If at first you don’t succeed, it doesn’t matter that you tried.
That seems to be the message of a working paper prepared recently by a team at Harvard Business School. The study found that when it comes to venture-backed entrepreneurship, the only experience that counts is success.
“The data are absolutely clear,” says Paul Gompers, a professor of business administration at the school and one of the study’s authors.
“Does failure breed new knowledge or experience that can be leveraged into performance the second time around?” he asks.
In some cases, yes, but overall, he says: “We found there is no benefit in terms of performance.”
The study looked at several thousand venture-capital-backed companies from 1986 to 2003.
Gompers and his co-authors Anna Kovner, Josh Lerner and David Scharfstein found that first-time entrepreneurs who received venture capital funding had a 22 percent chance of success. Success was defined as going public or filing to go public; Gompers says the results were similar when using other measures, like acquisition or merger.
Already-successful entrepreneurs were far more likely to succeed again — their success rate for later venture-backed companies was 34 percent.
But entrepreneurs whose companies had been liquidated or gone bankrupt and tried again had almost the same follow-on success rate as first-timers: 23 percent.
In other words, trying and failing bought the entrepreneurs nothing — it was as if they never tried.
Or, as Gompers puts it: “For the average entrepreneur who failed, no learning happened.”
This finding flies in the face of conventional wisdom in Silicon Valley, where failure is regarded as an important opportunity for learning.
No less an authority than Gordon Moore, a co-founder of Intel, says that in the Valley: “You’re more valuable because of the experiences you’ve been through under failures.”
The basic idea behind the embrace of failure is this: Entrepreneurs who have built and then tried to save a company have seen what does and doesn’t work. This experience is viewed as excellent preparation for tough situations that might arise in a new venture.
“Given conventional wisdom, we were expecting to find much lower differences between failed and successful entrepreneurs,” Gompers says.
Not all failures are equal, says William Davidow, a founding partner in the venture capital firm Mohr Davidow Ventures. A company might fail because its timing was bad or because the entrepreneur was a poor manager. Davidow, who says he would have expected “a higher follow-on success rate for the failed entrepreneurs,” says that an entrepreneur who has failed in a previous venture “would get in the door to talk to me” about a new idea.
But, he adds, “I would want to know why that last deal failed, and what the person learned from it.”
Mark Pincus, founder and chief executive of Zynga Inc, a San Francisco company that develops online games that can be played on social networks like Facebook and MySpace, says his previous company, Tribe.net, “is for sure a failure from the investors’ standpoint.” Tribe.net was an early social networking company that Pincus says raised US$9 million in venture capital before it was liquidated in 2006.
Despite this outcome at his previous company, Pincus has raised US$39 million in venture capital for Zynga, which he says is profitable and has 8 million daily active users. In part, the support he received from venture capitalists reflects the fact that Pincus founded two successful companies before Tribe.net.
But Pincus also thinks that in general, venture capitalists expect entrepreneurs to take risks and both groups anticipate occasional failures.
“As an entrepreneur, you have to get used to failure,” he says. “It is just part of the path to success.”
Although the study found that in general, failures are not a particularly effective teacher of entrepreneurship, Gompers said that “absolutely some entrepreneurs can learn” from them.
“There are some talented entrepreneurs who fail on the first time, learn and then succeed,” he said. But, he added, “that is not the rule.”
Where does Silicon Valley’s deep-rooted belief in the value of failure come from? Gompers suggests what he calls “attribution bias” — people generalizing from anecdotal success-after-failure stories.
“There is a lot of industry folklore and myth out there,” he says. “We tried to bring data to bear on it.”

SECURITY: As China is ‘reshaping’ Hong Kong’s population, Taiwan must raise the eligibility threshold for applications from Hong Kongers, Chiu Chui-cheng said When Hong Kong and Macau citizens apply for residency in Taiwan, it would be under a new category that includes a “national security observation period,” Mainland Affairs Council (MAC) Minister Chiu Chui-cheng (邱垂正) said yesterday. President William Lai (賴清德) on March 13 announced 17 strategies to counter China’s aggression toward Taiwan, including incorporating national security considerations into the review process for residency applications from Hong Kong and Macau citizens. The situation in Hong Kong is constantly changing, Chiu said to media yesterday on the sidelines of the Taipei Technology Run hosted by the Taipei Neihu Technology Park Development Association. With

CARROT AND STICK: While unrelenting in its military threats, China attracted nearly 40,000 Taiwanese to over 400 business events last year Nearly 40,000 Taiwanese last year joined industry events in China, such as conferences and trade fairs, supported by the Chinese government, a study showed yesterday, as Beijing ramps up a charm offensive toward Taipei alongside military pressure. China has long taken a carrot-and-stick approach to Taiwan, threatening it with the prospect of military action while reaching out to those it believes are amenable to Beijing’s point of view. Taiwanese security officials are wary of what they see as Beijing’s influence campaigns to sway public opinion after Taipei and Beijing gradually resumed travel links halted by the COVID-19 pandemic, but the scale of
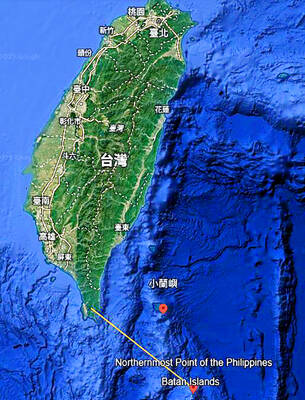
A US Marine Corps regiment equipped with Naval Strike Missiles (NSM) is set to participate in the upcoming Balikatan 25 exercise in the Luzon Strait, marking the system’s first-ever deployment in the Philippines. US and Philippine officials have separately confirmed that the Navy Marine Expeditionary Ship Interdiction System (NMESIS) — the mobile launch platform for the Naval Strike Missile — would take part in the joint exercise. The missiles are being deployed to “a strategic first island chain chokepoint” in the waters between Taiwan proper and the Philippines, US-based Naval News reported. “The Luzon Strait and Bashi Channel represent a critical access

Pope Francis is be laid to rest on Saturday after lying in state for three days in St Peter’s Basilica, where the faithful are expected to flock to pay their respects to history’s first Latin American pontiff. The cardinals met yesterday in the Vatican’s synod hall to chart the next steps before a conclave begins to choose Francis’ successor, as condolences poured in from around the world. According to current norms, the conclave must begin between May 5 and 10. The cardinals set the funeral for Saturday at 10am in St Peter’s Square, to be celebrated by the dean of the College