Rapid wage increases are threatening China’s competitiveness, but improved productivity and other advantages mean it will continue to attract investors, analysts say.
Labor costs in China would match those of the US within four years, catching up with eurozone countries in five years and with Japan in seven, the French bank Natixis said in a study last month.
China “will soon no longer be a competitive place for production given the strong rise in the cost of production,” the bank said.

Photo: AFP
It is a view backed by the respected Boston Consulting Group (BCG), which said in a study in August last year that by around 2015 manufacturing in some parts of the US would be “just as economical as manufacturing in China.”
Examples of major manufacturers leaving China abound — BCG said US technology giant NCR has moved its manufacture of ATMs to a factory in Columbus, Georgia, that will employ 870 workers as of 2014.
Adidas announced recently that it would close its only directly owned factory in China, becoming the latest major brand to shift its manufacturing to cheaper countries, though it maintains a network of 300 Chinese contractors.
Chinese workers making athletic shoes are paid at least 2,000 yuan, or 258 euros (US$313), a month, while their Adidas colleagues in Cambodia only earn the equivalent of 107 euros, the German company said.
Underlining the trend, the salaries of Chinese urban-dwellers rose 13 percent in the first half of this year, compared with the same period last year, the government said in the middle of this month. Migrant workers, who are among the lowest-paid in the country, saw raises of 14.9 percent for an average salary of 2,200 yuan a month.
The most significant wage hikes in 2010 and last year often came following strikes at Japanese companies such as Toyota and Honda and a wave of suicides at the factories of the Taiwanese electronics giant Foxconn (富士康).
Natixis said the increases could spur manufacturers to relocate to South and Southeast Asia, where labor costs are much lower, and could also benefit countries such as Egypt and Morocco, or even European ones like Romania and Bulgaria.
However, not all economists believe China will lose its manufacturing edge, thanks in part to improvements in productivity.
“Most of the increase in wages has been offset by strong productivity growth,” said Louis Kuijs, project director at the Fung Global Institute, a research body that specializes in Asian economies.
Worker productivity has increased at a faster rate than wages in the southern Pearl River Delta, the heart of China’s vast manufacturing industry, according to 200 companies surveyed early this year by Standard Chartered Bank.
“China’s share of the world’s low-end exports has started to fall after years of rapid rises in wages, land costs and appreciation of renminbi [the currency],” said Wang Qinwei (王秦偉), a China economist at Capital Economics.
“But this has been offset by a growing market share in high-end products,” he added.
Capital Economics said in a research note published in March: “China’s export sector overall appears no less competitive now than a few years ago,” adding that “Average margins in light industry have increased over the past three years thanks to rapid productivity growth.”
China’s coastal areas offered an effective business environment that would continue to draw investors, as would lower costs in inland provinces, said Alistair Thornton, a China economist at IHS Global Insight These advantages could limit a shift in manufacturing to lower-paying countries such as Vietnam, Bangladesh, Pakistan and Indonesia.
“Guangdong and other coastal provinces have a superb advantage over most of Southeast Asia and South Asia in their efficient supply chains, strong economies of scale and reliable business environment,” Thornton said.

Real estate agent and property developer JSL Construction & Development Co (愛山林) led the average compensation rankings among companies listed on the Taiwan Stock Exchange (TWSE) last year, while contract chipmaker Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co (TSMC, 台積電) finished 14th. JSL Construction paid its employees total average compensation of NT$4.78 million (US$159,701), down 13.5 percent from a year earlier, but still ahead of the most profitable listed tech giants, including TSMC, TWSE data showed. Last year, the average compensation (which includes salary, overtime, bonuses and allowances) paid by TSMC rose 21.6 percent to reach about NT$3.33 million, lifting its ranking by 10 notches

SEASONAL WEAKNESS: The combined revenue of the top 10 foundries fell 5.4%, but rush orders and China’s subsidies partially offset slowing demand Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co (TSMC, 台積電) further solidified its dominance in the global wafer foundry business in the first quarter of this year, remaining far ahead of its closest rival, Samsung Electronics Co, TrendForce Corp (集邦科技) said yesterday. TSMC posted US$25.52 billion in sales in the January-to-March period, down 5 percent from the previous quarter, but its market share rose from 67.1 percent the previous quarter to 67.6 percent, TrendForce said in a report. While smartphone-related wafer shipments declined in the first quarter due to seasonal factors, solid demand for artificial intelligence (AI) and high-performance computing (HPC) devices and urgent TV-related orders
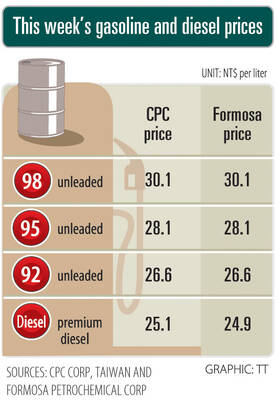
Prices of gasoline and diesel products at domestic fuel stations are this week to rise NT$0.2 and NT$0.3 per liter respectively, after international crude oil prices increased last week, CPC Corp, Taiwan (台灣中油) and Formosa Petrochemical Corp (台塑石化) said yesterday. International crude oil prices last week snapped a two-week losing streak as the geopolitical situation between Russia and Ukraine turned increasingly tense, CPC said in a statement. News that some oil production facilities in Alberta, Canada, were shut down due to wildfires and that US-Iran nuclear talks made no progress also helped push oil prices to a significant weekly gain, Formosa said

MINERAL DIPLOMACY: The Chinese commerce ministry said it approved applications for the export of rare earths in a move that could help ease US-China trade tensions Chinese Vice Premier He Lifeng (何立峰) is today to meet a US delegation for talks in the UK, Beijing announced on Saturday amid a fragile truce in the trade dispute between the two powers. He is to visit the UK from yesterday to Friday at the invitation of the British government, the Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs said in a statement. He and US representatives are to cochair the first meeting of the US-China economic and trade consultation mechanism, it said. US President Donald Trump on Friday announced that a new round of trade talks with China would start in London beginning today,