Hidden in a maze of factories in the heart of this northeastern Chinese port city is the house Gunther von Hagens built -- and, for many, a place where nightmares are created.
Inside von Hagens' sprawling, well-guarded compound, behind a leaning metal fence pocked with holes, are more than 800 human beings -- 200 of his staffers and 645 dead bodies in steel cases from almost a dozen nations.

PHOTO: AP
The anatomist, whose exhibits of preserved human corpses have riled religious leaders in Europe and attracted the curious and the outraged across the world, set up shop here three years ago to process bodies for his shows.
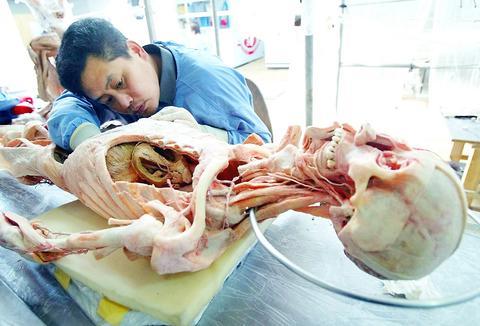
PHOTO: AP
Last month, media reports from von Hagens' native Germany asserted that at least two of the corpses, both Chinese, had bullet holes in their skulls -- the method China uses for execution. It's a charge that von Hagens rejects vehemently, saying all his specimens were donated by people who signed releases.
``I absolutely prohibit and do not accept death penalty bodies,'' von Hagens, a tall, thin man in a fedora, said this week during a rare tour of his Dalian facility.

PHOTO: AP
But, he added, ``Many things can happen. ... I cannot exclude that [possibility].''

PHOTO: AP
Von Hagens launched his Body Worlds exhibits in 1997 and has shown them to nearly 14 million people from Japan and South Korea to Britain and Germany. Shows are running now in Frankfurt, Germany, and Singapore.
The displays feature healthy and diseased body parts as well as skinned, whole corpses in assorted poses -- a rider atop a horse, a pregnant woman reclining -- that show off the preservation technique von Hagens developed in 1977.
Dubbed ``plastination,'' the process replaces bodily fluids and fat with epoxy and silicone, making the bodies durable for exhibition and study.
Though authorities in Dalian have made no public allegations against the operation, it has drawn the attention of the Chinese media. ``Does the corpse factory have a trade secret?'' asked theBeijing Morning Post.
``Investigation into the secrets of Dalian's corpse processing plant,'' read another in theBeijing Evening News.
Li Renzhen, a Dalian taxi driver, said, ``I don't know what they are doing in there. But according to Chinese tradition, we should show respect for dead bodies.''
He shook his head.
``If they are used to make money, it's unthinkable.''
The German weekly Der Spiegel said in January that von Hagens ran a ``shabby business,'' buying cheap corpses -- including executed Chinese -- and marketing them for profit. A British newspaper, The Daily Telegraph, said German lawyers also were investigating whether von Hagens used executed Chinese
prisoners.
The allegations echoed charges from 2001, when von Hagens was accused of using a Russian prisoner's body. Von Hagens said that corpse was a German who donated his body.
Von Hagens said his staff searched their cache of bodies after the Der Spiegel article appeared and found seven with ``different kinds of head injuries.'' He said he planned to incinerate those to be certain execution victims are not used.
``There is no case opened against me,'' said von Hagens, 59. ``Nobody accuses me ... of doing anything criminal, anything against the law.''
However, prosecutors in Heidelberg, Germany, say they are pursuing allegations that von Hagens used bodies of Chinese prisoners to determine whether they have grounds to launch a full-scale investigation into possible charges of human rights violations for using corpses of people who had not given consent while still living.
``We are looking into it right now,'' said Elke O'Donoghue, spokeswoman for prosecutors in Heidelberg. She could not say how long the process would take.
Critics, including the Lutheran and Roman Catholic churches, have also denounced von Hagens' work as disrespectful to the dead. He says he simply helps people understand their bodies.
In Frankfurt, authorities have warned parents not to allow children younger than 14 to view the exhibit, which they said could ``shock and frighten.''
At a London show, a visitor took a hammer to one of the bodies -- a man holding a liver -- while another threw a blanket over the corpse of a pregnant woman, saying he could not bear to look at the fetus.
``It's a very emotional topic,'' acknowledged von Hagens, dubbed ``Dr. Frankenstein'' in November after performing Britain's first public autopsy in more than 170 years. Even in Dalian, one of his employees jokingly referred to him as ``Dr. Death.''
In one airy room, skinned corpses wrapped in white cloth and covered in plastic lay stretched out on tables, surrounded by ``dissectors'' -- many of them medical students. They hunched over the bodies, picking out fat and tissue with tweezers. In another area, bodies hung ``curing'' with gas, light or heat.
Each body requires up to 1,500 hours of work to prepare, von Hagens says. In their final plasticized state, the corpses are rubbery to the touch with a crystalline finish -- the color of raw pork.
The room where the bodies are assembled into position is large and sunny and filled with models in different stages of production -- a snowboarder here, an ice-skater there. In one area, a dead man poses in an homage to Rodin's The Thinker.
Von Hagens, too, is thinking these days -- about how to quiet his critics without giving up his life's endeavor.
``I'm sure I will survive this storm in the water glass as I have survived so many before,'' von Hagens said. ``I touch here a taboo, which is our body, and nothing is so near as our body is to us.''
He adds, ``I know that I am innocent. This gives me a good feeling and good sleep every day.''

Taiwan has next to no political engagement in Myanmar, either with the ruling military junta nor the dozens of armed groups who’ve in the last five years taken over around two-thirds of the nation’s territory in a sprawling, patchwork civil war. But early last month, the leader of one relatively minor Burmese revolutionary faction, General Nerdah Bomya, who is also an alleged war criminal, made a low key visit to Taipei, where he met with a member of President William Lai’s (賴清德) staff, a retired Taiwanese military official and several academics. “I feel like Taiwan is a good example of

March 2 to March 8 Gunfire rang out along the shore of the frontline island of Lieyu (烈嶼) on a foggy afternoon on March 7, 1987. By the time it was over, about 20 unarmed Vietnamese refugees — men, women, elderly and children — were dead. They were hastily buried, followed by decades of silence. Months later, opposition politicians and journalists tried to uncover what had happened, but conflicting accounts only deepened the confusion. One version suggested that government troops had mistakenly killed their own operatives attempting to return home from Vietnam. The military maintained that the

“M yeolgong jajangmyeon (anti-communism zhajiangmian, 滅共炸醬麵), let’s all shout together — myeolgong!” a chef at a Chinese restaurant in Dongtan, located about 35km south of Seoul, South Korea, calls out before serving a bowl of Korean-style zhajiangmian —black bean noodles. Diners repeat the phrase before tucking in. This political-themed restaurant, named Myeolgong Banjeom (滅共飯館, “anti-communism restaurant”), is operated by a single person and does not take reservations; therefore long queues form regularly outside, and most customers appear sympathetic to its political theme. Photos of conservative public figures hang on the walls, alongside political slogans and poems written in Chinese characters; South

Taipei Mayor Chiang Wan-an (蔣萬安) announced last week a city policy to get businesses to reduce working hours to seven hours per day for employees with children 12 and under at home. The city promised to subsidize 80 percent of the employees’ wage loss. Taipei can do this, since the Celestial Dragon Kingdom (天龍國), as it is sardonically known to the denizens of Taiwan’s less fortunate regions, has an outsize grip on the government budget. Like most subsidies, this will likely have little effect on Taiwan’s catastrophic birth rates, though it may be a relief to the shrinking number of