported. “The Luzon Strait and Bashi Channel represent a critical access

Pope Francis is be laid to rest on Saturday after lying in state for three days in St Peter’s Basilica, where the faithful are expected to flock to pay their respects to history’s first Latin American pontiff. The cardinals met yesterday in the Vatican’s synod hall to chart the next steps before a conclave begins to choose Francis’ successor, as condolences poured in from around the world. According to current norms, the conclave must begin between May 5 and 10. The cardinals set the funeral for Saturday at 10am in St Peter’s Square, to be celebrated by the dean of the College