Wearing a white lab coat and with a gas mask within reach, Ole Jorgen Gronvold measures the humidity of an intriguing dark powder touted as the planet’s next “black gold.”
This “black gold” — a term that usually refers to oil — is actually good for the Earth.
In southeastern Norway lies Europe’s biggest plant for recycling used or defective electric vehicle batteries, turning them into a powder, or “black mass,” made up of nickel, manganese, cobalt, lithium and graphite.
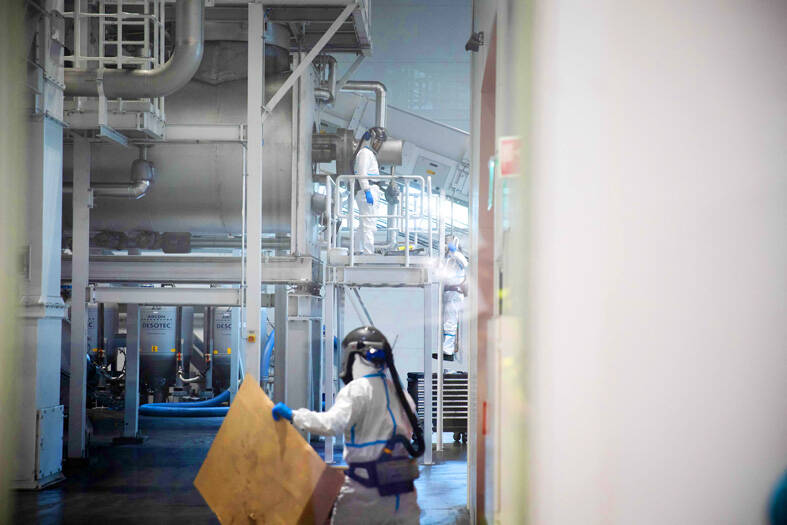

Photo: AFP
These so-called critical minerals — essential components in many clean energy technologies — are to be reused to make new batteries, key cogs in the transition to a decarbonized economy.
“The higher the quality of the components, the easier it is to use them for recycling,” said Gronvold, a laboratory technician at Hydrovolt AS, a joint venture between Norwegian aluminum giant Norsk Hydro ASA and Swedish electric battery maker Northvolt AB.
The Hydrovolt plant opened last year in the port city of Fredrikstad.
Within the next few months, the site is expected to be able to process 12,000 tonnes of lithium-ion battery packs per year, the equivalent of 25,000 electric vehicle batteries.
Industry leader Norway, where electricity is almost exclusively generated by renewable energies, is the uncontested world champion of zero-emission electric cars, with the latter accounting for more than 80 percent of new vehicle registrations.
Emptied of electricity, the imposing battery packs — they weigh half a tonne each — are methodically taken apart to recover up to 95 percent of the materials.
The aluminum is recycled by Norsk Hydro, while the “black mass” powder is sold to battery makers.
“This is the black gold that gives us life,” said Glenn Ostbye, the acting head of Hydrovolt, leading a tour of the plant clad in a safety helmet and goggles.
The “black gold” is touted as eco-friendly as it comes from the recycling process rather than being mined in faraway countries.
“Battery recycling is, in many ways, an alternative to mines. We have sort of built a mine above ground,” Hydrovolt director of operations Andreas Frydensvang said.
“A battery can be transformed into a new battery to infinity,” he said.
The recycling also helps boost Europe’s independence when it comes to critical minerals, with the COVID-19 pandemic and the war in Ukraine highlighting the continent’s problematic dependence on imported raw materials.
In Europe, “we have big markets for products, but we don’t actually have so much of our own resources,” Julia Poliscanova, head of electric mobility at the non-governmental organization Transport & Environment.
“Globally speaking, we’re not a mining superpower for copper, cobalt or nickel,” she said, adding that recycling waste was an obvious option.
“And you can recycle a lot quicker than you can start up a new mine,” she said.
Transport & Environment, a European clean transport campaign group, said that recycling old batteries could cover between at least 8 and 12 percent of Europe’s critical mineral needs in 2030, and between 12 and 14 percent in 2035.
The European Parliament recently adopted regulations aimed at making batteries more sustainable and more easily recyclable.
However, Europe also needs to stop exporting its precious “black mass” to third countries, primarily China and South Korea, and develop its own hydrometallurgic processing plants, Poliscanova said.
This other crucial link in the recycling chain, which makes it possible to extract the metals contained in the powder, is still low-scale in Europe, handled only by a few companies such as Revolt in Sweden and Eramet SA in France.
Government subsidies are also needed so that the many planned battery plants can see the light of day, creating an ecosystem favorable to recyclers, Poliscanova said.
The Fredrikstad plant is a pilot project and the blueprint is expected to be exported, with Hydrovolt planning a second site “in a year or two.”
“The most important thing for us is the degree of adoption of electric cars, so that there is a reservoir of end-of-life batteries,” Frydensvang said. “We’re therefore looking at countries like Germany, France and a little in the United States.”

