A new study by researchers at the US National Defense University argues that Washington should defend Taiwan’s sea and air space and all of the first island chain nations in the case of a clash with China.
The strategy, known as “Offshore Control,” is described as an effective and affordable approach to a conventional conflict with China.
Published this week in National Interest magazine, it is written by distinguished research fellow T.X. Hammes and director of the Institute for National Strategic Studies R.D. Hooker.
The plan can assure US allies that Washington has the “will and capability” to prevail in a military confrontation and that their goal is to convince China that great-power rivalry is a poor choice, they say.
“Offshore Control establishes concentric rings that deny China the use of the sea inside the first island chain, defend the sea and air space of the first island chain nations, and dominate the air and maritime space outside the island chain,” the study says.
“Offshore Control does not strike into China but takes advantage of geography to block China’s key imports and exports and thus severely weaken its economy,” it says.
The study emphasizes that no kinetic operations would penetrate Chinese airspace and would thus reduce the possibility of nuclear escalation and make it easier to end the conflict.
This approach would exploit China’s military weaknesses, which increase exponentially beyond the first island chair that runs through the Japanese Archipelago, the Ryukyu Islands, Taiwan, the northern Philippines and Borneo to the Malay Peninsula, the study says.
“Allied naval and air forces attempting to operate near or on the Chinese territory face daunting odds,” it says.
“In contrast, allied forces fighting as part of an integrated air-sea-land defense of the first island chain gain major tactical advantages over Chinese forces,” it says. “Outside that arc, Chinese capabilities dwindle markedly.”
While the US could not stop all sea traffic in the zone, it could prevent the passage of large cargo ships and large tankers, severely disrupting China’s economy, according to the study.
As an integral part of denial, any Chinese military assets outside the Chinese 19km limit would be subject to attack.
“Numerous small islands from Japan to Taiwan to Luzon and on to the Straits of Malacca provide dispersed land-basing options for air and sea defense of the apparent gaps in the first island chain,” the study says.
“Since Offshore Control will rely heavily on land-based air and sea defenses, to include mine and countermine capability, we can encourage potential partners to invest in these capabilities and exercise together regularly in peacetime,” it says.
Hammes and Hooker said that the US would not request Taiwan or other nations to allow the use of their bases to attack China.
“The strategy will only ask nations to allow the presence of US defensive systems to help defend that nation’s air, sea and land space,” the study says.
“While such a concentric blockade campaign will require a layered effort from the straits to China’s coast, it will mostly be fought at a great distance from China,” the study says. “The only ways for China to break the blockade are to build a global sea-control navy or develop alternative land routes.”
“A sea-control navy will require investing hundred of billions of dollars over decades,” it says. “Alternative overland routes simply cannot move the 9.74 billion tons [8.8 billion metric tonnes] of goods China exported by sea in 2012.”
The authors believe a major conflict with China is “highly unlikely,” but if it should happen they say that the concept of “Air-Sea Battle” which has been strongly promoted would be both provocative and ineffective.
Under the “Air-Sea Battle” plan, US forces would attack Chinese surveillance systems and China’s integrated air defense system and bomb Chinese land-based ballistic and antiship missile systems.
Replacing the “Air-Sea Battle” plan with “Offshore Control” might convince Beijing that great-power cooperation can bring maximum benefit to China, the US and the rest of the world, the study says.

A preclearance service to facilitate entry for people traveling to select airports in Japan would be available from Thursday next week to Feb. 25 at Taiwan Taoyuan International Airport, Taoyuan International Airport Corp (TIAC) said on Tuesday. The service was first made available to Taiwanese travelers throughout the winter vacation of 2024 and during the Lunar New Year holiday. In addition to flights to the Japanese cities of Hakodate, Asahikawa, Akita, Sendai, Niigata, Okayama, Takamatsu, Kumamoto and Kagoshima, the service would be available to travelers to Kobe and Oita. The service can be accessed by passengers of 15 flight routes operated by
Chinese spouse and influencer Guan Guan’s (關關) residency permit has been revoked for repeatedly posting pro-China videos that threaten national security, the National Immigration Agency confirmed today. Guan Guan has said many controversial statements in her videos posted to Douyin (抖音), including “the red flag will soon be painted all over Taiwan” and “Taiwan is an inseparable part of China,” and expressing hope for expedited reunification. The agency last year received multiple reports alleging that Guan Guan had advocated for armed reunification. After verifying the reports, the agency last month issued a notice requiring her to appear and explain her actions. Guan

GIVE AND TAKE: Blood demand continues to rise each year, while fewer young donors are available due to the nation’s falling birthrate, a doctor said Blood donors can redeem points earned from donations to obtain limited edition Formosan black bear travel mugs, the Kaohsiung Blood Center said yesterday, as it announced a goal of stocking 20,000 units of blood prior to the Lunar New Year. The last month of the lunar year is National Blood Donation Month, when local centers seek to stockpile blood for use during the Lunar New Year holiday. The blood demand in southern Taiwan — including Tainan and Kaohsiung, as well as Chiayi, Pingtung, Penghu and Taitung counties — is about 2,000 units per day, the center said. The donation campaign aims to boost
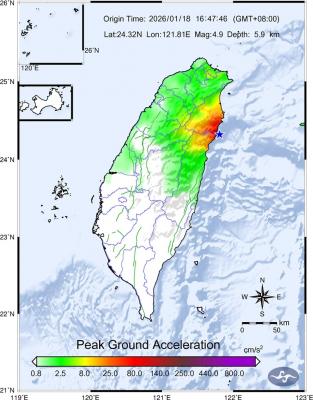
The Central Weather Administration (CWA) said a magnitude 4.9 earthquake that struck off the coast of eastern Taiwan yesterday was an independent event and part of a stress-adjustment process. The earthquake occurred at 4:47pm, with its epicenter at sea about 45.4km south of Yilan County Hall at a depth of 5.9km, the CWA said. The quake's intensity, which gauges the actual effects of a temblor, was highest in several townships in Yilan and neighboring Hualien County, where it measured 4 on Taiwan's seven-tier intensity scale, the CWA said. Lin Po-yu (林柏佑), a division chief at the CWA's Seismological Center, told a news conference