For more than a century, archaeologists have known that some of the stones at Stonehenge came from Wales and were transported — somehow — about 200km to the site of the Neolithic monument on Salisbury Plain.
Now, a “jaw-dropping” study has revealed that one of Stonehenge’s central megaliths is not Welsh at all — it is actually Scottish.
In a discovery described by one of the scientists involved as “genuinely shocking,” new analysis has found that the largest “bluestone” at Stonehenge was dragged or floated to the site from the very north-east corner of Scotland — a distance of at least about 750km.
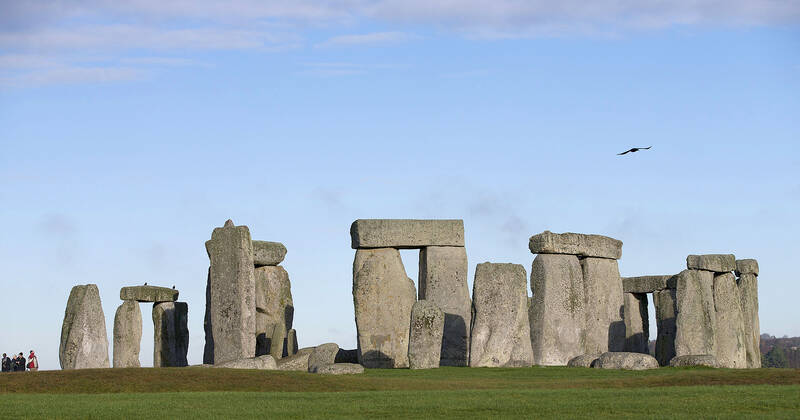

Photo: AP
The astonishing finding that the megalith, which is known as the “altar stone,” was transported by prehistoric people from at least as far as present day Inverness, and potentially from the Orkney islands, “doesn’t just alter what we think about Stonehenge, it alters what we think about the whole of the late Neolithic,” said Rob Ixer, an honorary senior research fellow at University College London (UCL) and one of the experts behind the study, which was published in Nature on Wednesday.
“It completely rewrites the relationships between the Neolithic populations of the whole of the British Isles,” he said. “The science is beautiful and it’s remarkable, and it’s going to be discussed for decades to come … It is jaw-dropping.”
The altar stone is not one of Stonehenge’s famous trilithons — the immense, lintel-topped sarsen stones, which originate from a mere 25km away, and which today form its outer circle. Instead, the huge sandstone block, 5 meters long and weighing 6 tonnes, lies flat and semi-buried at the heart of the monument, trapped under two fallen sarsens and barely visible to visitors.
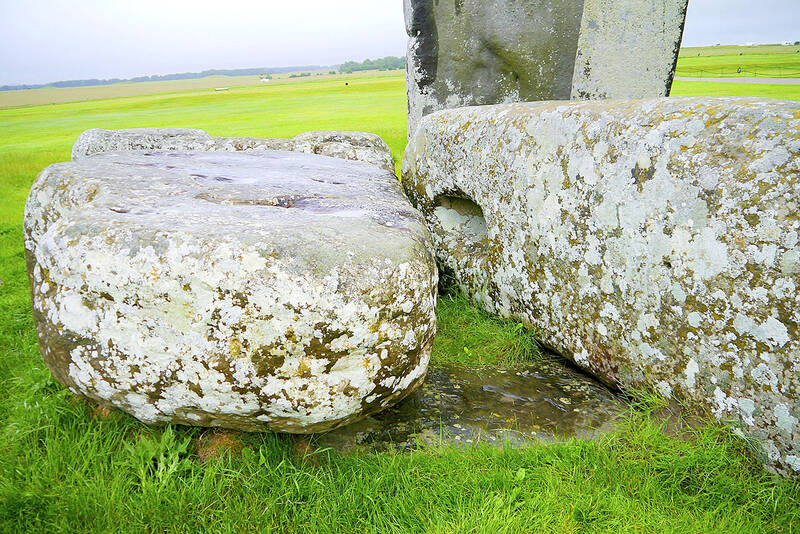