Real estate agent and property developer JSL Construction & Development Co (愛山林) led the average compensation rankings among companies listed on the Taiwan Stock Exchange (TWSE) last year, while contract chipmaker Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co (TSMC, 台積電) finished 14th. JSL Construction paid its employees total average compensation of NT$4.78 million (US$159,701), down 13.5 percent from a year earlier, but still ahead of the most profitable listed tech giants, including TSMC, TWSE data showed. Last year, the average compensation (which includes salary, overtime, bonuses and allowances) paid by TSMC rose 21.6 percent to reach about NT$3.33 million, lifting its ranking by 10 notches

SEASONAL WEAKNESS: The combined revenue of the top 10 foundries fell 5.4%, but rush orders and China’s subsidies partially offset slowing demand Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co (TSMC, 台積電) further solidified its dominance in the global wafer foundry business in the first quarter of this year, remaining far ahead of its closest rival, Samsung Electronics Co, TrendForce Corp (集邦科技) said yesterday. TSMC posted US$25.52 billion in sales in the January-to-March period, down 5 percent from the previous quarter, but its market share rose from 67.1 percent the previous quarter to 67.6 percent, TrendForce said in a report. While smartphone-related wafer shipments declined in the first quarter due to seasonal factors, solid demand for artificial intelligence (AI) and high-performance computing (HPC) devices and urgent TV-related orders
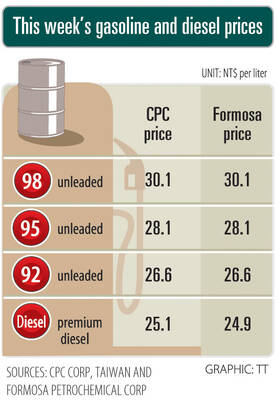
Prices of gasoline and diesel products at domestic fuel stations are this week to rise NT$0.2 and NT$0.3 per liter respectively, after international crude oil prices increased last week, CPC Corp, Taiwan (台灣中油) and Formosa Petrochemical Corp (台塑石化) said yesterday. International crude oil prices last week snapped a two-week losing streak as the geopolitical situation between Russia and Ukraine turned increasingly tense, CPC said in a statement. News that some oil production facilities in Alberta, Canada, were shut down due to wildfires and that US-Iran nuclear talks made no progress also helped push oil prices to a significant weekly gain, Formosa said

MINERAL DIPLOMACY: The Chinese commerce ministry said it approved applications for the export of rare earths in a move that could help ease US-China trade tensions Chinese Vice Premier He Lifeng (何立峰) is today to meet a US delegation for talks in the UK, Beijing announced on Saturday amid a fragile truce in the trade dispute between the two powers. He is to visit the UK from yesterday to Friday at the invitation of the British government, the Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs said in a statement. He and US representatives are to cochair the first meeting of the US-China economic and trade consultation mechanism, it said. US President Donald Trump on Friday announced that a new round of trade talks with China would start in London beginning today,