Kneeling before a chalk star outside his tumbledown house, an old man performed a ritual to rid himself of evil spirits — which many superstitious Turks believe exist.
Perched behind the camera, director Metin Kuru tried to encourage the actor to convey the sheer agony of being possessed by a genie.
However, there would not be many takes, because Kuru needs to finish his film fast to feed Turkey’s voracious appetite for low-budget horror flicks, with a new supernatural chiller released every week.
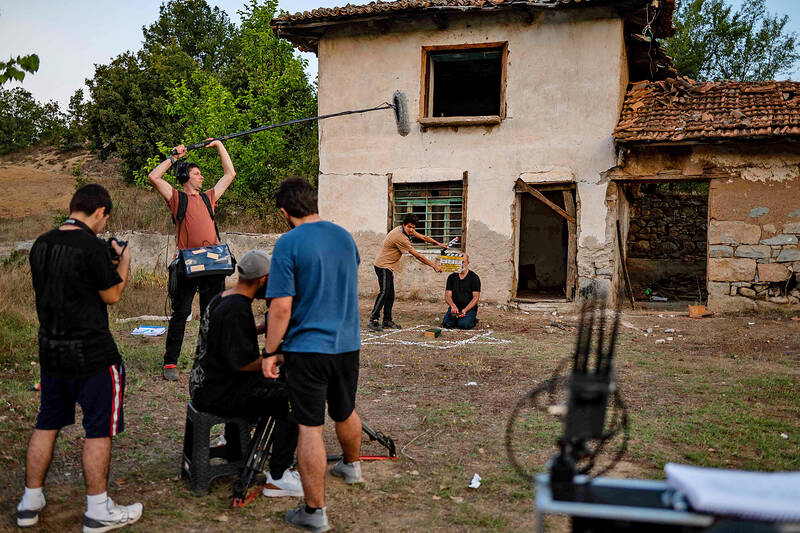
Photo: AFP
“At the end of the day, I try to produce films with as few technical issues as possible,” Kuru said between scenes of Muhr-u Musallat 2 — Yasak Dugun (Sealed Invasion 2 — Forbidden Wedding).
Filming many of the scenes in the dark helps.
“The color palette of horror movies is not as varied, which allows filmmakers to shoot with cheaper cameras, less light and smaller crews,” Kuru said.
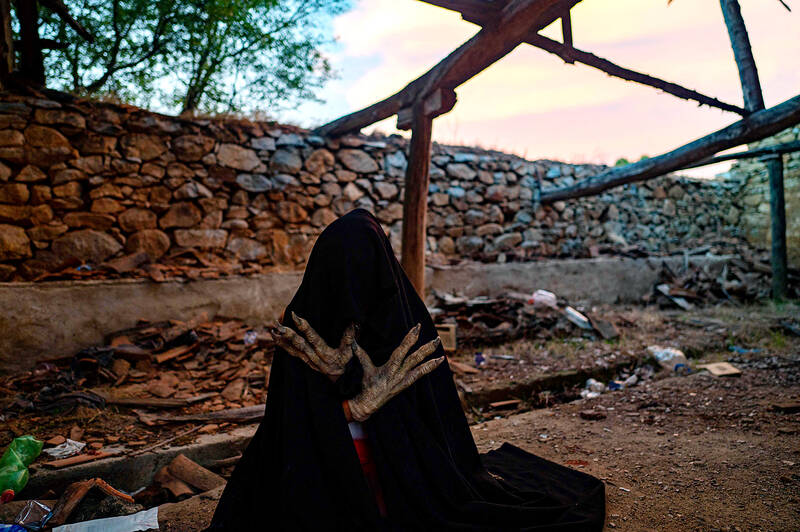

Photo: AFP
This year alone, 60 new homegrown horror movies are to hit screens in Turkey, where demand for entertainment has not waned despite — or maybe because of — the economic crises gripping the country.
Few horror films were made until the 1990s, their growth coinciding with the rise of Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan’s Islamic-rooted Justice and Development Party.
Its coming to power in 2002 after decades of more secular governments helped let the genie out of the bottle, with more religious Turks — and plenty of secular ones — lapping up superstitious tales that were previously frowned on.