Photo: AP
Made of a sedimentary rock called old red sandstone, the altar stone is classed as a non-local bluestone and was long thought to have been brought from somewhere in Wales, just as a separate group of Stonehenge’s bluestones are now known to have been quarried in the Preseli Hills in Pembrokeshire.
The altar stone was an outlier, however, and research in recent years led archaeologists, including Ixer, to question whether its origins were Welsh at all.
The new study, which involved experts from Curtin University in Perth, Australia; the University of Adelaide; Aberystwyth University; and UCL, aimed to find out more by examining the stone’s chemical composition and the age of minerals within it.
Taken together, these give a characteristic “age fingerprint” to the sandstone, said Nick Pearce, a professor of geography and earth sciences at Aberystwyth who is another of the report’s co-authors.
“With that age fingerprint, you can match it to the same sort of rocks around the UK — and the match for the age fingerprint was a dead ringer for the Orcadian Basin in north-east Scotland,” he said. “It was completely unexpected to us.”
The finding may be astonishing, but the science is not controversial, said Pearce. “It’s very, very well-established science. It’s not something that people can look at say: ‘Oh no, that can’t be right.’”
The odds of the stone coming from elsewhere are “fractions of a percent,” he said.
For many, the biggest question will be one not explored in detail in the scientific paper: how on earth did Stonehenge’s builders transport the giant stone from Scotland to Wiltshire?
“Given major overland barriers en route from north-east Scotland to Salisbury Plain, marine transport is one feasible option,” said the lead author, Anthony Clarke, of Curtin University.
But the archaeologist and writer Mike Pitts, who was not involved in the research but whose work on Neolithic monuments includes the book How to Build Stonehenge, said he believed it was more likely the stone was dragged overland than floated by sea.
“If you put a stone on a boat out to sea, not only do you risk losing the stone — but also nobody can see it,” he said.
Instead, a land journey, perhaps taking many years, would engage people en route, with the stone “becoming increasingly precious … as it travels south”, he added.
Impossible as it may seem today, an overland journey “was easily within the reach of Neolithic technology.”
“[The study] is exciting and it’s so significant,” Pitts said. “It’s long been known that the bluestones come from Wales, but this identifies links with a quite different part of Britain, and significantly more distant from Stonehenge. So it suggests that the site was known not just to people in the south, but over a much wider area — and that opens suggestions for the whole way we think about Neolithic Britain.”
Jacques Poissant’s suffering stopped the day he asked his daughter if it would be “cowardly to ask to be helped to die.” The retired Canadian insurance adviser was 93, and “was wasting away” after a long battle with prostate cancer. “He no longer had any zest for life,” Josee Poissant said. Last year her mother made the same choice at 96 when she realized she would not be getting out of hospital. She died surrounded by her children and their partners listening to the music she loved. “She was at peace. She sang until she went to sleep.” Josee Poissant remembers it as a beautiful

March 2 to March 8 Gunfire rang out along the shore of the frontline island of Lieyu (烈嶼) on a foggy afternoon on March 7, 1987. By the time it was over, about 20 unarmed Vietnamese refugees — men, women, elderly and children — were dead. They were hastily buried, followed by decades of silence. Months later, opposition politicians and journalists tried to uncover what had happened, but conflicting accounts only deepened the confusion. One version suggested that government troops had mistakenly killed their own operatives attempting to return home from Vietnam. The military maintained that the

Before the last section of the round-the-island railway was electrified, one old blue train still chugged back and forth between Pingtung County’s Fangliao (枋寮) and Taitung (台東) stations once a day. It was so slow, was so hot (it had no air conditioning) and covered such a short distance, that the low fare still failed to attract many riders. This relic of the past was finally retired when the South Link Line was fully electrified on Dec. 23, 2020. A wave of nostalgia surrounded the termination of the Ordinary Train service, as these train carriages had been in use for decades

Lori Sepich smoked for years and sometimes skipped taking her blood pressure medicine. But she never thought she’d have a heart attack. The possibility “just wasn’t registering with me,” said the 64-year-old from Memphis, Tennessee, who suffered two of them 13 years apart. She’s far from alone. More than 60 million women in the US live with cardiovascular disease, which includes heart disease as well as stroke, heart failure and atrial fibrillation. And despite the myth that heart attacks mostly strike men, women are vulnerable too. Overall in the US, 1 in 5 women dies of cardiovascular disease each year, 37,000 of them