Taiwan’s business climate monitor last month signaled green for a third consecutive month, indicating steady growth, after global inflation and China’s COVID-19 controls had weighed on earlier readings, the National Development Council said yesterday.
The total score of nine constituent readings held steady at 28.
However, challenges loom ahead for exports, which have fared well so far, council research director Wu Ming-huei (吳明蕙) said.
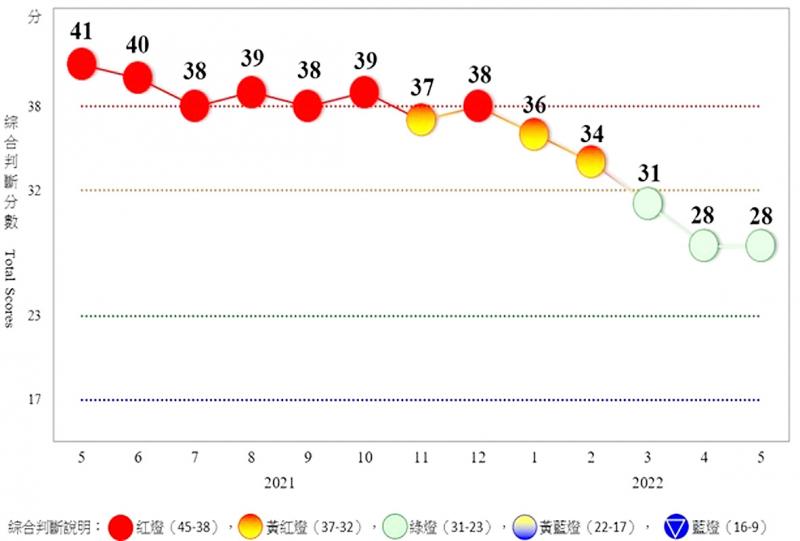
Photo courtesy of the National Development Council
The council uses a five-color system to depict the nation’s economic state, with “green” indicating steady growth, “red” suggesting a boom and “blue” signaling a recession. Dual colors indicate a shift to a stronger or weaker state.
Exports account for 60 to 70 percent of the nation’s GDP, as Taiwan is home to the world’s largest suppliers of chips used in smartphones, laptops, autos, and high-performance computing and Internet of Things applications.
Critical economic barometers such as exports, industrial production and export orders have shown signs of a slowdown, but remain in expansion territory, Wu said.
China’s virus controls have disrupted supply chain flows while the Ukraine war has been pushing up international energy and raw material prices — incidents over which Taiwanese firms do not have any control, he said.
Rising inflationary pressures worldwide have taken a toll on global demand for smartphones, laptops, TVs and vehicles.
Domestic demand, on the other hand, might soon come out of the woods, as local semiconductor companies press ahead with capacity expansion plans, which would shore up private investment, Wu said.
The government’s travel subsidies are to take effect next month, by which time the number of locally transmitted COVID-19 cases is expected to have fallen significantly, allowing business activity to recover, he said.
The index of leading indicators, which seeks to project the economic scene in the coming six months, fell 0.7 percent to 99.03, the council said, as almost all sub-indices fell, with the exception of the reading on new construction floor spaces.
The index of coincident indicators, which reflects the current economic situation, shrank 0.56 percent to 100.64, dragged by almost all components except for the gauge on exports, it said.
The gauge on retail sales last month rose from a year earlier, because the government did not tighten social distancing measures this year, as it seeks to live with COVID-19, similar to other countries, Wu said.

In Italy’s storied gold-making hubs, jewelers are reworking their designs to trim gold content as they race to blunt the effect of record prices and appeal to shoppers watching their budgets. Gold prices hit a record high on Thursday, surging near US$5,600 an ounce, more than double a year ago as geopolitical concerns and jitters over trade pushed investors toward the safe-haven asset. The rally is putting undue pressure on small artisans as they face mounting demands from customers, including international brands, to produce cheaper items, from signature pieces to wedding rings, according to interviews with four independent jewelers in Italy’s main

Japanese Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi has talked up the benefits of a weaker yen in a campaign speech, adopting a tone at odds with her finance ministry, which has refused to rule out any options to counter excessive foreign exchange volatility. Takaichi later softened her stance, saying she did not have a preference for the yen’s direction. “People say the weak yen is bad right now, but for export industries, it’s a major opportunity,” Takaichi said on Saturday at a rally for Liberal Democratic Party candidate Daishiro Yamagiwa in Kanagawa Prefecture ahead of a snap election on Sunday. “Whether it’s selling food or

CONCERNS: Tech companies investing in AI businesses that purchase their products have raised questions among investors that they are artificially propping up demand Nvidia Corp chief executive officer Jensen Huang (黃仁勳) on Saturday said that the company would be participating in OpenAI’s latest funding round, describing it as potentially “the largest investment we’ve ever made.” “We will invest a great deal of money,” Huang told reporters while visiting Taipei. “I believe in OpenAI. The work that they do is incredible. They’re one of the most consequential companies of our time.” Huang did not say exactly how much Nvidia might contribute, but described the investment as “huge.” “Let Sam announce how much he’s going to raise — it’s for him to decide,” Huang said, referring to OpenAI

The global server market is expected to grow 12.8 percent annually this year, with artificial intelligence (AI) servers projected to account for 16.5 percent, driven by continued investment in AI infrastructure by major cloud service providers (CSPs), market researcher TrendForce Corp (集邦科技) said yesterday. Global AI server shipments this year are expected to increase 28 percent year-on-year to more than 2.7 million units, driven by sustained demand from CSPs and government sovereign cloud projects, TrendForce analyst Frank Kung (龔明德) told the Taipei Times. Demand for GPU-based AI servers, including Nvidia Corp’s GB and Vera Rubin rack systems, is expected to remain high,