Photo: AFP
Film critic Gizem Simsek Kaya said there might be a link between the horror boom and broader social shifts in Turkey.
“The drive to brush aside superstition and come closer to science [of modern Turkey’s founders] began to regress in the late 1990s,” Kaya said.
Religious-themed horror movies became popular with Buyu (The Spell) in 2004, and reached an even bigger audience with the launch of the big-budget Dabbe series in 2006.
Director Hasan Karacadag made six Dabbe films, the last in 2015, breaking Turkish box office records.
Other blockbusters followed from the equally popular Siccin franchise from director Alper Mestci.
“Some Islamic tendencies and the rising tide of conservatism play a role in this,” Kaya said.
Turkish horror films mostly revolve around jinns or genies — potentially mischievous spirits that are a part of Islamic myths and theology.
This can be tricky for makeup artists like Yesim Vatansever.
Not only are genies supposed to be invisible, but there are also more than 70 types, making depicting them a challenge.
“It would be much easier to visualize, say, an alien,” Vatansever said.
Kaya, who teaches at Istanbul Kultur University, said that vampire movies do not work in Turkey because of religious sensitivities.
The idea of the living dead “in Islam is equal to committing shirk,” or the sin of idolatry, she said.
It might not have helped either that the inspiration for Dracula, the medieval Romanian ruler Vlad the Impaler, got his gory nickname from impaling Turks.
Ghosts and zombies also have issues.
“In Islam, the dead body is only seen covered in a shroud. When you try to resurrect something, it has to remove the shroud and walk naked,” Kaya said.
In one movie, a resurrected man who threw off his shroud put on some trousers he found on the street, she said.
“The moment he did that, the movie turned into a comedy,” she said.
These limitations can make Turkish horror movies look dreadful, she said.
“They are shot in a few days, the equipment is poor, and the film can come out blurry,” she said.
“I had never seen the words ‘error code’ accidentally appear in a movie” until it turned up in a Turkish horror flick this year, she said.
Screenwriter Ozlem Bolukbasi conceded that the films were not cinematic masterpieces.
“The budgets and production values are not high,” she said.
“But do we still draw audiences? Yes, we do,” she added.
Back on set with the old man possessed by a jinn, local villagers had flocked to see the filming.
“It’s fun. The whole town is here at the moment,” said Huseyin Aydemir, who runs a local restaurant in Buyukorhan, near Bursa in northwestern Turkey. “A cemetery scene was shot here two days ago. The locals went to the scene hours before the film crew.”

Sweeping policy changes under US Secretary of Health and Human Services Robert F. Kennedy Jr are having a chilling effect on vaccine makers as anti-vaccine rhetoric has turned into concrete changes in inoculation schedules and recommendations, investors and executives said. The administration of US President Donald Trump has in the past year upended vaccine recommendations, with the country last month ending its longstanding guidance that all children receive inoculations against flu, hepatitis A and other diseases. The unprecedented changes have led to diminished vaccine usage, hurt the investment case for some biotechs, and created a drag that would likely dent revenues and

Macronix International Co (旺宏), the world’s biggest NOR flash memory supplier, yesterday said it would spend NT$22 billion (US$699.1 million) on capacity expansion this year to increase its production of mid-to-low-density memory chips as the world’s major memorychip suppliers are phasing out the market. The company said its planned capital expenditures are about 11 times higher than the NT$1.8 billion it spent on new facilities and equipment last year. A majority of this year’s outlay would be allocated to step up capacity of multi-level cell (MLC) NAND flash memory chips, which are used in embedded multimedia cards (eMMC), a managed

CULPRITS: Factors that affected the slip included falling global crude oil prices, wait-and-see consumer attitudes due to US tariffs and a different Lunar New Year holiday schedule Taiwan’s retail sales ended a nine-year growth streak last year, slipping 0.2 percent from a year earlier as uncertainty over US tariff policies affected demand for durable goods, data released on Friday by the Ministry of Economic Affairs showed. Last year’s retail sales totaled NT$4.84 trillion (US$153.27 billion), down about NT$9.5 billion, or 0.2 percent, from 2024. Despite the decline, the figure was still the second-highest annual sales total on record. Ministry statistics department deputy head Chen Yu-fang (陳玉芳) said sales of cars, motorcycles and related products, which accounted for 17.4 percent of total retail rales last year, fell NT$68.1 billion, or

In the wake of strong global demand for AI applications, Taiwan’s export-oriented economy accelerated with the composite index of economic indicators flashing the first “red” light in December for one year, indicating the economy is in booming mode, the National Development Council (NDC) said yesterday. Moreover, the index of leading indicators, which gauges the potential state of the economy over the next six months, also moved higher in December amid growing optimism over the outlook, the NDC said. In December, the index of economic indicators rose one point from a month earlier to 38, at the lower end of the “red” light.